-
MSP432E401Y SimpleLink™ Ethernet Microcontroller
- 1Device Overview
- 2Revision History
- 3Device Characteristics
- 4Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
5Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Recommended DC Operating Conditions
- 5.5 Recommended GPIO Operating Characteristics
- 5.6 Recommended Fast GPIO Pad Operating Conditions
- 5.7 Recommended Slow GPIO Pad Operating Conditions
- 5.8 GPIO Current Restrictions
- 5.9 I/O Reliability
- 5.10 Current Consumption
- 5.11 Peripheral Current Consumption
- 5.12 LDO Regulator Characteristics
- 5.13 Power Dissipation
- 5.14 Thermal Resistance Characteristics, 128-Pin PDT (TQFP) Package
- 5.15
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 5.15.1 Load Conditions
- 5.15.2 Power Supply Sequencing
- 5.15.3 Reset Timing
- 5.15.4
Clock Specifications
- 5.15.4.1 PLL Specifications
- 5.15.4.2 PIOSC Specifications
- 5.15.4.3 Low-Frequency Oscillator Specifications
- 5.15.4.4 Hibernation Low-Frequency Oscillator Specifications
- 5.15.4.5 Main Oscillator Specifications
- 5.15.4.6 Main Oscillator Specification WIth ADC
- 5.15.4.7 System Clock Characteristics With USB Operation
- 5.15.5 Sleep Modes
- 5.15.6 Hibernation Module
- 5.15.7 Flash Memory
- 5.15.8 EEPROM
- 5.15.9 Input/Output Pin Characteristics
- 5.15.10 External Peripheral Interface (EPI)
- 5.15.11 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
- 5.15.12 Synchronous Serial Interface (SSI)
- 5.15.13 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Interface
- 5.15.14 Ethernet Controller
- 5.15.15 Universal Serial Bus (USB) Controller
- 5.15.16 Analog Comparator
- 5.15.17 Pulse-Width Modulator (PWM)
- 5.15.18 Emulation and Debug
-
6Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3 Arm Cortex-M4F Processor Core
- 6.4 On-Chip Memory
- 6.5
Peripherals
- 6.5.1 External Peripheral Interface (EPI)
- 6.5.2 Cyclical Redundancy Check (CRC)
- 6.5.3 Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) Accelerator
- 6.5.4 Data Encryption Standard (DES) Accelerator
- 6.5.5 Secure Hash Algorithm/Message Digest Algorithm (SHA/MD5) Accelerator
- 6.5.6 Serial Communications Peripherals
- 6.5.7 System Integration
- 6.5.8 Advanced Motion Control
- 6.5.9 Analog
- 6.5.10 JTAG and Arm Serial Wire Debug
- 6.5.11 Peripheral Memory Map
- 6.6 Identification
- 6.7 Boot Modes
- 7Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 8Device and Documentation Support
- 9Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PDT|128
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
MSP432E401Y SimpleLink™ Ethernet Microcontroller
1 Device Overview
1.1 Features
-
Core
- 120-MHz Arm® Cortex®-M4F Processor Core With Floating-Point Unit (FPU)
-
Connectivity
- Ethernet MAC: 10/100 Ethernet MAC With Integrated Ethernet PHY
- Ethernet PHY: PHY With IEEE 1588 PTP Hardware Support
- Universal Serial Bus (USB): USB 2.0 OTG, Host, or Device With ULPI Interface Option and Link Power Management (LPM)
- Eight Universal Asynchronous Receivers/Transmitters (UARTs), Each With Independently Clocked Transmitter and Receiver
- Four Quad Synchronous Serial Interface (QSSI): With Bi-, Quad-, and Advanced-SSI Support
- Ten Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Modules With High-Speed Mode Support
- Two CAN 2.0 A and B Controllers: Multicast Shared Serial-Bus Standard
-
Memories
- 1024KB of Flash Memory With 4-Bank Configuration Supports an Independent Code Protection for Each Bank
- 256KB of SRAM With Single-Cycle Access, Provides Nearly 2-GB/s Memory Bandwidth at 120-MHz Clock Frequency
- 6KB EEPROM: 500-kwrite per 2 Page Block, Leveling, Lock Protection
- Internal ROM: Loaded With SimpleLink™ SDK Software
- Peripheral Driver Library
- Bootloader
- External Peripheral Interface (EPI): 8-, 16-, or 32-Bit Dedicated Parallel Interface to Access External Devices and Memory (SDRAM, Flash, or SRAM)
-
Security
- Advanced Encryption Standard (AES): Hardware Accelerated Data Encryption and Decryption Based on 128-, 192-, and 256-Bit Keys
- Data Encryption Standard (DES): Hardware Accelerated Data Encryption and Decryption Supported by Block Cipher Implementation With 168-Bit Effective Key Length
- Secure Hash Algorithm/Message Digest Algorithm (SHA/MD5): Advanced Hash Engine That Supports SHA-1, SHA-2, and MD5 Hash Computation
- Cyclical Redundancy Check (CRC) Hardware
- Tamper: Support for Four Tamper Inputs and Configurable Tamper Event Response
-
Analog
- Two 12-Bit SAR-Based ADC Modules, Each Supports Up to 2 Million Samples per Second (2 Msps)
- Three Independent Analog Comparator Controllers
- 16 Digital Comparators
-
System Management
- JTAG and Serial Wire Debug (SWD): One JTAG Module With Integrated Arm SWD Provides a Means of Accessing and Controlling Design-for-Test Features Such as I/O Pin Observation and Control, Scan Testing, and Debugging.
