-
LM5105 100-V Half-Bridge Gate Driver With Programmable Dead Time
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DPR|10
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
LM5105 100-V Half-Bridge Gate Driver With Programmable Dead Time
1 Features
- Drives Both a High-Side and Low-Side N-Channel MOSFET
- 1.8-A Peak Gate Drive Current
- Bootstrap Supply Voltage Range up to 118-V DC
- Integrated Bootstrap Diode
- Single TTL Compatible Input
- Programmable Turnon Delays (Dead Time)
- Enable Input Pin
- Fast Turnoff Propagation Delays (26 ns Typical)
- Drives 1000 pF With 15-ns Rise and Fall Time
- Supply Rail Undervoltage Lockout
- Low Power Consumption
- Package: Thermally Enhanced 10-Pin WSON
(4 mm × 4 mm)
2 Applications
- Solid-State Motor Drives
- Half- and Full-Bridge Power Converters
3 Description
The LM5105 is a high-voltage gate driver designed to drive both the high-side and low-side N–Channel MOSFETs in a synchronous buck or half-bridge configuration. The floating high-side driver is capable of working with rail voltages up to 100 V. The single control input is compatible with TTL signal levels and a single external resistor programs the switching transition dead time through tightly matched turnon delay circuits. A high-voltage diode is provided to charge the high-side gate-drive bootstrap capacitor. The robust level shift technology operates at high speed while consuming low power and provides clean output transitions. Undervoltage lockout disables the gate driver when either the low-side or the bootstrapped high-side supply voltage is below the operating threshold. The LM5105 is offered in the thermally enhanced WSON plastic package.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| LM5105 | WSON (10) | 4.00 mm × 4.00 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the datasheet.
Simplified Application Diagram

4 Revision History
Changes from D Revision (March 2016) to E Revision
- Updated values in the Thermal Information table to align with JEDEC standardsGo
Changes from C Revision (March 2013) to D Revision
- Added Device Information table, ESD Ratings, Detailed Description section, Application and Implementation section, Layout section, Device and Documentation Support section, and Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information sectionGo
Changes from B Revision (March 2013) to C Revision
- Changed layout of National Semiconductor Data Sheet to TI formatGo
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
Pin Functions
| PIN | TYPE(1) | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NO. | NAME | ||
| 1 | VDD | P | Positive gate drive supply. Decouple VDD to VSS using a low ESR/ESL capacitor, placed as close to the IC as possible. |
| 2 | HB | P | High-side gate driver bootstrap rail. Connect the positive terminal of bootstrap capacitor to the HB pin and connect negative terminal to HS. The Bootstrap capacitor must be placed as close to IC as possible. |
| 3 | HO | O | High-side gate driver output. Connect to the gate of high side N-MOS device through a short, low inductance path. |
| 4 | HS | P | High-side MOSFET source connection. Connect to the negative terminal of the bootstrap capacitor and to the source of the high side N-MOS device. |
| 5 | NC | — | Not connected. |
| 6 | RDT | I | Dead-time programming pin. A resistor from RDT to VSS programs the turnon delay of both the high and low side MOSFETs. The resistor must be placed close to the IC to minimize noise coupling from adjacent PCB traces. |
| 7 | EN | I | Logic input for driver disable or enable. TTL compatible threshold with hysteresis. LO and HO are held in the low state when EN is low. |
| 8 | IN | I | Logic input for gate driver. TTL compatible threshold with hysteresis. The high side MOSFET is turned on and the low side MOSFET turned off when IN is high. |
| 9 | VSS | G | Ground return. All signals are referenced to this ground. |
| 10 | LO | O | Low-side gate driver output. Connect to the gate of the low side N-MOS device with a short, low inductance path. |
