TIDUFB8 December 2024
- 1
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 6
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
- 3Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 4Design and Documentation Support
- 5About the Author
3.3.3.5 Phase Calibration
After performing power gain correction, do the phase calibration. To perform phase correction calibration, complete the following steps:
- If the AC test source has been turned OFF or reconfigured, perform Step 1 through Step 3 from Section 3.3.3.2 using the identical voltages and currents used in that section.
- Modify only the phase-shift to a non-zero value; typically, +60° is chosen. The
reference meter now displays a different % error for active power measurement.
Note: This value can be negative.
- If the error from Step 3 is not close to zero, or is unacceptable, perform phase
correction by following these steps:
- Enter a value as an update for the Phase correction field for the phase that is being calibrated. Usually, a small ± integer must be entered to bring the error closer to zero. Additionally, for a phase shift greater than 0 (for example: +60°), a positive (negative) error requires a positive (negative) number as correction.
- Click on the Update meter button and monitor the error values on the reference meter.
- If this measurement error (%) is not accurate enough, fine-tune by incrementing or decrementing by a value of 1 based on Step 4. After a certain point, the fine-tuning only results in the error oscillating on either side of zero. The value that has the smallest absolute error must be selected.
- Change the phase now to –60° and check if this error is still acceptable. In best practice, errors must be symmetric for the same phase shift on lag and lead conditions.
After performing phase calibration, calibration is complete. Figure 3-12 shows the new calibration factors.
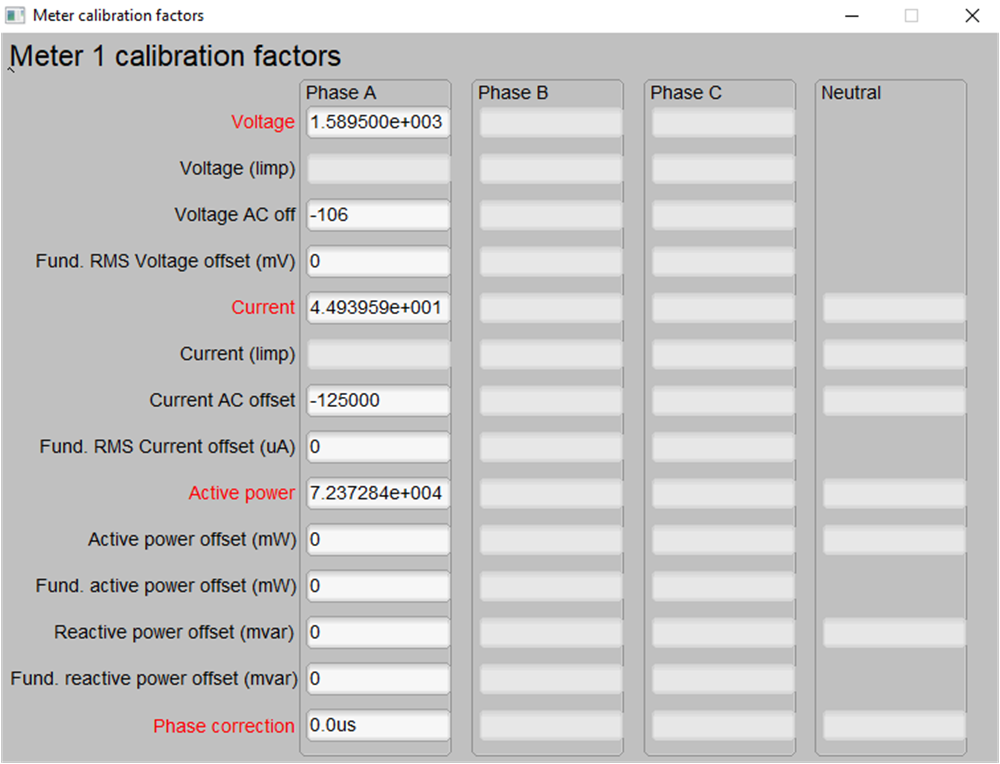 Figure 3-12 Calibration Factors
Window
Figure 3-12 Calibration Factors
Window