-
Development Kits and Software (See Tools and Software)
- SimpleLink™ MSP-EXP432E401Y LaunchPad™ Development Kit
- SimpleLink MSP432E4 Software Development Kit (SDK)
-
Package Information
- Package: 128-Pin TQFP (PDT)
- Extended Operating Temperature (Ambient) Range: –40°C to 105°C
1.2 Applications
- Industrial Ethernet Gateway
- Industrial Smart Gateway
- Zone Controllers for Building Automation
- Factory Automation Data Collectors and Gateway
- Data Concentrators for Grid Infrastructure
- Wireless to Ethernet Gateway
1.3 Description
The SimpleLink MSP432E401Y Arm® Cortex®-M4F microcontrollers provide top performance and advanced integration. The product family is positioned for cost-effective applications requiring significant control processing and connectivity capabilities.
The MSP432E401Y microcontrollers integrate a large variety of rich communication features to enable a new class of highly connected designs with the ability to allow critical real-time control between performance and power. The microcontrollers feature integrated communication peripherals along with other high-performance analog and digital functions to offer a strong foundation for many different target uses, spanning from human-machine interface (HMI) to networked system management controllers.
In addition, the MSP432E401Y microcontrollers offer the advantages of widely available development tools, system-on-chip (SoC) infrastructure, and a large user community for Arm-based microcontrollers. Additionally, these microcontrollers use the Arm Thumb®-compatible Thumb-2® instruction set to reduce memory requirements and, thereby, cost. When using the SimpleLink MSP432™ SDK, the MSP432E401Y microcontroller is code compatible with all members of the extensive SimpleLink family, providing flexibility to fit precise needs.
The MSP432E401Y device is part of the SimpleLink microcontroller (MCU) platform, which consists of Wi-Fi®, Bluetooth® low energy, Sub-1 GHz, Ethernet, Zigbee, Thread, and host MCUs, which all share a common, easy-to-use development environment with a single core software development kit (SDK) and rich tool set. A one-time integration of the SimpleLink platform enables you to add any combination of the portfolio's devices into your design, allowing 100 percent code reuse when your design requirements change. For more information, visit www.ti.com/simplelink.
1.4 Functional Block Diagram
Figure 1-1 shows the functional block diagram.
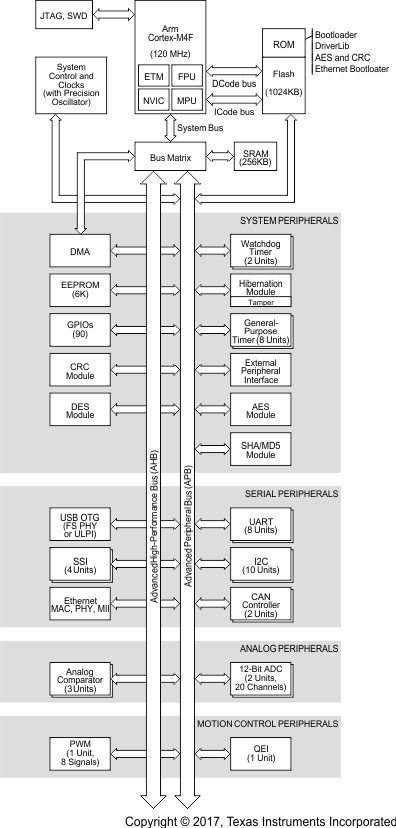 Figure 1-1 MSP432E401Y Functional Block Diagram
Figure 1-1 MSP432E401Y Functional Block Diagram
2 Revision History
| DATE | REVISION | NOTES |
|---|---|---|
| October 2017 | * | Initial Release |
3 Device Characteristics
Table 3-1 lists the characteristics of the MSP432E401Y MCU.
