-
TPS7A4701-EP 36-V, 1-A, 4-µVRMS, RF LDO Voltage Regulator
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGW|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGW|20
Orderable Information
TPS7A4701-EP 36-V, 1-A, 4-µVRMS, RF LDO Voltage Regulator
1 Features
- Input Voltage Range: 3 V to 36 V
- Output Voltage Noise:
4 µVRMS (10 Hz, 100 kHz) - Power-Supply Ripple Rejection:
- 82 dB (100 Hz)
- ≥ 55 dB (10 Hz, 10 MHz)
- Two Output Voltage Modes:
- ANY-OUT™ Version (User-Programmable Output via PCB Layout):
- No External Feedback Resistors or Feed-Forward Capacitors Required
- Output Voltage Range: 1.4 V to 20.5 V
- Adjustable Version:
- Output Voltage Range: 1.4 V to 34 V
- ANY-OUT™ Version (User-Programmable Output via PCB Layout):
- Output Current: 1 A
- Dropout Voltage: 307 mV at 1 A
- CMOS Logic Level-Compatible Enable Pin
- Built-In Fixed Current Limit and
Thermal Shutdown - Available in High-Performance Thermal Package: 5-mm × 5-mm QFN
- Operating Temperature Range:
–55°C to 125°C -
Supports Defense, Aerospace, and Medical Applications:
- Controlled Baseline
- One Assembly/Test Site
- One Fabrication Site
- Available in Extended (–55°C to 125°C) Temperature Range
- Extended Product Life Cycle
- Extended Product-Change Notification
- Product Traceability
Simplified Schematic
2 Applications
- Voltage-Controlled Oscillators (VCO)
- Frequency Synthesizers
- Test and Measurement
- Instrumentation, Medical, and Audio
- RX, TX, and PA Circuitry
- Supply Rails for Operational Amplifiers,
DACs, ADCs, and Other High-Precision Analog Circuitry - Post DC-DC Converter Regulation and
Ripple Filtering - Base Stations and Telecom Infrastructure
- 12-V and 24-V Industrial Buses
3 Description
The TPS7A4701-EP is a positive voltage (36 V), ultra-low-noise (4 µVRMS) low-dropout linear regulators (LDO) capable of sourcing a 1-A load.
The TPS7A4701-EP output voltage can be configured with a user-programmable PCB layout (up to 20.5 V), or adjustable (up to 34 V) with external feedback resistors.
The TPS7A4701-EP is designed with bipolar technology primarily for high-accuracy, high-precision instrumentation applications where clean voltage rails are critical to maximize system performance. This feature makes the device ideal for powering operational amplifiers, analog-to-digital converters (ADCs), digital-to-analog converters (DACs), and other high-performance analog circuitry in critical applications such as medical, radio frequency (RF), and test-and-measurement.
In addition, the TPS7A4701-EP is ideal for post DC-DC converter regulation. By filtering out the output voltage ripple inherent to DC-DC switching conversions, maximum system performance is ensured in sensitive instrumentation, test-and-measurement, audio, and RF applications.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| TPS7A4701-EP | VQFN (20) | 5.00 mm × 5.00 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the datasheet.
4 Revision History
| DATE | REVISION | NOTES |
|---|---|---|
| February 2017 | * | Initial release. |
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| 0P1V | 12 | I | When connected to GND, this pin adds 0.1 V to the nominal output voltage of the regulator. |
| Do not connect any voltage other than GND to this pin. If not used, leave this pin floating. | |||
| 0P2V | 11 | I | When connected to GND, this pin adds 0.2 V to the nominal output voltage of the regulator. |
| Do not connect any voltage other than GND to this pin. If not used, leave this pin floating. | |||
| 0P4V | 10 | I | When connected to GND, this pin adds 0.4 V to the nominal output voltage of the regulator. |
| Do not connect any voltage other than GND to this pin. If not used, leave this pin floating. | |||
| 0P8V | 9 | I | When connected to GND, this pin adds 0.8 V to the nominal output voltage of the regulator. |
