TIDUFB8 December 2024
- 1
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 6
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
- 3Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 4Design and Documentation Support
- 5About the Author
3.3.3.2 Voltage and Current Gain Calibration
To calibrate the voltage and current readings, perform the following steps:
- Connect the GUI to view results for voltage, current, active power, and the other metering parameters.
- Configure the test source to supply the desired voltage and current for all phases. Make sure that these are the voltage and current calibration points with a zero-degree phase shift between each phase voltage and current. For example, for 120V, 10A, 0° (PF = 1). Typically, these values are the same for every phase.
- Click on the Manual cal.
button as illustrated in Figure 3-10.
The screen in Figure 3-11 pops up:
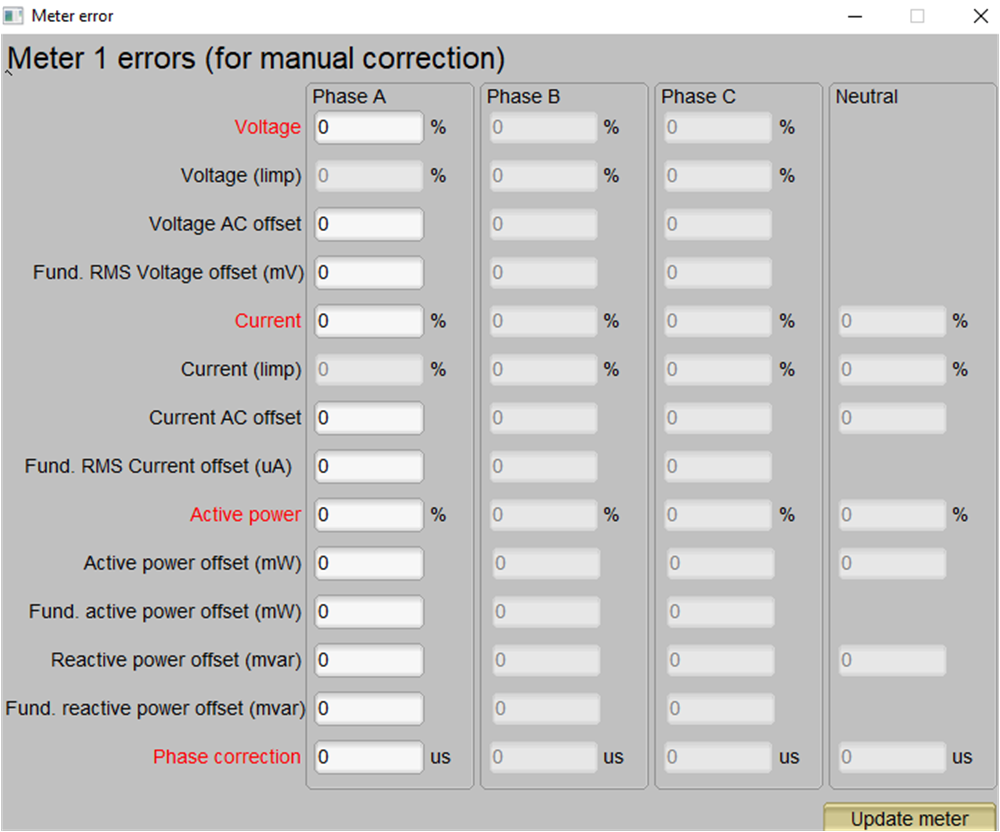 Figure 3-11 Manual Calibration
Window
Figure 3-11 Manual Calibration
Window - Calculate the correction values for each voltage and current. The correction
values that must be entered for the voltage and current fields are calculated
using Equation 15.Equation 15.
where
- valueobserved is the value measured by the TI meter
- valuedesired is the calibration point configured in the AC test source