-
LMV93x-N Single, Dual, Quad 1.8-V, RRIO Operational Amplifiers
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings (Commercial)
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Ratings
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 DC Electrical Characteristics 1.8 V
- 6.6 AC Electrical Characteristics 1.8 V
- 6.7 DC Electrical Characteristics 2.7 V
- 6.8 AC Electrical Characteristics 2.7 V
- 6.9 Electrical Characteristics 5 V DC
- 6.10 AC Electrical Characteristics 5 V
- 6.11 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
LMV93x-N Single, Dual, Quad 1.8-V, RRIO Operational Amplifiers
1 Features
- Typical 1.8-V Supply Values; Unless Otherwise Noted
- Specified at 1.8 V, 2.7 V and 5 V
- Output Swing
- With 600-Ω Load 80 mV from Rail
- With 2-kΩ Load 30 mV from Rail
- VCM 200 mV Beyond Rails
- Supply Current (per Channel) 100 μA
- Gain Bandwidth Product 1.4 MHz
- Maximum VOS 4 mV
- Ultra Tiny Packages
- Temperature Range −40°C to +125°C
- Create a Custom Design Using the LMV93x-N With the WEBENCH® Power Designer
2 Applications
- Phones
- Tablets
- Wearables
- Health Monitoring
- Portable and Battery-Powered Electronic Equipment
- Battery Monitoring
High-Side Current Sense Amplifier
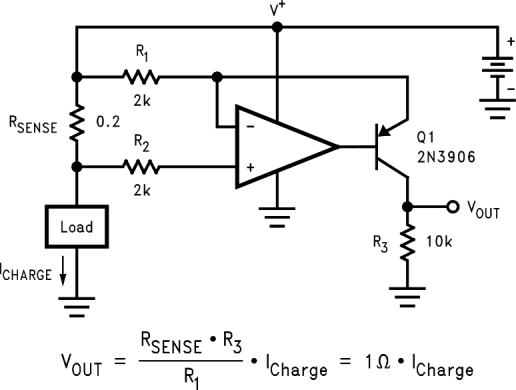
3 Description
The LMV93x-N family (LMV931-N single, LMV932-N dual and LMV934-N quad) are low-voltage, low-power operational amplifiers. The LMV93x-N family operates from 1.8-V to 5.5-V supply voltages and have rail-to-rail input and output. The input common-mode voltage extends 200 mV beyond the supplies which enables user enhanced functionality beyond the supply voltage range. The output can swing rail-to-rail unloaded and within 105 mV from the rail with 600-Ω load at 1.8-V supply. The LMV93x-N devices are optimized to work at 1.8 V, which make them ideal for portable two-cell, battery-powered systems and single-cell Li-Ion systems.
LMV93x-N devices exhibit an excellent speed-power ratio, achieving 1.4-MHz gain bandwidth product at 1.8-V supply voltage with very low supply current. The LMV93x-N devices can drive a 600-Ω load and up to 1000-pF capacitive load with minimal ringing. These devices also have a high DC gain of 101 dB, making them suitable for low-frequency applications.
The single LMV93x-N is offered in space-saving 5-pin SC70 and SOT-23 packages. The dual LMV932-N are in 8-pin VSSOP and SOIC packages and the quad LMV934-N are in 14-pin TSSOP and SOIC packages. These small packages are ideal solutions for area constrained PC boards and portable electronics such as mobile phones and tablets.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| LMV931-N | SOT-23 (5) | 2.90 mm × 1.60 mm |
| SC-70 (5) | 2.00 mm × 1.25 mm | |
| LMV932-N | VSSOP (8) | 3.00 mm × 3.00 mm |
| SOIC (8) | 4.90 mm × 3.91 mm | |
| LMV934-N | TSSOP (8) | 5.00 mm × 4.40 mm |
| SOIC (14) | 8.60 mm × 3.90 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the datasheet.