| Do not connect any voltage other than GND to this pin. If not used, leave this pin floating. | |||
| 1P6V | 8 | I | When connected to GND, this pin adds 1.6 V to the nominal output voltage of the regulator. |
| Do not connect any voltage other than GND to this pin. If not used, leave this pin floating. | |||
| 3P2V | 6 | I | When connected to GND, this pin adds 3.2 V to the nominal output voltage of the regulator. |
| Do not connect any voltage other than GND to this pin. If not used, leave this pin floating. | |||
| 6P4V1 | 5 | I | When connected to GND, this pin adds 6.4 V to the nominal output voltage of the regulator. |
| Do not connect any voltage other than GND to this pin. If not used, leave this pin floating. | |||
| 6P4V2 | 4 | I | When connected to GND, this pin adds 6.4 V to the nominal output voltage of the regulator. |
| Do not connect any voltage other than GND to this pin. If not used, leave this pin floating. | |||
| EN | 13 | I | Enable pin. The device is enabled when the voltage on this pin exceeds the maximum enable voltage, VEN(HI). If enable is not required, tie EN to IN. |
| GND | 7 | — | Ground. |
| IN | 15, 16 | I | Input supply. A capacitor greater than or equal to 1 µF must be tied from this pin to ground to assure stability. A 10-µF capacitor is recommended to be connected from IN to GND (as close to the device as possible) to reduce circuit sensitivity to printed circuit board (PCB) layout, especially when long input traces or high source impedances are encountered. |
| NC | 2, 17-19 | — | This pin can be left open or tied to any voltage between GND and IN. |
| NR | 14 | — | Noise reduction pin. When a capacitor is connected from this pin to GND, RMS noise can be reduced to very low levels. A capacitor greater than or equal to 10 nF must be tied from this pin to ground to assure stability. A 1-µF capacitor is recommended to be connected from NR to GND (as close to the device as possible) to maximize ac performance and minimize noise. |
| OUT | 1, 20 | O | Regulator output. A capacitor greater than or equal to 10 µF must be tied from this pin to ground to assure stability. A 47-µF ceramic output capacitor is highly recommended to be connected from OUT to GND (as close to the device as possible) to maximize ac performance. |
| SENSE/FB | 3 | I | Control-loop error amplifier input. |
| This is the SENSE pin if the device output voltage is programmed using ANY-OUT (no external feedback resistors). This pin must be connected to OUT. Connect this pin to the point of load to maximize accuracy. | |||
| This is the FB pin if the device output voltage is set using external resistors. See the Adjustable Operation section for more details. | |||
| SENSE | 3 | I | This is the SENSE pin of the device and must be connected to OUT. Connect this pin to the point of load to maximize accuracy. |
| Thermal Pad | — | Connect the thermal pad to a large-area ground plane. The thermal pad is internally connected to GND. | |
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
Over junction temperature range, unless otherwise noted(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage(2) | IN pin to GND pin | –0.4 | 36 | V | ||
| EN pin to GND pin | –0.4 | 36 | V | |||
| EN pin to IN pin | –36 | 0.4 | V | |||
| OUT pin to GND pin | –0.4 | 36 | V | |||
| NR pin to GND pin | –0.4 | 36 | V | |||
| SENSE/FB pin to GND pin | –0.4 | 36 | V | |||
| 0P1V pin to GND pin | –0.4 | 36 | V | |||
| 0P2V pin to GND pin | –0.4 | 36 | V | |||
| 0P4V pin to GND pin | –0.4 | 36 | V | |||
| 0P8V pin to GND pin | –0.4 | 36 | V | |||
| 1P6V pin to GND pin | –0.4 | 36 | V | |||
| 3P2V pin to GND pin | –0.4 | 36 | V | |||
| 6P4V1 pin to GND pin | –0.4 | 36 | V | |||
| 6P4V2 pin to GND pin | –0.4 | 36 | V | |||
| Current | Peak output | Internally limited | ||||
| TJ | Operating virtual junction | –55 | 150 | °C | ||
