SBAS661C February 2015 – May 2021 ADS1262 , ADS1263
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8.1 Offset Temperature Drift Measurement
- 8.2 Gain Temperature Drift Measurement
- 8.3 Common-Mode Rejection Ratio Measurement
- 8.4 Power-Supply Rejection Ratio Measurement
- 8.5 Crosstalk Measurement (ADS1263)
- 8.6 Reference-Voltage Temperature-Drift Measurement
- 8.7 Reference-Voltage Thermal-Hysteresis Measurement
- 8.8 Noise Performance
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Multifunction Analog Inputs
- 9.3.2 Analog Input Description
- 9.3.3 Sensor Bias
- 9.3.4 Temperature Sensor
- 9.3.5 Power-Supply Monitor
- 9.3.6 PGA
- 9.3.7 PGA Voltage Overrange Monitors
- 9.3.8 ADC Reference Voltage
- 9.3.9 ADC1 Modulator
- 9.3.10 Digital Filter
- 9.3.11 Sensor-Excitation Current Sources (IDAC1 and IDAC2)
- 9.3.12 Level-Shift Voltage
- 9.3.13 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 9.3.14 Test DAC (TDAC)
- 9.3.15 ADC2 (ADS1263)
- 9.4
Device Functional Modes
- 9.4.1 Conversion Control
- 9.4.2 Conversion Latency
- 9.4.3 Programmable Time Delay
- 9.4.4 Serial Interface
- 9.4.5 Data Ready Pin (DRDY)
- 9.4.6 Conversion Data Software Polling
- 9.4.7 Read Conversion Data
- 9.4.8 ADC Clock Modes
- 9.4.9
Calibration
- 9.4.9.1 Offset and Full-Scale Calibration
- 9.4.9.2 ADC1 Offset Self-Calibration (SFOCAL1)
- 9.4.9.3 ADC1 Offset System Calibration (SYOCAL1)
- 9.4.9.4 ADC2 Offset Self-Calibration ADC2 (SFOCAL2)
- 9.4.9.5 ADC2 Offset System Calibration ADC2 (SYOCAL2)
- 9.4.9.6 ADC1 Full-Scale System Calibration (SYGCAL1)
- 9.4.9.7 ADC2 Full-Scale System Calibration ADC2 (SYGCAL2)
- 9.4.9.8 Calibration Command Procedure
- 9.4.9.9 User Calibration Procedure
- 9.4.10 Reset
- 9.4.11 Power-Down Mode
- 9.4.12 Chop Mode
- 9.5 Programming
- 9.6
Register Maps
- 9.6.1 Device Identification Register (address = 00h) [reset = x]
- 9.6.2 Power Register (address = 01h) [reset = 11h]
- 9.6.3 Interface Register (address = 02h) [reset = 05h]
- 9.6.4 Mode0 Register (address = 03h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.5 Mode1 Register (address = 04h) [reset = 80h]
- 9.6.6 Mode2 Register (address = 05h) [reset = 04h]
- 9.6.7 Input Multiplexer Register (address = 06h) [reset = 01h]
- 9.6.8 Offset Calibration Registers (address = 07h, 08h, 09h) [reset = 00h, 00h, 00h]
- 9.6.9 Full-Scale Calibration Registers (address = 0Ah, 0Bh, 0Ch) [reset = 40h, 00h, 00h]
- 9.6.10 IDACMUX Register (address = 0Dh) [reset = BBh]
- 9.6.11 IDACMAG Register (address = 0Eh) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.12 REFMUX Register (address = 0Fh) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.13 TDACP Control Register (address = 10h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.14 TDACN Control Register (address = 11h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.15 GPIO Connection Register (address = 12h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.16 GPIO Direction Register (address = 13h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.17 GPIO Data Register (address = 14h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.18 ADC2 Configuration Register (address = 15h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.19 ADC2 Input Multiplexer Register (address = 16h) [reset = 01h]
- 9.6.20 ADC2 Offset Calibration Registers (address = 17h, 18h) [reset = 00h, 00h]
- 9.6.21 ADC2 Full-Scale Calibration Registers (address = 19h, 1Ah) [reset = 00h, 40h]
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PW|28
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.3.3 Sensor Bias
The ADC incorporates a sensor bias current source that can be used to apply a small test current to diagnose broken sensor leads or problems existing in the sensor. Figure 9-3 shows the sensor bias block diagram. The sensor bias circuit consists of programmable current sources and bias resistors. The sensor bias circuit connects to the outputs of either the ADC1 or ADC2 multiplexers. Program the sensor bias to either pull-up or pull-down mode. In pull-up mode, the current flows into the positive input and flows out of the negative input. In pull-down mode, the polarities are reversed. Configure the sensor bias either to a 10-MΩ bias resistor, or to current with magnitudes of ±0.5, ±2, ±10, ±50, or ±200 µA.
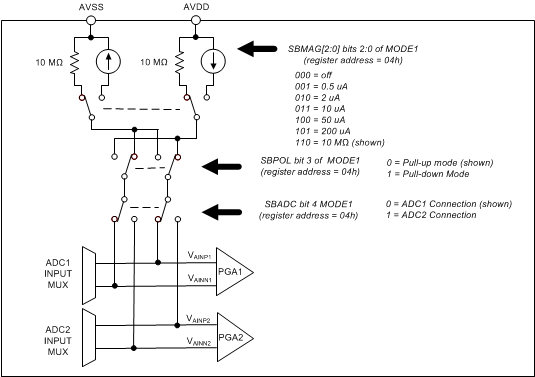 Figure 9-3 Sensor Bias Block Diagram
Figure 9-3 Sensor Bias Block DiagramIn pull-up mode, an open sensor results in the positive input pulled to VAVDD, and the negative input pulled to VAVSS. An open sensor in pull-up mode results in a positive full-scale reading. A full-scale reading can also be an indication of sensor overload or that the reference voltage is lower than expected. The sensor bias can remain on while actively converting, or pulsed on periodically to test the sensor. When pulsed on, allow time for settling because external capacitance loads the sensor bias when first enabled. Be aware of offset error as a result of sensor bias current flowing through the multiplexer switch resistance.