Table 3-1 Device Characteristics
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Performance | |
| Core | Arm Cortex-M4F processor core |
| Performance | 120-MHz operation, 150-DMIPS performance |
| Flash | 1024KB of flash memory |
| System SRAM | 256KB of single-cycle system SRAM |
| EEPROM | 6KB of EEPROM |
| Internal ROM | Internal ROM loaded with SimpleLink SDK software |
| External Peripheral Interface (EPI) | 8-, 16-, or 32-bit dedicated interface for peripherals and memory |
| Security | |
| Cyclical Redundancy Check (CRC) | 16- or 32-bit hash function that supports four CRC forms |
| Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) | Hardware accelerated data encryption and decryption based on 128-, 192-, and 256-bit keys |
| Data Encryption Standard (DES) | Block cipher implementation with 168-bit effective key length |
| Hardware Accelerated Hash (SHA/MD5) | Advanced hash engine that supports SHA-1, SHA-2, or MD5 hash computation |
| Tamper | Support for four tamper inputs and configurable tamper event response |
| Communication Interfaces | |
| Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART) | Eight UARTs |
| Quad Synchronous Serial Interface (QSSI) | Four SSI modules with bi-, quad-, and advanced-SSI support |
| Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) | Ten I2C modules with four transmission speeds including high-speed mode |
| Controller Area Network (CAN) | Two CAN 2.0 A/B controllers |
| Ethernet MAC | 10/100 Ethernet MAC |
| Ethernet PHY | PHY with IEEE 1588 PTP hardware support |
| Universal Serial Bus (USB) | USB 2.0 OTG, Host, and Device with ULPI interface option and Link Power Management (LPM) support |
| System Integration | |
| Micro Direct Memory Access (µDMA) | Arm PrimeCell® 32-channel configurable µDMA controller |
| General-Purpose Timer (GPTM) | Eight 16- or 32-bit GPTM blocks |
| Watchdog Timer (WDT) | Two watchdog timers |
| Hibernation Module (HIB) | Low-power battery-backed Hibernation module |
| General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) | 15 physical GPIO blocks |
| Advanced Motion Control | |
| Pulse Width Modulator (PWM) | One PWM module, with four PWM generator blocks and a control block, for a total of 8 PWM outputs |
| Quadrature Encoder Interface (QEI) | One QEI module |
| Analog Support | |
| Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) | Two 12-bit ADC modules, each with a maximum sample rate of 2 Msps |
| Analog Comparator Controller | Three independent integrated analog comparators |
| Digital Comparator | 16 digital comparators |
| System Management | |
| JTAG and Serial Wire Debug (SWD) | One JTAG module with integrated Arm SWD |
| Package Information | |
| Package | 128-pin TQFP (PDT) |
| Operating Range (Ambient) | Extended temperature range (–40°C to 105°C) |
3.1 Related Products
For information about other devices in this family of products or related products, see the following links.
-
Products for TI Microcontrollers Low-power and high-performance MCUs, with wired and wireless connectivity options.
-
Products for SimpleLink MSP432 MCUs SimpleLink MSP432 MCUs with an ultra-low-power Arm Cortex-M4 core are optimized for Internet-of-Things sensor node applications. With an integrated ADC, the family enables acquisition and processing of high-precision signals without sacrificing power and is an optimal host MCU for TI's SimpleLink wireless connectivity solutions.
-
Companion Products for MSP432E401Y Review products that are frequently purchased or used with this product.
-
Reference Designs The TI Designs Reference Design Library is a robust reference design library that spans analog, embedded processor, and connectivity. Created by TI experts to help you jump start your system design, all TI Designs include schematic or block diagrams, BOMs, and design files to speed your time to market.