| Tstg | Storage temperature | –65 | 150 | °C | ||
6.2 ESD Ratings
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001, all pins(1) | –2500 | 2500 | V | |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101, all pins(2) | –500 | 500 | ||||
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over junction temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VI | 3.0 | 35 | V | ||
| VO | 1.4 | 34 | V | ||
| VEN | 0 | VIN | V | ||
| IO | 0 | 1 | A | ||
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | TPS7A4701-EP | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RGW | |||
| 20 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 32.5 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 27 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 11.9 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.3 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 11.9 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 1.7 | °C/W |
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
At –55°C ≤ TJ ≤ 125°C; VI = VO(nom) + 1 V or VI = 3 V (whichever is greater); VEN = VI; IO = 0 mA; CIN = 10 µF; COUT = 10 µF; CNR = 10 nF; SENSE/FB tied to OUT; and 0P1V, 0P2V, 0P4V, 0P8V, 1P6V, 3P2V, 6P4V1, 6P4V2 pins OPEN, unless otherwise noted.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VI | Input voltage range | 3 | 35 | V | ||||
| VUVLO | Under-voltage lockout threshold | VI rising | 2.67 | V | ||||
| VI falling | 2.5 | |||||||
| V(REF) | Reference voltage | V(REF) = V(FB) | 1.4 | V | ||||
| VUVLO(HYS) | Under-voltage lockout hysteresis | 177 | mV | |||||
| VNR | Noise reduction pin voltage | Using ANY-OUT option | VOUT | V | ||||
| Using adjustable option | 1.4 | |||||||
| VO | Output voltage range | VI ≥ VO(nom) + 1 V or 3 V (whichever is greater), COUT = 20 µF |
Using ANY-OUT option | 1.4 | 20.5 | V | ||
| Using adjustable option | 1.4 | 34 | ||||||
| Nominal accuracy | TJ = 25°C, COUT = 20 µF | –1 | 1 | %VO | ||||
| Overall accuracy | VO(nom) + 1 V ≤ VI ≤ 35 V, 0 mA ≤ IO ≤ 1 A, COUT = 20 µF |
–3.5 | 3.5 | |||||
| ΔVO(ΔVI) | Line regulation | VO(nom) + 1 V ≤ VI ≤ 35 V | 0.092 | %VO | ||||
| ΔVO(ΔIO) | Load regulation | 0 mA ≤ IO ≤ 1 A | 0.3 | %VO | ||||
| V(DO) | Dropout voltage | VI = 95% VO(nom), IO = 0.5 A | 216 | mV | ||||
| VI = 95% VO(nom), IO = 1 A | 307 | 450 | ||||||
| I(CL) | Current limit | VO = 90% VO(nom) | 1 | 1.26 | A | |||
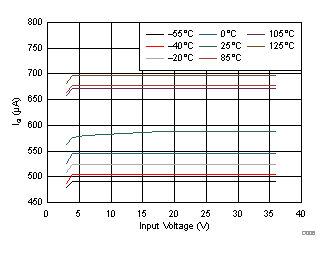
| I(GND) | Ground pin current | IO = 0 mA | 0.58 | 1 | mA | |||
| IO = 1 A | 6.1 | |||||||
| I(EN) | Enable pin current | VEN = VI | 0.78 | 2 | µA | |||
| VI = VEN = 35 V | 0.81 | 2 | ||||||
| I(SHDN) | Shutdown supply current | VEN = 0.4 V | 2.55 | 8 | µA | |||
| VEN = 0.4 V, VI = 35 V | 3.04 | 60 | ||||||
| V+EN(HI) | Enable high-level voltage | 2 | VI | V | ||||
| V+EN(LO) | Enable low-level voltage | 0 | 0.4 | V | ||||
| I(FB) | Feedback pin current | 350 | nA | |||||
| PSRR | Power-supply rejection ratio | VI = 16 V, VO(nom) = 15 V, COUT = 50 µF, IO = 500 mA, CNR = 1 µF, f = 1 kHz |
78 | dB | ||||
| Vn | Output noise voltage | VI = 3 V, VO(nom) = 1.4 V, COUT = 50 µF, CNR = 1 µF, BW = 10 Hz to 100 kHz |
4.17 | µVRMS | ||||
| VIN = 6 V, VO(nom) = 5 V, COUT = 50 µF, CNR = 1 µF, BW = 10 Hz to 100 kHz |
4.67 | |||||||
| Tsd | Thermal shutdown temperature | Shutdown, temperature increasing | 170 | °C | ||||
| Reset, temperature decreasing | 150 | |||||||
| TJ | Operating junction temperature | –55 | 125 | °C | ||||
6.6 Typical Characteristics
At –55°C ≤ TJ ≤ 125°C; VI = VO(nom) + 1 V or VI = 3 V (whichever is greater); VEN = VI; IO = 0 mA; CIN = 10 µF; COUT = 10 µF; CNR = 1 µF; SENSE/FB tied to OUT; and 0P1V, 0P2V, 0P4V, 0P8V, 1P6V, 3P2V, 6P4V1, 6P4V2 pins OPEN, unless otherwise noted.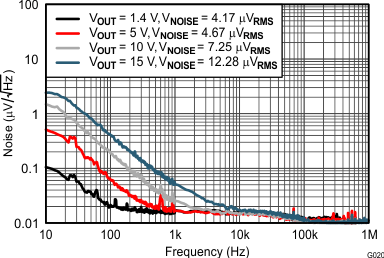
| IOUT = 500 mA | COUT = 50 µF | CNR = 1 µF |
| BWRMSNOISE (10 Hz, 100 kHz) | ||





