The SN65LVDM31 incorporates four differential line drivers that implement the electrical characteristics
of low-voltage differential signaling. This product offers a low-power alternative to 5-V
PECL drivers with similar signal levels. Any of the four current-mode drivers will deliver a minimum
differential output voltage magnitude of 540 mV into a 100- load when enabled by either an
active-low or active-high enable input.
load when enabled by either an
active-low or active-high enable input.
The intended application of this device and signaling technique is for both point-to-point and
multiplexed baseband data transmission over controlled impedance media of approximately 100  . The transmission media may be printed-circuit board
traces, backplanes, or cables. The ultimate rate and distance of data transfer is dependent upon the attenuation
characteristics of the media and the noise coupling to the environment.
. The transmission media may be printed-circuit board
traces, backplanes, or cables. The ultimate rate and distance of data transfer is dependent upon the attenuation
characteristics of the media and the noise coupling to the environment.
The SN65LVDM31 is characterized for operation from -40°C to 85°C.
The SN65LVDM31 incorporates four differential line drivers that implement the electrical characteristics
of low-voltage differential signaling. This product offers a low-power alternative to 5-V
PECL drivers with similar signal levels. Any of the four current-mode drivers will deliver a minimum
differential output voltage magnitude of 540 mV into a 100- load when enabled by either an
active-low or active-high enable input.
load when enabled by either an
active-low or active-high enable input.
The intended application of this device and signaling technique is for both point-to-point and
multiplexed baseband data transmission over controlled impedance media of approximately 100  . The transmission media may be printed-circuit board
traces, backplanes, or cables. The ultimate rate and distance of data transfer is dependent upon the attenuation
characteristics of the media and the noise coupling to the environment.
. The transmission media may be printed-circuit board
traces, backplanes, or cables. The ultimate rate and distance of data transfer is dependent upon the attenuation
characteristics of the media and the noise coupling to the environment.
The SN65LVDM31 is characterized for operation from -40°C to 85°C.
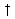 Up to 150 Mbps
Up to 150 Mbps Load
Load