-
Step 5 to Build a Smart Thermostat Using an MCU – Adding Network Connectivity
Step 5 to Build a Smart Thermostat Using an MCU – Adding Network Connectivity
Bhargavi Nisarga Britta Ruelander
Internet of Things (IoT) technology makes products like thermostats smarter by connecting them to the network and enabling remote user access.
The previous four technical articles - How to build a smart thermostat using an MCU – 7 steps to make it happen!, Step 2 to build a smart thermostat using an MCU– It’s all about the sensing, Step 3 to build a smart thermostat using an MCU – What to do with all the data?, and Step 4 to build a smart thermostat using an MCU – adding HMI of this “How to build a smart thermostat” series have covered key aspects of building a smart thermostat, including analog sensing, analog-to-digital conversion, data processing and human machine interface (HMI). This fifth technical article will discuss how to add network connectivity, a key ingredient to making your thermostat smart.
Understanding the Network
Figure 1 gives a high-level overview of typical IoT components:
- The end nodes are the “things” in IoT (in our case, it is the smart thermostat).
- The local area network (LAN) includes a gateway device that communicates with the end nodes and connects to the internet.
- The internet.
- Back-end services handle remote storage and analysis, and apps.
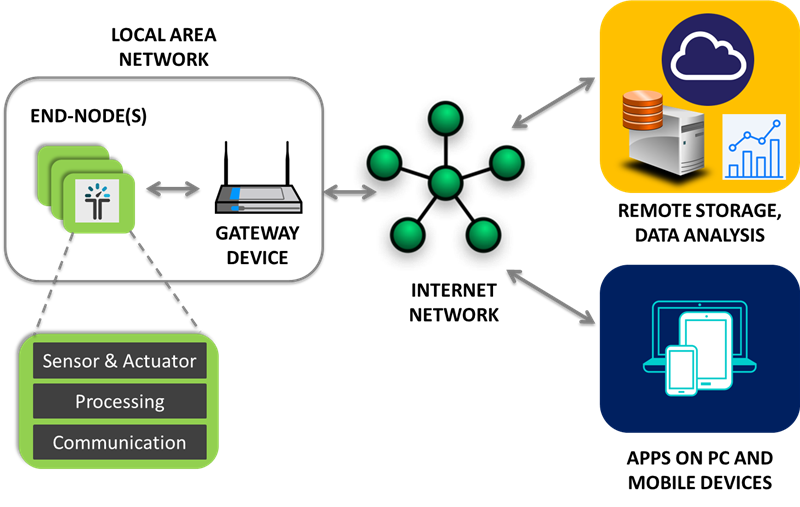 Figure 1 Typical Network-Connected IoT
System
Figure 1 Typical Network-Connected IoT
SystemThis technical article will focus on adding connectivity to your smart thermostat end node using one of the LAN communication protocols.
Benefits of Network Connectivity
Adding network connectivity to a smart thermostat offers consumers many benefits, including:
- Remote and local-area access to control and configure thermostat settings and monitor its status with a computer or mobile device.
- The collection of thermostat data coupled with external weather data to give consumers access to data analysis so that they can optimize their energy use, thus benefitting their wallets and the environment.
Local Area Connectivity Options
Commonly used local area wireless connectivity standards include Bluetooth®, Bluetooth low energy, Zigbee® (based on the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers [IEEE] 802.15.4 standard), 6LoWPAN, radio transceivers, and proprietary protocols using Sub-1 GHz frequency bands and Wi-Fi® (based on the IEEE 802.11 standard).
The wireless connectivity market is rapidly growing because of the IoT. Nevertheless, many IoT applications are connected to the Internet with wires – especially in buildings and factories. Ethernet connectivity, power line communication (PLC), RS-485, and industrial communication standards such as Fieldbus and Modbus are a few examples of wired standards.
Wired or Wireless
For a smart thermostat application, you can opt for wired and/or wireless connectivity. Wireless connectivity has many benefits. It’s easy to install and scale (especially if there’s no existing wiring in place or if you need to cover areas that wiring cannot reach). It’s also cost-effective and has less maintenance overhead. On the other hand, wired connections can achieve higher network communication speeds.
With respect to local area communication security, a wired connection requires that an attacker have physical access to the cables to perform eavesdropping, man-in-the-middle or replay attacks. But wireless communication protocols have advanced encryption methods, offering increased levels of security for communicating data and sharing cryptographic keys.
In the scope of this smart thermostat application, assuming that there is no pre-wiring and no large payload for communication, we’ll focus on wireless connectivity.