| IOUT = 1 A | COUT = 50 µF | VIN = 3 V |
| VOUT = 1.4 V |

| CNR = 1 µF | COUT = 50 µF | VIN = 3 V |
| VOUT = 1.4 V |

| VOUT = 3.3 V | CNR = 1 µF | COUT = 50 µF |
| IOUT = 500 mA |

| CNR = 1 µF | COUT = 50 µF | IOUT = 500 mA |

| VIN = 5 V | VOUT = 3.3 V | IOUT = 10 mA to 845 mA |

| Startup Time = 65 ms | VIN = 6 V | VOUT = 5 V |
| IOUT = 500 mA | CIN = 10 µF | COUT = 50 µF |
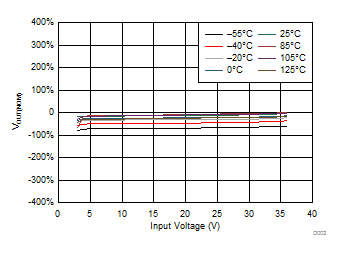

| IOUT = 0 µA |

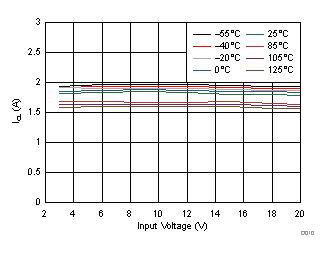
| VOUT = 90% VOUT(NOM) | ||
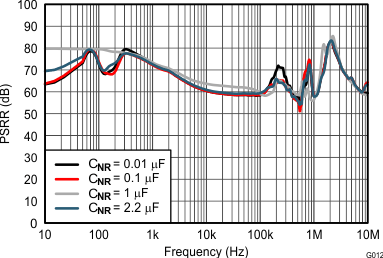
| IOUT = 0.5 A | COUT = 50 µF | VIN = 3 V |
| VOUT = 1.4 V |

