SNVSAF2A February 2016 – February 2016 LM36922H
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4
Device Functional Modes
- 7.4.1 Brightness Control Modes
- 7.4.2 Boost Switching Frequency
- 7.4.3 Auto-Switching Frequency
- 7.4.4 I2C Address Select (ASEL)
- 7.4.5
Fault Protection/Detection
- 7.4.5.1
Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 7.4.5.1.1 Case 1 OVP Fault Only (OVP Threshold Hit and All Enabled Current Sink Inputs > 40 mV)
- 7.4.5.1.2 Case 2a OVP Fault and Open LED String Fault (OVP Threshold Occurrence and Any Enabled Current Sink Input ≤ 40 mV)
- 7.4.5.1.3 Case 2b OVP Fault and Open LED String Fault (OVP Threshold Duration and Any Enabled Current Sink Input ≤ 40 mV)
- 7.4.5.1.4 OVP/LED Open Fault Shutdown
- 7.4.5.1.5 Testing for LED String Open
- 7.4.5.2 Voltage Limitations on LED1, LED2
- 7.4.5.3 LED String Short Fault
- 7.4.5.4 Overcurrent Protection (OCP)
- 7.4.5.5 Device Overtemperature
- 7.4.5.1
Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 Register Maps
- 8 Applications and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- YFF|12
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
1 Features
- 1% Matched Current Sinks Across Process, Voltage, Temperature
- 3% Current-Sink Accuracy Across Process, Voltage, Temperature
- 11-Bit Dimming Resolution
- Up to 90% Solution Efficiency
- Drives from One to Two Parallel LED Strings at up to 38 V at 25 mA per String
- PWM Dimming Input
- I2C Programmable
- Selectable 500-kHz and 1-MHz Switching Frequency With Optional –12% shift
- Auto Switch Frequency Mode (250 kHz, 500 kHz, 1 MHz)
- Four Configurable Overvoltage Protection Thresholds (17 V, 24 V, 31 V, 38 V)
- Four Configurable Overcurrent Protection Thresholds (750 mA, 1000 mA, 1250 mA,
1500 mA) - Thermal Shutdown Protection
- Externally Selectable I2C Address Options via ASEL Input
2 Applications
- Power Source for Smart Phone and Tablet Backlighting
- LCD Panels With up to 24 LEDs
3 Description
The LM36922H is an ultra-compact, highly efficient, two-string white-LED driver designed for LCD display backlighting. The device can power up to 12 series LEDs at up to 25 mA per string. An adaptive current regulation method allows for different LED voltages in each string while maintaining current regulation.
The LED current is adjusted via an I2C interface or through a logic level PWM input. The PWM duty cycle is internally sensed and mapped to an 11-bit current thus allowing for a wide range of PWM frequencies with noise-free operation from 50 µA to 25 mA.
Other features include an auto-frequency mode, which can automatically change the frequency based on load current in order to optimize efficiency.
The device operates over the 2.5-V to 5.5-V input voltage range and a –40°C to +85°C temperature range.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (MAX) |
|---|---|---|
| LM36922H | DSBGA (12) | 1.756 mm × 1.355 mm |
space
space
space
space
space
space
space
space
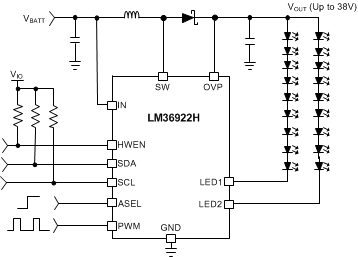
Simplified Schematic
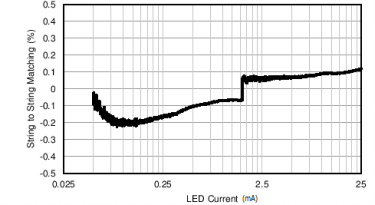
Typical String-to-String Matching vs LED Current