Wireless Connectivity Options
Various wireless connectivity standards cater to different connectivity requirements, including:
- Network range, which can range from a few meters or less (Bluetooth, Bluetooth low energy) to hundreds of meters (Wi-Fi, Zigbee, 6LoPan) to even a few kilometers (with Sub-1 GHz frequency bands).
- Data throughput, which refers to how fast a data payload is communicated and is measured in bits per second (bps). Data throughput can typically range from a low of 20 kbps (Bluetooth low energy, Zigbee, 6LowPAN, Sub-1 GHz) to 2 Mbps (Bluetooth, Bluetooth low energy) and even 20 Mbps (with Wi-Fi).
- Battery life, which for a specific type of battery (coin cell, AA, AAA) may need to range from several months to years.
- Network topologies, which correspond to a specific way the end nodes in the LAN connect to each other. Fundamental topologies such as star and mesh topologies are worth considering if there are multiple end nodes in the LAN.
For more details regarding these standards and a comparison of their characteristics, download the Wireless connectivity for the Internet of Things white paper.
It’s up to you to choose one or even multiple wireless connectivity standards to fit your smart thermostat application. TI SimpleLink™ microcontrollers (MCUs) offer a wide range of stand-alone wireless MCUs and network processors with different connectivity options. Additionally, the SimpleLink MCU software development kit (SDK) enables you to easily develop your application with different connectivity standards. With the SDK, you can add other connectivity options later on if you wish without a huge software redesign effort.
The Host MCU and When You Need It
In many scenarios, stand-alone wireless MCUs alone cannot support the application’s memory (code or data), inputs/outputs (I/Os) or processing power. Such cases require a host microcontroller to provide these features and interface to the network processor. For example, as discussed in the fourth technical article of this series, you may opt to include interfacing to segment liquid crystal display (LCD) or dot-matrix displays, or use voice-recognition algorithms. The more features there are in a smart thermostat, the more I/Os, processing power and memory you’ll need, so using a host MCU to offload these functions is the way to go. Figure 2 is an example block diagram of a connected thermostat with a host MCU interfacing to a network processor.
 Figure 2 Typical Block Diagram of a Smart Thermostat with a Host MCU and Network Processor
Figure 2 Typical Block Diagram of a Smart Thermostat with a Host MCU and Network ProcessorThe SimpleLink™ MSP432™ host MCU supports up to 2-MB flash and can operate up to 48 MHz. More importantly, the SimpleLink MSP432 SDK offers software support for interfacing to different SimpleLink network processors. It is up to you whether you go for a Bluetooth low energy CC2640R2F or SimpleLink Wi-Fi CC3120 SDK plug-in.
Finally, here are the key takeaways from our fifth blog post:
- Network connectivity adds many benefits to thermostat applications, including remote access to configure, control and monitor the thermostat, while additionally enabling energy optimization.
- You can choose from various wired or wireless standards based on pre-wiring options, network range, data throughput and power consumption.
- Consider using a SimpleLink MSP432 host MCU along with the SimpleLink network processors for enabling features to your smart thermostat application which requires more performance, memory and IO.
- Get started with adding smartness to your thermostat application now and take a look at the TI SimpleLink™ MSP432 SDK and get some inspiration!
Make sure to check out the next article in this series about energy optimization for your smart thermostat.
Additional Resources:
IMPORTANT NOTICE AND DISCLAIMER
TI PROVIDES TECHNICAL AND RELIABILITY DATA (INCLUDING DATASHEETS), DESIGN RESOURCES (INCLUDING REFERENCE DESIGNS), APPLICATION OR OTHER DESIGN ADVICE, WEB TOOLS, SAFETY INFORMATION, AND OTHER RESOURCES “AS IS” AND WITH ALL FAULTS, AND DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESS AND IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR NON-INFRINGEMENT OF THIRD PARTY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS.
These resources are intended for skilled developers designing with TI products. You are solely responsible for (1) selecting the appropriate TI products for your application, (2) designing, validating and testing your application, and (3) ensuring your application meets applicable standards, and any other safety, security, or other requirements. These resources are subject to change without notice. TI grants you permission to use these resources only for development of an application that uses the TI products described in the resource. Other reproduction and display of these resources is prohibited. No license is granted to any other TI intellectual property right or to any third party intellectual property right. TI disclaims responsibility for, and you will fully indemnify TI and its representatives against, any claims, damages, costs, losses, and liabilities arising out of your use of these resources.
TI’s products are provided subject to TI’s Terms of Sale (www.ti.com/legal/termsofsale.html) or other applicable terms available either on ti.com or provided in conjunction with such TI products. TI’s provision of these resources does not expand or otherwise alter TI’s applicable warranties or warranty disclaimers for TI products.
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright © 2023, Texas Instruments Incorporated