4 Revision History
Changes from O Revision (December 2014) to P Revision
- Deleted information specific to automotive grade - created separate automotive data sheet SNOSD49 Go
- Added links for WEBENCH Go
- Moved storage temperature to Abs Max table and changed Handling Ratings tables to ESD Ratings tables per new formatGo
- Changed values in the Thermal Information table to align with JEDEC standardsGo
- Changed Slew Rate vs Supply Voltage title to reflect LMV931 and LMV934 onlyGo
- Added Slew Rate vs Supply graph for LMV932 onlyGo
- Added Receiving Notification of Documentation Updates and Community Resources subsectionsGo
Changes from N Revision (June 2014) to O Revision
- Added Pin Configuration and Functions section, Handling Rating table, Feature Description section, Device Functional Modes, Application and Implementation, Power Supply Recommendations, Layout , Device and Documentation Support , and Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information sections Go
Changes from M Revision (November 2013) to N Revision
- Complete rewrite for GDS standard.Go
- Added LMV934-N-Q1. The other Q grades were added in previous revision.Go
Changes from L Revision (March 2013) to M Revision
- Added Automotive Q Grade. Go
5 Pin Configuration and Functions



Pin Functions: LMV931
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | LMV931 DBV, DCK | ||||
| +IN | 1 | I | Noninverting Input | ||
| -IN | 3 | I | Inverting Input | ||
| OUT | 4 | O | Output | ||
| V- | 2 | P | Negative Supply | ||
| V+ | 5 | P | Positive Supply | ||
Pin Functions: LMV932 and LMV934
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | LMV932 D, DGK | LMV934 D, PW | |||
| +IN A | 3 | 3 | I | Noninverting input, channel A | |
| +IN B | 5 | 5 | I | Noninverting input, channel B | |
| +IN C | — | 10 | I | Noninverting input, channel C | |
| +IN D | — | 12 | I | Noninverting input, channel D | |
| –IN A | 2 | 2 | I | Inverting input, channel A | |
| –IN B | 6 | 6 | I | Inverting input, channel B | |
| –IN C | — | 9 | I | Inverting input, channel C | |
| –IN D | — | 13 | I | Inverting input, channel D | |
| OUT A | 1 | 1 | O | Output, channel A | |
| OUT B | 7 | 7 | O | Output, channel B | |
| OUT C | — | 8 | O | Output, channel C | |
| OUT D | — | 14 | O | Output, channel D | |
| V+ | 8 | 4 | P | Positive (highest) power supply | |
| V– | 4 | 11 | P | Negative (lowest) power supply | |
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
See (1)(2).| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage ( V+– V− ) | –0.3 | 6 | V | |
| Differential input voltage | V– | V+ | V | |
| Voltage at input/output pins | (V– ) - 0.3 | (V+) + 0.3 | V | |
| Junction temperature(3) | –40 | 150 | °C | |
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C | |
6.2 ESD Ratings (Commercial)
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±2000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±750 | |||
| Machine model (MM)(3) | ±200 | |||
6.3 Recommended Operating Ratings
See(1).| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage range ( V+– V− ) | 1.8 | 5.5 | V | |
| Ambient temperature | −40 | 125 | °C | |