| — | Exposed Pad | — | It is recommended that the exposed pad on the bottom of the package be soldered to ground plane on the PCB to aid thermal dissipation. |
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)(2)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| VDD to VSS | –0.3 | 18 | V |
| HB to HS | –0.3 | 18 | V |
| IN and EN to VSS | –0.3 | VDD + 0.3 | V |
| LO to VSS | –0.3 | VDD + 0.3 | V |
| HO to VSS | HS – 0.3 | HB + 0.3 | V |
| HS to VSS(3) | −5 | 100 | V |
| HB to VSS | 118 | V | |
| RDT to VSS | –0.3 | 5 | V |
| Junction temperature, TJ | 150 | °C | |
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –55 | 150 | °C |
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM)(1)(2) | ±2000 | V |
500 V.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VDD | 8 | 14 | V | |||
| HS(1) | –1 | 100 | V | |||
| HB | HS + 8 | HS + 14 | V | |||
| HS | Slew rate | <50 | V/ns | |||
| TJ | Junction temperature | –40 | 125 | °C | ||
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | LM5105 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DPR (WSON) | |||
| 10 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 37.8 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 36.2 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 14.9 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.3 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 15.2 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 4.4 | °C/W |
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
Unless otherwise noted, VDD = HB = 12 V, VSS = HS = 0 V, EN = 5 V, no load on LO or HO, RDT= 100 kΩ(1). Typical limits are for TJ = 25°C, and minimum and maximum limits apply over the operating junction temperature range (–40°C to 125°C).| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUPPLY CURRENTS | ||||||
| IDD | VDD quiescent current | IN = EN = 0 V | 0.34 | 0.6 | mA | |
| IDDO | VDD operating current | f = 500 kHz | 1.65 | 3 | mA | |
| IHB | Total HB quiescent current | IN = EN = 0 V | 0.06 | 0.2 | mA | |
| IHBO | Total HB operating current | f = 500 kHz | 1.3 | 3 | mA | |
| IHBS | HB to VSS current, quiescent | HS = HB = 100 V | 0.05 | 10 | µA | |
| IHBSO | HB to VSS current, operating | f = 500 kHz | 0.1 | mA | ||
| INPUT IN AND EN | ||||||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage threshold | 0.8 | 1.8 | V | ||
| VIH | High-level input voltage threshold | 1.8 | 2.2 | V | ||
| Rpd | Input pulldown resistance pin IN and EN | 100 | 200 | 500 | kΩ | |
| DEAD-TIME CONTROLS | ||||||
| VRDT | Nominal voltage at RDT | 2.7 | 3 | 3.3 | V | |
| IRDT | RDT pin current limit | RDT = 0 V | 0.75 | 1.5 | 2.25 | mA |
| UNDER VOLTAGE PROTECTION | ||||||
| VDDR | VDD rising threshold | 6 | 6.9 | 7.4 | V | |
| VDDH | VDD threshold hysteresis | 0.5 | V | |||
| VHBR | HB rising threshold | 5.7 | 6.6 | 7.1 | V | |
| VHBH | HB threshold hysteresis | 0.4 | V | |||
| BOOT STRAP DIODE | ||||||
| VDL | Low-current forward voltage | IVDD-HB = 100 µA | 0.6 | 0.9 | V | |
| VDH | High-current forward voltage | IVDD-HB = 100 mA | 0.85 | 1.1 | V | |
| RD | Dynamic resistance | IVDD-HB = 100 mA | 0.8 | 1.5 | Ω | |
| LO GATE DRIVER | ||||||
| VOLL | Low-level output voltage | ILO = 100 mA | 0.25 | 0.4 | V | |
| VOHL | High-level output voltage | ILO = –100 mA, VOHL = VDD – VLO |
0.35 | 0.55 | V | |
| IOHL | Peak pullup current | LO = 0 V | 1.8 | A | ||
| IOLL | Peak pulldown current | LO = 12 V | 1.6 | A | ||
| HO GATE DRIVER | ||||||
| VOLH | Low-level output voltage | IHO = 100 mA | 0.25 | 0.4 | V | |
| VOHH | High-level output voltage | IHO = –100 mA, VOHH = HB – HO |
0.35 | 0.55 | V | |
| IOHH | Peak pullup current | HO = 0 V | 1.8 | A | ||
| IOLH | Peak pulldown current | HO = 12 V | 1.6 | A | ||
6.6 Switching Characteristics
Unless otherwise noted, VDD = HB = 12 , VSS = HS = 0 V, no Load on LO or HO(1). Typical limits are for TJ = 25°C, and minimum and maximum limits apply over the operating junction temperature range (–40°C to 125°C).| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tLPHL | Lower turnoff propagation delay | 26 | 56 | ns | ||
