-
SN75LVCP601 Two-Channel 6-Gbps SATA Redriver
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RTJ|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RTJ|20
Orderable Information
SN75LVCP601 Two-Channel 6-Gbps SATA Redriver
1 Features
- 1.5-, 3-, or 6-Gbps Two-Channel Redriver
- Integrated Output Squelch
- Programmable RX and TX Equalization and
De-Emphasis Width Control - Power-Save Feature Lowers Power by >80%
in Auto Low-Power Mode - Low Power
- <220 mW (Typ)
- <50 mW (in Auto Low-Power Mode)
- <5 mW (in Standby Mode)
- Excellent Jitter and Loss Compensation
Capability to Over 24-Inch (61-cm) FR4 Trace - 20-Pin 4-mm × 4-mm QFN Package
- High Protection Against ESD Transient
- HBM: 10,000 V
- CDM: 1,500 V
- MM: 200 V
- Pin-Compatible With LVCP412A and MAX4951
2 Applications
- Notebooks
- Desktops
- Docking Stations
- Servers
- Workstations
3 Description
The SN75LVCP601 device is a dual-channel, single-lane SATA redriver and signal conditioner supporting data rates up to 6 Gbps. The device complies with SATA physical link 2m and 3i specifications. The SN75LVCP601 operates from one 3.3-V supply and has 100-Ω line termination with a self-biasing feature, making the device suitable for ac coupling. The inputs incorporate an out-of-band (OOB) detector, which automatically squelches the output while maintaining a stable common-mode voltage compliant to the SATA link. The device design also handles spread-spectrum clocking (SSC) transmission per the SATA specification.
The SN75LVCP601 device handles interconnect losses at both its input and output. The input stage of each channel offers selectable equalization settings that are programmable to match the loss in the channel. The differential outputs provide selectable de-emphasis to compensate for the expected distortion that the SATA signal experiences. The level of equalization and de-emphasis settings depends on the length of interconnect and its characteristics. The setting of signal control pins EQ1, EQ2, DE1, and DE2 controls both equalization and de-emphasis levels.
This device is hot-plug capable (requires the use of ac-coupling capacitors at differential inputs and outputs), thus preventing device damage under device hot-insertion, in such cases as: async signal plug or removal, unpowered plug or removal, powered plug or removal, surprise plug or removal
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| SN75LVCP601 | WQFN (20) | 4.00 mm × 4.00 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the data sheet.
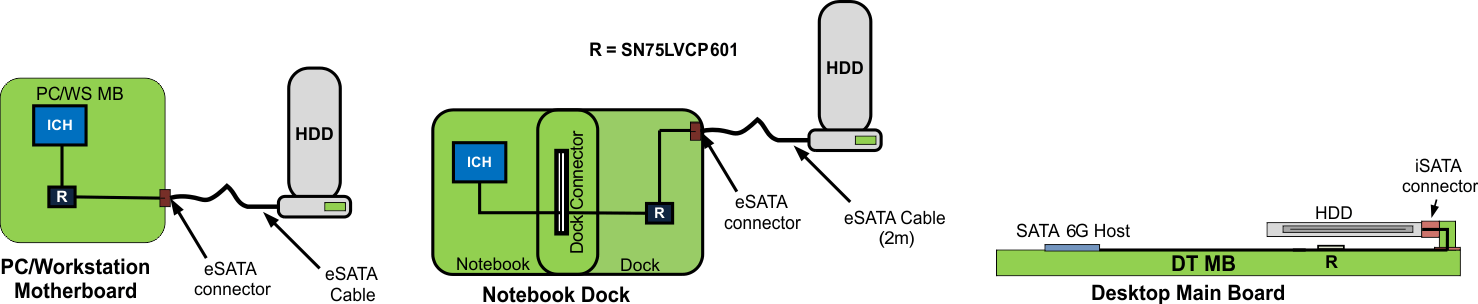
Typical Application
4 Revision History
Changes from G Revision (January 2016) to H Revision
- Changed pin DE1 number From: 8 To: 9 in the Pin Functions table Go
- Changed pin DE2 number From: 9 To: 8 in the Pin Functions table Go
Changes from F Revision (June 2015) to G Revision
Changes from E Revision (January 2014) to F Revision
- Added Pin Configuration and Functions section, ESD Ratings table, Feature Description section, Device Functional Modes, Application and Implementation section, Power Supply Recommendations section, Layout section, Device and Documentation Support section, and Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information section Go
- Added Storage temperature to the Absolute Maximum Ratings tableGo
- Moved timing parameters out of Electrical Characteristics and into Timing Requirements Go
- Moved switching parameters out of Electrical Characteristics and into Switching Characteristics Go
Changes from D Revision (January 2013) to E Revision
- Changed DJTX (UI = 333 ps) From: Max = 0.19 To: Max = 0.07Go