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | LMV931-N | LMV932-N | LMV934-N | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DBV (SOT-23) |
DCK (SC70) |
D (SOIC) |
DGK (VSSOP) |
D (SOIC) |
PW (TSSOP) |
|||
| 5 PINS | 5 PINS | 8 PINS | 8 PINS | 14 PINS | 14 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 197.2 | 285.9 | 125.9 | 184.5 | 94.4 | 124.8 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 156.7 | 115.9 | 70.2 | 74.3 | 52.5 | 51.4 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 55.6 | 63.7 | 66.5 | 105.1 | 48.9 | 67.2 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 41.4 | 4.5 | 19.8 | 13.1 | 14.3 | 6.6 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 55 | 62.9 | 65.9 | 103.6 | 48.6 | 66.6 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | — | — | — | — | — | — | °C/W |
6.5 DC Electrical Characteristics 1.8 V
Unless otherwise specified, all limits specified for TJ = 25°C. V+ = 1.8 V, V − = 0 V, VCM = V+/2, VO = V+/2 and RL > 1 MΩ.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP (1) | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VOS | Input Offset Voltage | LMV931 (Single) | 25°C | 1 | 4 | mV | |
| Full Range | 6 | ||||||
| LMV932 (Dual), LMV934 (Quad) |
25°C | 1 | 5.5 | mV | |||
| Full Range | 7.5 | ||||||
| TCVOS | Input Offset Voltage Average Drift |
Full Range | 5.5 | μV/°C | |||
| IB | Input Bias Current | 25°C | 15 | 35 | nA | ||
| Full Range | 50 | ||||||
| IOS | Input Offset Current | 25°C | 13 | 25 | nA | ||
| Full Range | 40 | ||||||
| IS | Supply Current (per channel) | 25°C | 103 | 185 | μA | ||
| Full Range | 205 | ||||||
| CMRR | Common-Mode Rejection Ratio | LMV931, 0 ≤ VCM ≤ 0.6 V 1.4 V ≤ VCM ≤ 1.8 V(3) |
25°C | 60 | 78 | dB | |
| Full Range | 55 | ||||||
| LMV932 and LMV934 0 ≤ VCM ≤ 0.6 V 1.4 V ≤ VCM ≤ 1.8 V(3) |
25°C | 55 | 76 | dB | |||
| Full Range | 50 | ||||||
| −0.2 V ≤ VCM ≤ 0 V 1.8 V ≤ VCM ≤ 2.0 V |
25°C | 50 | 72 | dB | |||
| PSRR | Power Supply Rejection Ratio | 1.8 V ≤ V+ ≤ 5 V | 25°C | 75 | 100 | dB | |
| Full Range | 70 | ||||||
| CMVR | Input Common-Mode Voltage Range | For CMRR Range ≥ 50dB | 25°C | V− − 0.2 | −0.2 to 2.1 |
V+ + 0.2 | V |
| −40°C to 85°C | V− | V+ | |||||
| 125°C | V− + 0.2 | V+ − 0.2 | |||||
| AV | Large Signal Voltage Gain LMV931-N (Single) |
RL = 600 Ω to 0.9 V, VO = 0.2 V to 1.6 V, VCM = 0.5 V |
25°C | 77 | 101 | dB | |
| Full Range | 73 | ||||||
| RL = 2 kΩ to 0.9 V, VO = 0.2 V to 1.6 V, VCM = 0.5 V |
25°C | 80 | 105 | dB | |||
| Full Range | 75 | ||||||
| Large Signal Voltage Gain LMV932-N (Dual) LMV934-N (Quad) |
RL = 600 Ω to 0.9 V, VO = 0.2 V to 1.6 V, VCM = 0.5 V |
25°C | 75 | 90 | dB | ||
| Full Range | 72 | ||||||
| RL = 2 kΩ to 0.9 V, VO = 0.2 V to 1.6 V, VCM = 0.5 V |
25°C | 78 | 100 | dB | |||
| Full Range | 75 | ||||||
| VO | Output Swing | RL = 600 Ω to 0.9 V VIN = ±100 mV |
25°C | 1.65 | 1.72 | V | |
| 0.077 | 0.105 | ||||||
| Full Range | 1.63 | 0.120 | |||||
| RL = 2 kΩ to 0.9 V VIN = ±100 mV |
25°C | 1.75 | 1.77 | V | |||
| 0.024 | 0.035 | ||||||
| Full Range | 1.74 | 0.04 | |||||
| IO | Output Short Circuit Current(2) | Sourcing, VO = 0 V VIN = 100 mV |
25°C | 4 | 8 | mA | |
| Full Range | 3.3 | ||||||
| Sinking, VO = 1.8 V VIN = −100 mV |
25°C | 7 | 9 | mA | |||
