SNOSA03H November 2002 – May 2016 LMH6702
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
1 Features
- 2nd and 3rd Harmonics (5 MHz, SOT-23) −100/−96 dBc
- −3-dB Bandwidth (VOUT = 0.5 VPP) 1.7 GHz
- Low Noise 1.83 nV/√Hz
- Fast Settling to 0.1% 13.4 ns
- Fast Slew Rate 3100 V/μs
- Supply Current 12.5 mA
- Output Current 80 mA
- Low Intermodulation Distortion (75 MHz) −67 dBc
- Improved Replacement for CLC409 and CLC449
VS = ±5 V, TA = 25°C, AV = 2V/V, RL = 100 Ω, VOUT = 2 VPP, Typical Unless Noted:
2 Applications
- Flash A-D Driver
- D-A Transimpedance Buffer
- Wide Dynamic Range IF Amp
- Radar and Communication Receivers
- Line Driver
- High Resolution Video
3 Description
The LMH6702 is a very wideband, DC-coupled monolithic operational amplifier designed specifically for wide dynamic range systems requiring exceptional signal fidelity. Benefitting from current feedback architecture, the LMH6702 offers unity gain stability at exceptional speed without need for external compensation.
With its 720-MHz bandwidth (AV = 2 V/V, VO = 2 VPP), 10-bit distortion levels through 60-MHz (RL = 100 Ω), 1.83-nV/√Hz input referred noise and 12.5-mA supply current, the LMH6702 is the ideal driver or buffer for high-speed flash A-D and D-A converters.
Wide dynamic range systems such as radar and communication receivers that require a wideband amplifier offering exceptional signal purity will find the low input referred noise and low harmonic and intermodulation distortion of the LMH6702 an attractive high speed solution.
The LMH6702 is constructed using VIP10™ complimentary bipolar process and proven current feedback architecture. The LMH6702 is available in SOIC and SOT-23 packages.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| LMH6702 | SOIC (8) | 4.90 mm × 3.91 mm |
| SOT-23 (5) | 2.90 mm × 1.60 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the datasheet.
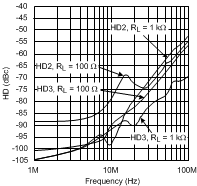
Inverting Frequency Response
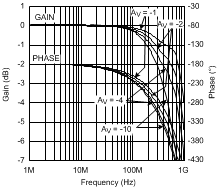
Harmonic Distortion vs Load and Frequency