- Changed DJTX (UI = 167 ps) From: Max = 0.34 To: Max = 0.16Go
Changes from C Revision (October 2012) to D Revision
- Corrected formatting of the Differential output-voltage swing dc level section of the Electrical Characteristics tableGo
Changes from B Revision (February 2012) to C Revision
- Deleted DiffVppTX rowGo
- Inserted DiffVppTX_DE rowGo
- Changed Figure 5 captionGo
- Revised text of the Output Ed-Emphasis sectionGo
- Deleted setting recommendations on pulse durations for DEW1 and DEW2Go
Changes from A Revision (October 2011) to B Revision
- Changed pin type from CML to VML for pins 4, 5, 14, 15 in the Pin Functions tableGo
Changes from * Revision (June 2010) to A Revision
- Changed pin EN number From: 4 To: 7 in the Pin Functions tableGo
5 Pin Configuration and Functions

Pin Functions
| PIN | PIN TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| CONTROL PINS | |||
| DE1(1) | 9 | I, LVCMOS | Selects de-emphasis settings for CH 1 and CH 2 per Table 1. Internally tied to VCC / 2. |
| DE2(1) | 8 | ||
| DEW1 | 16 | I, LVCMOS | De-emphasis width control for CH 1 and CH 2. 0 = De-emphasis pulse duration, short 1 = De-emphasis pulse duration, long (default) |
| DEW2 | 6 | ||
| EN | 7 | I, LVCMOS | Device enable and disable pin, internally pulled to VCC. 0 = Device in standby mode 1 = Device enabled (default) |
| EQ1(1) | 17 | I, LVCMOS | Selects equalization settings for CH 1 and CH 2 per Table 1. Internally tied to VCC / 2. |
| EQ2(1) | 19 | ||
| HIGH-SPEED DIFFERENTIAL I/O | |||
| RX1N | 2 | I, CML | Noninverting and inverting CML differential input for CH 1 and CH 2. These pins connect to an internal voltage bias via a dual-termination resistor circuit. |
| RX1P | 1 | I, CML | |
| RX2N | 12 | I, CML | |
| RX2P | 11 | I, CML | |
| TX1N | 14 | O, VML | Noninverting and inverting VML differential output for CH 1 and CH 2. These pins connect internally to voltage bias via termination resistors. |
| TX1P | 15 | O, VML | |
| TX2N | 4 | O, VML | |
| TX2P | 5 | O, VML | |
| POWER | |||
| GND | 3, 13, 18 | Power | Supply ground |
| VCC | 10, 20 | Power | Positive supply must be 3.3 V ± 10% |
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC | Supply voltage range(2) | –0.5 | 4 | V |
| Voltage range | Differential I/O | –0.5 | 4 | V |
| Control I/O | –0.5 | VCC + 0.5 | V | |
| Continuous power dissipation | See Power Dissipation Characteristics | |||
| Tstg | Storage temperature | 150 | °C | |
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±10000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±1500 | |||
| Machine model(3) | ±200 | |||
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
typical values for all parameters are VCC = 3.3 V and TA = 25°C; all temperature limits are specified by design| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC | Supply voltage | 3 | 3.3 | 3.6 | V |
| CCOUPLING | Coupling capacitor | 12 | nF | ||
| Operating free-air temperature | 0 | 85 | °C | ||
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | SN75LVCP601 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RTJ (WQFN) | |||
| 20 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 38 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 40 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 10 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.5 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 0.9 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 15.2 | °C/W |
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEVICE PARAMETERS | ||||||
| PD | Power dissipation in active mode | DEWx = EN = VCC, EQx = DEx = NC, K28.5 pattern at 6 Gbps, VID = 700 mVp-p | 215 | 288 | mW | |