| Full Range | 5 | ||||||
6.6 AC Electrical Characteristics 1.8 V
Unless otherwise specified, all limits specified for TJ = 25°C. V+ = 1.8 V, V − = 0 V, VCM = V+/2, VO = V+/2 and RL > 1 MΩ.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP (1) | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR | Slew Rate | See (4). | 0.35 | V/μs | ||
| GBW | Gain-Bandwidth Product | 1.4 | MHz | |||
| Φm | Phase Margin | 67 | deg | |||
| Gm | Gain Margin | 7 | dB | |||
| en | Input-Referred Voltage Noise | f = 10 kHz, VCM = 0.5 V | 60 | nV/√Hz | ||
| in | Input-Referred Current Noise | f = 10 kHz | 0.08 | pA/√Hz | ||
| THD | Total Harmonic Distortion | f = 1 kHz, AV = +1 RL = 600 Ω, VIN = 1 VPP |
0.023% | |||
| Amplifier-to-Amplifier Isolation | See(5) | 123 | dB | |||
6.7 DC Electrical Characteristics 2.7 V
Unless otherwise specified, all limits specified for TJ = 25°C. V+ = 2.7 V, V − = 0 V, VCM = V+/2, VO = V+/2 and RL > 1 MΩ.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP (1) | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VOS | Input Offset Voltage | LMV931 (Single) | 25°C | 1 | 4 | mV | |
| Full Range | 6 | ||||||
| LMV932 (Dual) LMV934 (Quad) |
25°C | 1 | 5.5 | mV | |||
| Full Range | 7.5 | ||||||
| TCVOS | Input Offset Voltage Average Drift | Full Range | 5.5 | μV/°C | |||
| IB | Input Bias Current | 25°C | 15 | 35 | nA | ||
| Full Range | 50 | ||||||
| IOS | Input Offset Current | 25°C | 8 | 25 | nA | ||
| Full Range | 40 | ||||||
| IS | Supply Current (per channel) | 25°C | 105 | 190 | μA | ||
| Full Range | 210 | ||||||
| CMRR | Common-Mode Rejection Ratio | LMV931, 0 ≤ VCM ≤ 1.5 V 2.3 V ≤ VCM ≤ 2.7 V(3) |
25°C | 60 | 81 | dB | |
| Full Range | 55 | ||||||
| LMV932 and LMV934 0 ≤ VCM ≤ 1.5 V 2.3 V ≤ VCM ≤ 2.7 V(3) |
25°C | 55 | 80 | dB | |||
| Full Range | 50 | ||||||
| −0.2 V ≤ VCM ≤ 0 V 2.7 V ≤ VCM ≤ 2.9 V |
25°C | 50 | 74 | dB | |||
| PSRR | Power Supply Rejection Ratio | 1.8 V ≤ V+ ≤ 5 V VCM = 0.5 V |
25°C | 75 | 100 | dB | |
| Full Range | 70 | ||||||
| VCM | Input Common-Mode Voltage Range | For CMRR Range ≥ 50 dB | 25°C | V− − 0.2 | −0.2 to 3.0 |
V+ + 0.2 | V |
| −40°C to 85°C | V− | V+ | |||||
| 125°C | V− + 0.2 | V+ − 0.2 | |||||
| AV | Large Signal Voltage Gain LMV931-N (Single) |
RL = 600 Ω to 1.35 V, VO = 0.2 V to 2.5 V |
25°C | 87 | 104 | dB | |
| Full Range | 86 | ||||||
| RL = 2 kΩ to 1.35 V, VO = 0.2 V to 2.5 V |
25°C | 92 | 110 | dB | |||
| Full Range | 91 | ||||||
| Large Signal Voltage Gain LMV932-N (Dual) LMV934-N (Quad) |
RL = 600 Ω to 1.35 V, VO = 0.2 V to 2.5 V |
25°C | 78 | 90 | dB | ||
| Full Range | 75 | ||||||
| RL = 2 kΩ to 1.35 V, VO = 0.2 V to 2.5 V |
25°C | 81 | 100 | dB | |||
| Full Range | 78 | ||||||
| VO | Output Swing | RL = 600 Ω to 1.35 V VIN = ±100 mV |
25°C | 2.55 | 2.62 | V | |
| 0.083 | 0.110 | ||||||
| Full Range | 2.53 | 0.130 | |||||
| RL = 2 kΩ to 1.35 V VIN = ±100 mV |
25°C | 2.65 | 2.675 | V | |||
| 0.025 | 0.04 | ||||||
| Full Range | 2.64 | 0.045 | |||||
| IO | Output Short Circuit Current(2) | Sourcing, VO = 0 V VIN = +100 mV |
25°C | 20 | 30 | mA | |
| Full Range | 15 | ||||||
| Sinking, VO = 2.7 V VIN = −100 mV |
25°C | 18 | 25 | mA | |||
| Full Range | 12 | ||||||