| VOUT = 3.3 V | CNR = 1 µF | COUT = 50 µF |
| IOUT = 50 mA |

| VOUT = 3.3 V | CNR = 1 µF | COUT = 50 µF |
| IOUT = 1 A |

| CNR = 1 µF | COUT = 50 µF | IOUT = 1000 mA |

| VIN = 5 V to 15 V | VOUT = 3.3 V | IOUT = 845 mA |

| VOUT = 4.7 V | COUT = 10 µF | CNR = 1 µF |
| BWRMSNOISE (10 Hz, 100 kHz) | ||
7 Detailed Description
7.1 Overview
The TPS7A4701-EP is a positive voltage (36 V), ultra-low-noise (4 µVRMS) LDOs capable of sourcing a 1-A load. The TPS7A4701-EP is designed with bipolar technology primarily for high-accuracy, high-precision instrumentation applications where clean voltage rails are critical to maximize system performance. This feature makes the device ideal for powering operational amplifiers, analog-to-digital converters (ADCs), digital-to-analog converters (DACs), and other high-performance analog circuitry.
7.2 Functional Block Diagram

7.3 Feature Description
7.3.1 Internal Current Limit (ICL)
The internal current limit circuit is used to protect the LDO against high-load current faults or shorting events. The LDO is not designed to operate at a steady-state current limit. During a current-limit event, the LDO sources constant current. Therefore, the output voltage falls while load impedance decreases. Note also that when a current limit occurs while the resulting output voltage is low, excessive power is dissipated across the LDO, which results in a thermal shutdown of the output.
7.3.2 Enable (EN) And Under-Voltage Lockout (UVLO)
The TPS7A4701-EP only turns on when both EN and UVLO are above the respective voltage thresholds. The UVLO circuit monitors input voltage (VI) to prevent device turnon before VI rises above the lockout voltage. The UVLO circuit also causes a shutdown when VI falls below lockout. The EN signal allows independent logic-level turnon and shutdown of the LDO when the input voltage is present. EN can be connected directly to VI if independent turnon is not needed.
7.3.3 Soft-Start and Inrush Current
Soft-start refers to the ramp-up characteristic of the output voltage during LDO turnon after EN and UVLO have achieved threshold voltage. The noise reduction capacitor serves a dual purpose of both governing output noise reduction and programming the soft-start ramp during turnon.
Inrush current is defined as the current through the LDO from IN to OUT during the time of the turnon ramp up. Inrush current then consists primarily of the sum of load and charge current to the output capacitor. Inrush current can be estimated by Equation 1:

where
7.4 Device Functional Modes
The TPS7A4701-EP has the following functional modes:
- Enabled: When EN goes above V+EN(HI), the device is enabled.
- Disabled: When EN goes below V+EN(LO), the device is disabled. During this time, OUT is high impedance, and the current into IN does not exceed I(SHDN).
7.5 Programming
7.5.1 ANY-OUT Programmable Output Voltage
TPS7A4701-EP can be used in ANY-OUT mode. For ANY-OUT operation, the device does not use external resistors to set the output voltage, but uses device pins 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 11, and 12 to program the regulated output voltage. Each pin is either connected to ground (active) or is left open (floating). The ANY-OUT programming is set by Equation 2 as the sum of the internal reference voltage (V(REF) = 1.4 V) plus the accumulated sum of the respective voltages assigned to each active pin; that is, 100 mV (pin 12), 200 mV (pin 11), 400 mV (pin 10), 800 mV (pin 9), 1.6 V (pin 8), 3.2 V (pin 6), 6.4 V (pin 5), or 6.4 V (pin 4). Table 1 summarizes these voltage values associated with each active pin setting for reference. By leaving all program pins open, or floating, the output is thereby programmed to the minimum possible output voltage equal to V(REF).