| PSD | Power dissipation in standby mode | EN = 0 V, DEWx = EQx = DEx = NC, K28.5 pattern at 6 Gbps, VID = 700 mVp-p | 5 | mW | ||
| ICC | Active-mode supply current | EN = 3.3 V, DEWx = 0 V, EQx = DEx = NC, K28.5 pattern at 6 Gbps, VID = 700 mVp-p |
65 | 80 | mA | |
| ICC_ALP | Acive power-save mode ICC | When device is enabled and auto low-power conditions are met | 6.5 | 10 | mA | |
| ICC_STDBY | Standby mode supply current | EN = 0 V | 1 | mA | ||
| Maximum data rate | 1 | 6 | Gbps | |||
| OUT-OF-BAND (OOB) | ||||||
| VOOB | Input OOB threshold | f = 750 MHz | 50 | 78 | 150 | mVpp |
| DVdiffOOB | OOB differential delta | 25 | mV | |||
| DVCMOOB | OOB common-mode delta | 50 | mV | |||
| CONTROL LOGIC | ||||||
| VIH | Input high voltage | For all control pins | 1.4 | V | ||
| VIL | Input low voltage | 0.5 | V | |||
| VINHYS | Input hysteresis | 115 | mV | |||
| IIH | High-level input current | EQx, DEx = VCC | 30 | µA | ||
| EN, DEWx = VCC | 1 | |||||
| IIL | Low-level input current | EQx, DEx = GND | –30 | µA | ||
| EN, DEWx = GND | –10 | |||||
| RECEIVER AC/DC | ||||||
| ZDIFFRX | Differential-input impedance | 85 | 100 | 115 | Ω | |
| ZSERX | Single-ended input impedance | 40 | Ω | |||
| VCMRX | Common-mode voltage | 1.8 | V | |||
| RLDiffRX | Differential-mode return loss (RL) | f = 150 MHz to 300 MHz | 18 | 28 | dB | |
| f = 300 MHz to 600 MHz | 14 | 17 | ||||
| f = 600 MHz to 1.2 GHz | 10 | 12 | ||||
| f = 1.2 GHz to 2.4 GHz | 8 | 9 | ||||
| f = 2.4 GHz to 3 GHz | 3 | 9 | ||||
| RXDiffRLSlope | Differential-mode RL slope | f = 300 MHz to 6 GHz (see Figure 1) | –13 | dB/dec | ||
| RLCMRX | Common-mode return loss | f = 150 MHz to 300 MHz | 5 | 10 | dB | |
| f = 300 MHz to 600 MHz | 5 | 17 | ||||
| f = 600 MHz to 1.2 GHz | 2 | 23 | ||||
| f = 1.2 GHz to 2.4 GHz | 1 | 16 | ||||
| f = 2.4 GHz to 3 GHz | 1 | 12 | ||||
| VdiffRX | Differential input voltage PP | f = 1.5 GHz and 3 GHz | 120 | 1600 | mVppd | |
| IBRX | Impedance balance | f = 150 MHz to 300 MHz | 30 | 41 | dB | |
| f = 300 MHz to 600 MHz | 30 | 38 | ||||
| f = 600 MHz to 1.2 GHz | 20 | 32 | ||||
| f = 1.2 GHz to 2.4 GHz | 10 | 26 | ||||
| f = 2.4 GHz to 3 GHz | 10 | 25 | ||||
| f = 3 GHz to 5 GHz | 4 | 20 | ||||
| f = 5 GHz to 6.5 GHz | 4 | 17 | ||||
| TRANSMITTER AC/DC | ||||||
| ZdiffTX | Pair differential impedance | 85 | 100 | 122 | Ω | |
| ZSETX | Single-ended impedance | 40 | Ω | |||
| VTXtrans | Sequencing transient voltage | Transient voltages on the serial data bus during power sequencing (lab load) | –1.2 | 1.2 | V | |
| RLDiffTX | Differential-mode return loss | f = 150 MHz to 300 MHz | 14 | 24 | dB | |
| f = 300 MHz to 600 MHz | 8 | 19 | ||||
| f = 600 MHz to 1.2 GHz | 6 | 14 | ||||
| f = 1.2 GHz to 2.4 GHz | 6 | 10 | ||||
| f = 2.4 GHz to 3 GHz | 3 | 10 | ||||
| TXDiffRLSlope | Differential-mode RL slope | f = 300 MHz to 3 GHz (see Figure 1) | –13 | dB/dec | ||
| RLCMTX | Common-mode return loss | f = 150 MHz to 300 MHz | 5 | 20 | dB | |
| f = 300 MHz to 600 MHz | 5 | 19 | ||||
| f = 600 MHz to 1.2 GHz | 2 | 17 | ||||
| f = 1.2 GHz to 2.4 GHz | 1 | 12 | ||||
| f = 2.4 GHz to 3.0 GHz | 1 | 11 | ||||
| IBTX | Impedance balance | f = 150 MHz to 300 MHz | 30 | 41 | dB | |
| f = 300 MHz to 600 MHz | 30 | 38 | ||||
| f = 600 MHz to 1.2 GHz | 20 | 33 | ||||
| f = 1.2 GHz to 2.4 GHz | 10 | 24 | ||||
| f = 2.4 GHz to 3 GHz | 10 | 26 | ||||
| f = 3 GHz to 5 GHz | 4 | 22 | ||||
| f = 5 GHz to 6.5 GHz | 4 | 21 | ||||
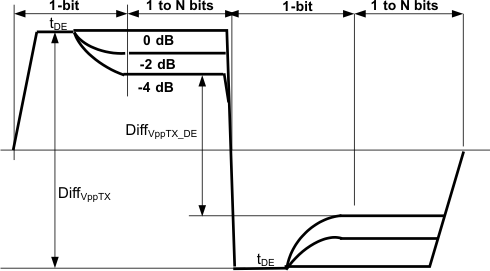
| DE | Output de-emphasis (relative to transition bit) | f = 3 GHz, DE1 or DE2 = 0 | 0 | dB | ||