| tHPHL | Upper turnoff propagation delay | 26 | 56 | ns | ||
| tLPLH | Lower turnon propagation delay | RDT = 100 k | 485 | 595 | 705 | ns |
| tHPLH | Upper turnon propagation delay | RDT = 100 k | 485 | 595 | 705 | ns |
| tLPLH | Lower turnon propagation delay | RDT = 10 k | 75 | 105 | 150 | ns |
| tHPLH | Upper turnon propagation delay | RDT = 10 k | 75 | 105 | 150 | ns |
| ten, tsd | Enable and shutdown propagation delay | 28 | ns | |||
| DT1, DT2 | Dead-time LO OFF to HO ON and HO OFF to LO ON |
RDT = 100 k | 570 | ns | ||
| RDT = 10 k | 80 | ns | ||||
| MDT | Dead-time matching | RDT = 100 k | 50 | ns | ||
| tR, tF | Either output rise or fall time | CL = 1000 pF | 15 | ns | ||
| tBS | Bootstrap diode turnon or turnoff time | IF = 20 mA, IR = 200 mA | 50 | ns | ||
 Figure 1. LM5105 Input - Output Waveforms
Figure 1. LM5105 Input - Output Waveforms
 Figure 2. LM5105 Switching Time Definitions: TLPLH, TLPHL, THPLH, THPHL
Figure 2. LM5105 Switching Time Definitions: TLPLH, TLPHL, THPLH, THPHL
 Figure 3. LM5105 Enable: Tsd
Figure 3. LM5105 Enable: Tsd
 Figure 4. LM5105 Dead-Time: DT
Figure 4. LM5105 Dead-Time: DT
6.7 Typical Characteristics
 Figure 5. VDD Operating Current vs Frequency
Figure 5. VDD Operating Current vs Frequency
 Figure 7. Quiescent Current vs Supply Voltage
Figure 7. Quiescent Current vs Supply Voltage
 Figure 9. HB Operating Current vs Frequency
Figure 9. HB Operating Current vs Frequency
 Figure 11. Diode Forward Voltage
Figure 11. Diode Forward Voltage
 Figure 13. Undervoltage Rising Threshold vs Temperature
Figure 13. Undervoltage Rising Threshold vs Temperature
 Figure 15. LO & HO Low-Level Output Voltage
Figure 15. LO & HO Low-Level Output Voltagevs Temperature
 Figure 17. Dead-Time vs RT Resistor Value
Figure 17. Dead-Time vs RT Resistor Value
 Figure 19. Dead-Time vs Temperature (RT = 100 k)
Figure 19. Dead-Time vs Temperature (RT = 100 k)
 Figure 6. Operating Current vs Temperature
Figure 6. Operating Current vs Temperature
 Figure 8. Quiescent Current vs Temperature
Figure 8. Quiescent Current vs Temperature
 Figure 10. HO & LO Peak Output Current vs Output Voltage
Figure 10. HO & LO Peak Output Current vs Output Voltage
 Figure 12. Undervoltage Hysteresis vs Temperature
Figure 12. Undervoltage Hysteresis vs Temperature
 Figure 14. LO & HO High-Level Output Voltage
Figure 14. LO & HO High-Level Output Voltagevs Temperature
 Figure 16. Input Threshold vs Temperature
Figure 16. Input Threshold vs Temperature
 Figure 18. Dead-Time vs Temperature (RT = 10 k)
Figure 18. Dead-Time vs Temperature (RT = 10 k)
7 Detailed Description
7.1 Overview
The LM5105 is a single PWM input Gate Driver with Enable that offers a programmable dead time. The dead time is set with a resistor at the RDT pin and can be adjusted from 100 ns to 600 ns. The wide dead-time programming range provides the flexibility to optimize drive signal timing for a wide range of MOSFETS and applications.
The RDT pin is biased at 3 V and current-limited to 1-mA maximum programming current. The time delay generator accommodates resistor values from 5 k to 100 k with a dead time that is proportional to the RDT resistance. Grounding the RDT pin programs the LM5105 to drive both outputs with minimum dead time.
7.2 Functional Block Diagram

7.3 Feature Description
7.3.1 Start-Up and UVLO
Both top and bottom drivers include undervoltage lockout (UVLO) protection circuitry, which monitors the supply voltage (VDD) and bootstrap capacitor voltage (HB – HS) independently. The UVLO circuit inhibits each driver until sufficient supply voltage is available to turn on the external MOSFETs, and the UVLO hysteresis prevents chattering during supply voltage transitions. When the supply voltage is applied to the VDD pin of LM5105, the top and bottom gates are held low until VDD exceeds the UVLO threshold, typically about 6.9 V. Any UVLO condition on the bootstrap capacitor disables only the high-side output (HO).
7.4 Device Functional Modes
Table 1 lists the functional modes for LM5105.