Table 1. ANY-OUT Programmable Output Voltage
| ANY-OUT PROGRAM PINS (Active Low) | ADDITIVE OUTPUT VOLTAGE LEVEL |
|---|---|
| Pin 4 (6P4V2) | 6.4 V |
| Pin 5 (6P4V1) | 6.4 V |
| Pin 6 (3P2) | 3.2 V |
| Pin 8 (1P6) | 1.6 V |
| Pin 9 (0P8) | 800 mV |
| Pin 10 (0P4) | 400 mV |
| Pin 11 (0P2) | 200 mV |
| Pin 12 (0P1) | 100 mV |
Table 2 shows a list of the most common output voltages and the corresponding pin settings. The voltage setting pins have a binary weight; therefore, the output voltage can be programmed to any value from 1.4 V to 20.5 V in 100-mV steps.
Table 2. Common Output Voltages and Corresponding Pin Settings
| VO (V) | PIN NAMES AND VOLTAGE PER PIN | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0P1V 100 mV |
0P2V 200 mV |
0P4V 400 mV |
0P8V 800 mV |
1P6V 1.6 V |
3P2V 3.2 V |
6P4V1 6.4 V |
6P4V2 6.4 V |
|
| 1.4 | Open | Open | Open | Open | Open | Open | Open | Open |
| 1.5 | GND | Open | Open | Open | Open | Open | Open | Open |
| 1.8 | Open | Open | GND | Open | Open | Open | Open | Open |
| 2.5 | GND | GND | Open | GND | Open | Open | Open | Open |
| 3 | Open | Open | Open | Open | GND | Open | Open | Open |
| 3.3 | GND | GND | Open | Open | GND | Open | Open | Open |
| 4.5 | GND | GND | GND | GND | GND | Open | Open | Open |
| 5 | Open | Open | GND | Open | Open | GND | Open | Open |
| 10 | Open | GND | GND | Open | GND | Open | GND | Open |
| 12 | Open | GND | Open | GND | Open | GND | GND | Open |
| 15 | Open | Open | Open | GND | Open | Open | GND | GND |
| 18 | Open | GND | GND | Open | Open | GND | GND | GND |
| 20.5 | GND | GND | GND | GND | GND | GND | GND | GND |
7.5.2 Adjustable Operation
The TPS7A4701-EP has an output voltage range of 1.4 V to 34 V. For adjustable operation, set the nominal output voltage of the device using two external resistors, as shown in Figure 23.
 Figure 23. Adjustable Operation for Maximum AC Performance
Figure 23. Adjustable Operation for Maximum AC Performance
R1 and R2 can be calculated for any output voltage within the operational range. The current through feedback resistor R2 must be at least 5 µA to ensure stability. Additionally, the current into the FB pin (I(FB), typically 350 nA) creates an additional output voltage offset that depends on the resistance of R1. For high-accuracy applications, select R2 such that the current through R2 is at least 35 µA to minimize any effects of I(FB) variation on the output voltage; 10 kΩ is recommended. R1 can be calculated using Equation 3.
Use 0.1% tolerance resistors to minimize the effects of resistor inaccuracy on the output voltage.
Table 3 shows the resistor combinations to achieve some standard rail voltages with commercially-available 1% tolerance resistors. The resulting output voltages yield a nominal error of < 0.5%.
Table 3. Suggested Resistors for Common Voltage Rails
| VOUT | R1, Calculated | R1, Closest 1% Value | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.4 V | 0 Ω | 0 Ω | ∞ |
| 1.8 V | 2.782 kΩ | 2.8 kΩ | 9.76 kΩ |
| 3.3 V | 13.213 kΩ | 13.3 kΩ | 9.76 kΩ |
| 5 V | 25.650 kΩ | 25.5 kΩ | 10 kΩ |
| 12 V | 77.032 kΩ | 76.8 kΩ | 10.2 kΩ |
| 15 V | 101.733 kΩ | 102 kΩ | 10.5 kΩ |
| 18 V | 118.276 kΩ | 118 kΩ | 10 kΩ |
| 24 V | 164.238 kΩ | 165 kΩ | 10.2 kΩ |
To achieve higher nominal accuracy, two resistors can be used in the place of R1. Select the two resistor values such that the sum results in a value as close as possible to the calculated R1 value.
There are several alternative ways to set the output voltage. The program pins can be pulled low using external general-purpose input/output pins (GPIOs), or can be hardwired by the given layout of the printed circuit board (PCB) to set the ANY-OUT voltage. The TPS7A4701 evaluation module (EVM), available for purchase from the TI eStore, allows the output voltage to be programmed using jumpers.