| f = 3 GHz, DE1 or DE2 = 1 | –2 | |||||
| f = 3 GHz, DE1 or DE2 = NC | –4 | |||||
| DiffVppTX_DE | Differential output-voltage swing dc level | f = 3 GHz, DE1 or DE2 = 0 | 550 | mV | ||
| f = 3 GHz, DE1 or DE2 = 1 | 830 | |||||
| f = 3 GHz, DE1or DE2 = NC | 630 | |||||
| VCMAC_TX | TX AC CM voltage | At 1.5 GHz | 20 | 50 | mVppd | |
| At 3 GHz | 12 | 26 | dBmV (rms) | |||
| At 6 GHz | 13 | 30 | ||||
| VCMTX | Common-mode voltage | 1.8 | V | |||
| TxR/FImb | TX rise-fall imbalance | At 3 Gbps | 6% | 20% | ||
| TxAmpImb | TX amplitude imbalance | 2% | 10% | |||
6.6 Power Dissipation Characteristics
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PD | Device power dissipation in active mode | 215 | 288 | mW | |
| PSD | Device power dissipation under standby mode | 5 | mW | ||
6.7 Timing Requirements
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEVICE PARAMETERS | ||||||
| AutoLPENTRY | Auto low-power entry time | Electrical idle at input (see Figure 4) | 80 | 105 | 130 | µs |
| AutoLPEXIT | Auto low-power exit time | After first signal activity (see Figure 4) | 42 | 50 | ns | |
| TRANSMITTER AC/DC | ||||||
| tDE | De-emphasis duration | DEW1 or DEW2 = 0 | 94 | ps | ||
| DEW1 or DEW2 = 1 | 215 | |||||
| OUT-OF-BAND (OOB) | ||||||
| tOOB1 | OOB mode enter | See Figure 4 | 3 | 5 | ns | |
| tOOB2 | OOB mode exit | See Figure 4 | 3 | 5 | ns | |
6.8 Switching Characteristics
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEVICE PARAMETERS | ||||||
| tPDelay | Propagation delay | Measured using K28.5 pattern (see Figure 2) | 323 | 400 | ps | |
| tENB | Device enable time | EN 0 → 1 | 5 | µs | ||
| tDIS | Device disable time | EN 1 → 0 | 2 | µs | ||
| RECEIVER AC/DC | ||||||
| t20-80RX | Rise/fall time | Rise times and fall times measured between 20% and 80% of the signal. SATA 6-Gbps speed measured 1 in, (2.5 cm) from device pin. | 62 | 75 | ps | |
| tskewRX | Differential skew | Difference between the single-ended midpoint of the RX+ signal rising or falling edge, and the single-ended midpoint of the RX– signal falling or rising edge. | 30 | ps | ||
| TRANSMITTER AC/DC | ||||||
| t20-80TX | Rise/fall time | Rise times and fall times measured between 20% and 80% of the signal. At 6 Gbps under no load conditions. | 42 | 55 | 75 | ps |
| tskewTX | Differential skew | Difference between the single-ended mid-point of the TX+ signal rising or falling edge, and the single-ended mid-point of the TX– signal falling or rising edge. | 6 | 20 | ps | |
| TRANSMITTER JITTER | ||||||
| DJTX | Deterministic jitter(1) at CP in Figure 9 | VID = 500 mVpp, UI = 333 ps, K28.5 control character |
0.06 | 0.07 | UIp-p | |
| RJTX | Residual random jitter(1) | VID = 500 mVpp, UI = 333 ps, K28.7 control character |
0.01 | 2 | ps-rms | |
| DJTX | Deterministic jitter(1) at CP in Figure 9 | VID = 500 mVpp, UI = 167 ps, K28.5 control character |
0.08 | 0.16 | UIp-p | |
| RJTX | Residual random jitter(1) | VID = 500 mVpp, UI = 167 ps, K28.7 control character |
0.09 | 2 | ps-rms | |
 Figure 1. TX, RX Differential Return Loss Limits
Figure 1. TX, RX Differential Return Loss Limits
 Figure 2. OOB Enter and Exit Timing
Figure 2. OOB Enter and Exit Timing
 Figure 3. Propagation Delay Timing Diagram
Figure 3. Propagation Delay Timing Diagram
 Figure 4. Auto Low-Power Mode Enter and Exit Timing
Figure 4. Auto Low-Power Mode Enter and Exit Timing
6.9 Typical Characteristics
 Figure 6. Residual DJ and Eye Opening
Figure 6. Residual DJ and Eye Opening vs Input Trace Length
 Figure 7. Residual DJ and Eye Opening
Figure 7. Residual DJ and Eye Opening vs Output Trace Length