6.8 AC Electrical Characteristics 2.7 V
Unless otherwise specified, all limits specified for TJ = 25°C. V+ = 2.7 V, V − = 0 V, VCM = 1.0 V, VO = 1.35 V and RL > 1 MΩ.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP (1) | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR | Slew Rate | See(4) | 0.4 | V/µs | ||
| GBW | Gain-Bandwidth Product | 1.4 | MHz | |||
| Φm | Phase Margin | 70 | deg | |||
| Gm | Gain Margin | 7.5 | dB | |||
| en | Input-Referred Voltage Noise | f = 10 kHz, VCM = 0.5 V | 57 | nV√Hz | ||
| in | Input-Referred Current Noise | f = 10 kHz | 0.08 | pA/√Hz | ||
| THD | Total Harmonic Distortion | f = 1 kHz, AV = +1 RL = 600 Ω, VIN = 1 VPP |
0.022% | |||
| Amp-to-Amp Isolation | See(5) | 123 | dB | |||
6.9 Electrical Characteristics 5 V DC
Unless otherwise specified, all limits specified for TJ = 25°C. V+ = 5 V, V − = 0 V, VCM = V+/2, VO = V+/2 and RL > 1 MΩ.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP (1) | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VOS | Input Offset Voltage | LMV931 (Single) | 25°C | 1 | 4 | mV | |
| Full Range | 6 | ||||||
| LMV932 (Dual) LMV934 (Quad) |
25°C | 1 | 5.5 | mV | |||
| Full Range | 7.5 | ||||||
| TCVOS | Input Offset Voltage Average Drift | 5.5 | μV/°C | ||||
| IB | Input Bias Current | 25°C | 14 | 35 | nA | ||
| Full Range | 50 | ||||||
| IOS | Input Offset Current | 25°C | 9 | 25 | nA | ||
| Full Range | 40 | ||||||
| IS | Supply Current (per channel) | 25°C | 116 | 210 | μA | ||
| Full Range | 230 | ||||||
| CMRR | Common-Mode Rejection Ratio | 0 ≤ VCM ≤ 3.8 V 4.6 V ≤ VCM ≤ 5 V(3) |
25°C | 60 | 86 | dB | |
| Full Range | 55 | ||||||
| −0.2 V ≤ VCM ≤ 0 V 5 V ≤ VCM ≤ 5.2 V |
25°C | 50 | 78 | dB | |||
| PSRR | Power Supply Rejection Ratio | 1.8 V ≤ V+ ≤ 5 V VCM = 0.5 V |
25°C | 75 | 100 | dB | |
| Full Range | 70 | ||||||
| CMVR | Input Common-Mode Voltage Range | For CMRR Range ≥ 50 dB | 25°C | V− − 0.2 | −0.2 to 5.3 |
V+ + 0.2 | V |
| −40°C to 85°C | V− | V+ | |||||
| 125°C | V− + 0.3 | V+ − 0.3 | |||||
| AV | Large Signal Voltage Gain LMV931-N (Single) |
RL = 600 Ω to 2.5 V, VO = 0.2 V to 4.8 V |
25°C | 88 | 102 | dB | |
| Full Range | 87 | ||||||
| RL = 2 kΩ to 2.5 V, VO = 0.2 V to 4.8 V |
25°C | 94 | 113 | dB | |||
| Full Range | 93 | ||||||
| Large Signal Voltage Gain LMV932-N (Dual) LMV934-N (Quad) |
RL = 600 Ω to 2.5 V, VO = 0.2 V to 4.8 V |
25°C | 81 | 90 | dB | ||
| Full Range | 78 | ||||||
| RL = 2 kΩ to 2.5 V, VO = 0.2 V to 4.8 V |
25°C | 85 | 100 | dB | |||
| Full Range | 82 | ||||||
| VO | Output Swing | RL = 600 Ω to 2.5 V VIN = ±100 mV |
25°C | 4.855 | 4.890 | V | |
| 0.120 | 0.160 | ||||||
| Full Range | 4.835 | 0.180 | |||||
| RL = 2 kΩ to 2.5 V VIN = ±100 mV |
25°C | 4.945 | 4.967 | V | |||
| 0.037 | 0.065 | ||||||
| Full Range | 4.935 | 0.075 | |||||
| IO | Output Short Circuit Current(2) | LMV931, Sourcing, VO = 0 V VIN = +100 mV |
25°C | 80 | 100 | mA | |
| Full Range | 68 | ||||||
| Sinking, VO = 5 V VIN = −100 mV |
25°C | 58 | 65 | mA | |||
| Full Range | 45 | ||||||
6.10 AC Electrical Characteristics 5 V
Unless otherwise specified, all limits specified for TJ = 25°C. V+ = 5 V, V − = 0 V, VCM = V+/2, VO = 2.5 V and R L > 1 MΩ.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP (1) | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR | Slew Rate | See .(4) | 0.42 | V/µs | ||