Table 1. Function Table
| EN | IN PIN | LO PIN | HO PIN |
|---|---|---|---|
| L | Any | L | L |
| H | H | L | H |
| H | L | H | L |
8 Application and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
8.1 Application Information
The LM5105 is one of the latest generation of high-voltage gate drivers which are designed to drive both the high-side and low-side N-channel MOSFETs in a half-bridge or full-bridge configuration or in a synchronous buck circuit. The floating high-side driver can operate with supply voltages up to 110 V. This allows for N-channel MOSFET control in half-bridge, full-bridge, push-pull, two-switch forward, and active clamp topologies.
The outputs of the LM5105 are controlled from a single input. The rising edge of each output can be delayed with a programming resistor.
8.2 Typical Application
 Figure 20. LM5105 Driving MOSFETS Connected in Half-Bridge Configuration
Figure 20. LM5105 Driving MOSFETS Connected in Half-Bridge Configuration
8.2.1 Design Requirements
Table 2 lists the design parameters for this application example.
Table 2. Design Parameters
| PARAMETER | VALUE |
|---|---|
| Gate Drive IC | LM5105 |
| Mosfet | CSD18531Q5A |
| VDD | 10 V |
| Qgmax | 43 nC |
| Fsw | 100 kHz |
| DMax | 95% |
| IHBS | 10 µA |
| VDH | 1.1 V |
| VHBR | 7.1 V |
| VHBH | 0.4 V |
8.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
where
- VDD = Supply voltage of the gate drive IC
- VDH = Bootstrap diode forward voltage drop
- Vgsmin = Minimum gate source threshold voltage


The quiescent current of the bootstrap circuit is 10 µA, which is negligible compared to the Qgs of the MOSFET.

In practice the value for the CBOOT capacitor should be greater than that calculated to allow for situations where the power stage may skip pulse due to load transients. In this circumstance the boot capacitor must maintain the HB pin voltage above the UVLO voltage for the HB circuit.
As a general rule the local VDD bypass capacitor should be 10 times greater than the calculated value of CBOOT.
In practice, the value of CBoot is greater than the calculated value. This allows for the capacitance shift caused by the DC bias voltage and for situations where the power stage would otherwise skip pulses due to load transients. Therefore, it is recommended to include a safety-related margin in the CBoot value and place it as close to the VDD and VSS pins as possible. A 50-V, 0.1-µF capacitor is chosen in this example.
The bootstrap and bias capacitors should be ceramic types with X7R dielectric. The voltage rating should be twice that of the maximum VDD to allow for loss of capacitance once the devices have a DC bias voltage across them and to ensure long-term reliability of the devices.
The resistor values, RT, for setting turnon delay can be found in Figure 17.
8.2.3 Application Curves
 Figure 21. Diode Power Dissipation, VIN = 80 V
Figure 21. Diode Power Dissipation, VIN = 80 V
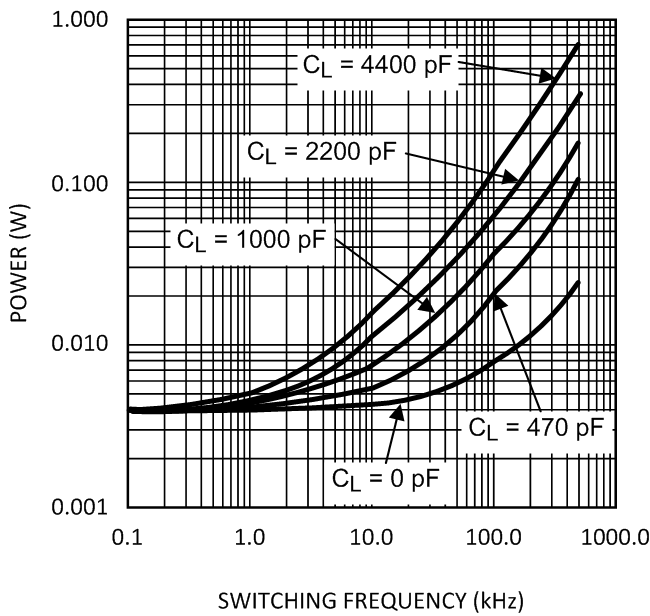 Figure 23. Gate Driver Power Dissipation (LO + HO)
Figure 23. Gate Driver Power Dissipation (LO + HO)VCC = 12 V, Neglecting Diode Losses
 Figure 22. Diode Power Dissipation, VIN = 40 V
Figure 22. Diode Power Dissipation, VIN = 40 V