| GBW | Gain-Bandwidth Product | 1.5 | MHz | |||
| Φm | Phase Margin | 71 | deg | |||
| Gm | Gain Margin | 8 | dB | |||
| en | Input-Referred Voltage Noise | f = 10 kHz, VCM = 1 V | 50 | nV/√Hz | ||
| in | Input-Referred Current Noise | f = 10 kHz | 0.08 | pA/√Hz | ||
| THD | Total Harmonic Distortion | f = 1 kHz, AV = 1 RL = 600 Ω, VO = 1 VPP |
0.022% | |||
| Amplifier-to-Amplifier Isolation | See(5) | 123 | dB | |||
6.11 Typical Characteristics
Unless otherwise specified, VS = 5 V, single-supply, TA = 25°C. Figure 1. Supply Current vs Supply Voltage (LMV931-N)
Figure 1. Supply Current vs Supply Voltage (LMV931-N)
 Figure 3. Offset Voltage vs Common-Mode Range
Figure 3. Offset Voltage vs Common-Mode Range
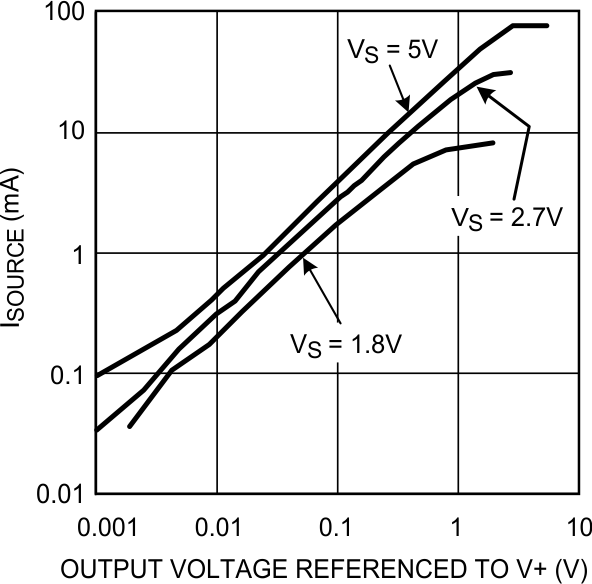 Figure 5. Sourcing Current vs Output Voltage
Figure 5. Sourcing Current vs Output Voltage
 Figure 7. Output Voltage Swing vs Supply Voltage
Figure 7. Output Voltage Swing vs Supply Voltage
 Figure 9. Gain and Phase vs Frequency
Figure 9. Gain and Phase vs Frequency
 Figure 11. Gain and Phase vs Frequency
Figure 11. Gain and Phase vs Frequency
 Figure 13. CMRR vs Frequency
Figure 13. CMRR vs Frequency
 Figure 15. Input Voltage Noise vs Frequency
Figure 15. Input Voltage Noise vs Frequency
 Figure 17. THD vs Frequency
Figure 17. THD vs Frequency
 Figure 21. Small Signal Noninverting Response
Figure 21. Small Signal Noninverting Response
 Figure 23. Small Signal Noninverting Response
Figure 23. Small Signal Noninverting Response
 Figure 25. Large Signal Noninverting Response
Figure 25. Large Signal Noninverting Response
 Figure 27. Short Circuit Current vs Temperature (Sinking)
Figure 27. Short Circuit Current vs Temperature (Sinking)
 Figure 2. Offset Voltage vs Common-Mode Range
Figure 2. Offset Voltage vs Common-Mode Range
 Figure 4. Offset Voltage vs Common-Mode Range
Figure 4. Offset Voltage vs Common-Mode Range
 Figure 6. Sinking Current vs Output Voltage
Figure 6. Sinking Current vs Output Voltage
 Figure 8. Output Voltage Swing vs Supply Voltage
Figure 8. Output Voltage Swing vs Supply Voltage
 Figure 10. Gain and Phase vs Frequency
Figure 10. Gain and Phase vs Frequency
 Figure 12. Gain and Phase vs Frequency
Figure 12. Gain and Phase vs Frequency
 Figure 14. PSRR vs Frequency
Figure 14. PSRR vs Frequency
 Figure 16. Input Current Noise vs Frequency
Figure 16. Input Current Noise vs Frequency
 Figure 18. THD vs Frequency
Figure 18. THD vs Frequency
 Figure 22. Small Signal Noninverting Response
Figure 22. Small Signal Noninverting Response
 Figure 24. Large Signal Noninverting Response
Figure 24. Large Signal Noninverting Response
 Figure 26. Large Signal Noninverting Response
Figure 26. Large Signal Noninverting Response
 Figure 28. Short Circuit Current vs Temperature (Sourcing)
Figure 28. Short Circuit Current vs Temperature (Sourcing)
7 Detailed Description
7.1 Overview
The LMV93x-N are low-voltage, low-power operational amplifiers (op-amp) operating from 1.8-V to 5.5-V supply voltages and have rail-to-rail input and output. LMV93x-N input common-mode voltage extends 200 mV beyond the supplies which enables user enhanced functionality beyond the supply voltage range.
7.2 Functional Block Diagram

7.3 Feature Description
The differential inputs of the amplifier consist of a noninverting input (+IN) and an inverting input (–IN). The amplifer amplifies only the difference in voltage between the two inputs, which is called the differential input voltage. The output voltage of the op-amp VOUT is given by Equation 1:
where
- AOL is the open-loop gain of the amplifier, typically around 100 dB (100,000x, or 10 µV per volt).
7.4 Device Functional Modes
7.4.1 Input and Output Stage
The rail-to-rail input stage of this family provides more flexibility for the designer. The LMV93x-N use a complimentary PNP and NPN input stage in which the PNP stage senses common-mode voltage near V− and the NPN stage senses common-mode voltage near V+. The transition from the PNP stage to NPN stage occurs 1 V below V+. Because both input stages have their own offset voltage, the offset of the amplifier becomes a function of the input common-mode voltage and has a crossover point at 1 V below V+.
This VOS crossover point can create problems for both DC− and AC-coupled signals if proper care is not taken. Large input signals that include the VOS crossover point will cause distortion in the output signal. One way to avoid such distortion is to keep the signal away from the crossover. For example, in a unity gain buffer configuration with VS = 5 V, a 5-V peak-to-peak signal will contain input-crossover distortion while a 3-V peak-to-peak signal centered at 1.5 V will not contain input-crossover distortion as it avoids the crossover point. Another way to avoid large signal distortion is to use a gain of −1 circuit which avoids any voltage excursions at the input terminals of the amplifier. In that circuit, the common-mode DC voltage can be set at a level away from the VOS cross-over point. For small signals, this transition in VOS shows up as a VCM dependent spurious signal in series with the input signal and can effectively degrade small signal parameters such as gain and common-mode rejection ratio. To resolve this problem, the small signal should be placed such that it avoids the VOS crossover point. In addition to the rail-to-rail performance, the output stage can provide enough output current to drive 600-Ω loads. Because of the high-current capability, take care not to exceed the 150°C maximum junction temperature specification.
7.4.2 Input Bias Current Consideration
The LMV93x-N family has a complementary bipolar input stage. The typical input bias current (IB) is 15 nA. The input bias current can develop a significant offset voltage. This offset is primarily due to IB flowing through the negative feedback resistor, RF. For example, if IB is 50 nA and RF is 100 kΩ, then an offset voltage of 5 mV will develop (VOS = IB x RF). Using a compensation resistor (RC), as shown in Figure 30, cancels this effect. But the input offset current (IOS) will still contribute to an offset voltage in the same manner.
 Figure 30. Canceling the Offset Voltage due to Input Bias Current
Figure 30. Canceling the Offset Voltage due to Input Bias Current


