Typical values at TA = +25°C, ADC
Sampling Rate = 2949.12 GHz. Default conditions: output sample rate = 491.52MSPS
(decimate by 6), PLL clock mode with fREF = 491.52MHz, AIN =
–3 dBFS, DSA setting = 4 dB.
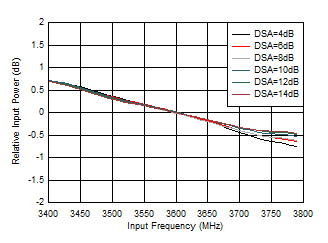
| With 3.6 GHz matching, normalized to 3.6 GHz |
|
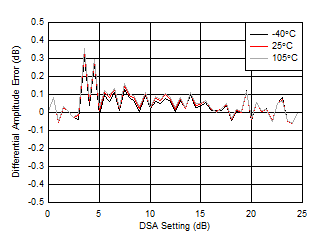
| With 3.6 GHz matching |
| Differential Amplitude Error = PIN(DSA Setting – 1) – PIN(DSA Setting) + 1 |
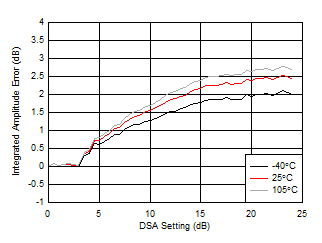
| With 3.6 GHz matching |
| Integrated Amplitude Error = PIN(DSA Setting) – PIN(DSA Setting = 0) + (DSA Setting) |
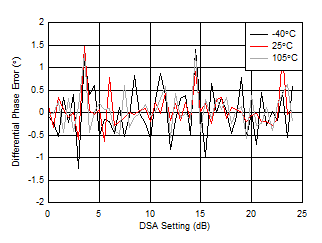
| With 3.6 GHz matching |
| Differential Phase Error = PhaseIN(DSA Setting – 1) – PhaseIN(DSA Setting) |
| With 3.6 GHz matching |
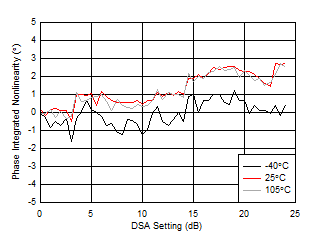
| Integrated Phase Error = Phase(DSA Setting) – Phase(DSA Setting = 0) |
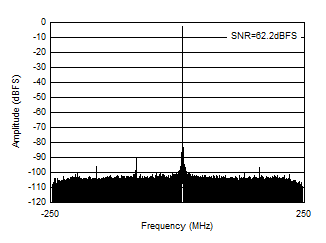
| With 3.6 GHz matching , fIN = 3610 MHz, AIN = –3 dBFS |
|
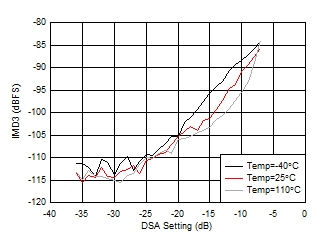
| With 3.5 GHz matching, 20-MHz tone spacing |
|
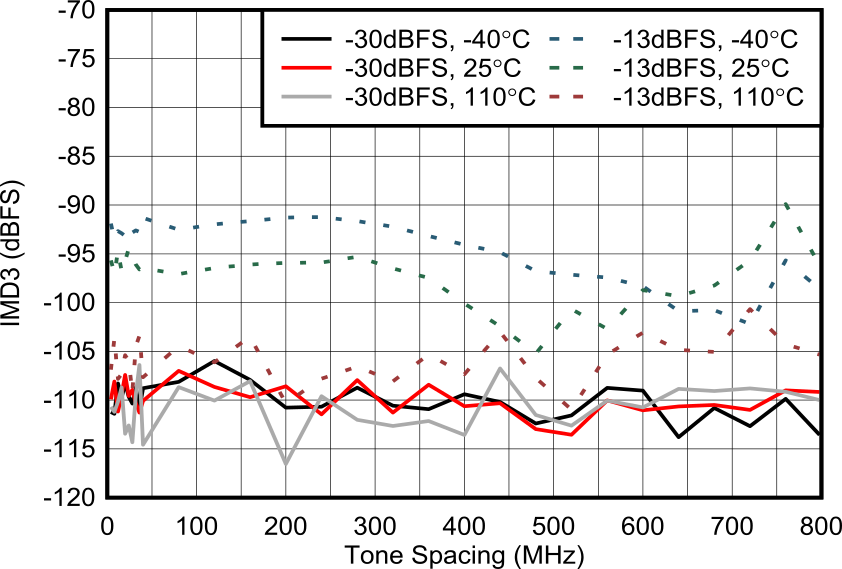
| External clock mode, 2x
Decimation |
|
Figure 6-151 RX IMD3 vs Tone
Spacing at 3.76GHz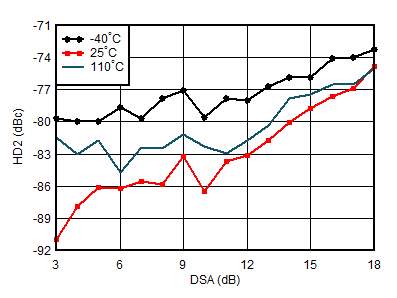
| With 3.5 GHz matching, DDC bypass mode (TI only mode for characterization) |
| With 3.5 GHz matching, DDC bypass mode (TI only mode for characterization) |

| External clock mode, 25°C, 2x
Decimation |
Figure 6-157 RX HD2 vs Input
Level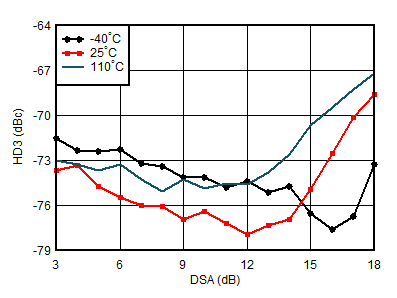
| With 3.5 GHz matching, DDC bypass mode (TI only mode for characterization) |
| With 3.5 GHz matching, DDC bypass mode (TI only mode for characterization) |
| External clock mode, 25°C, 2x
Decimation |
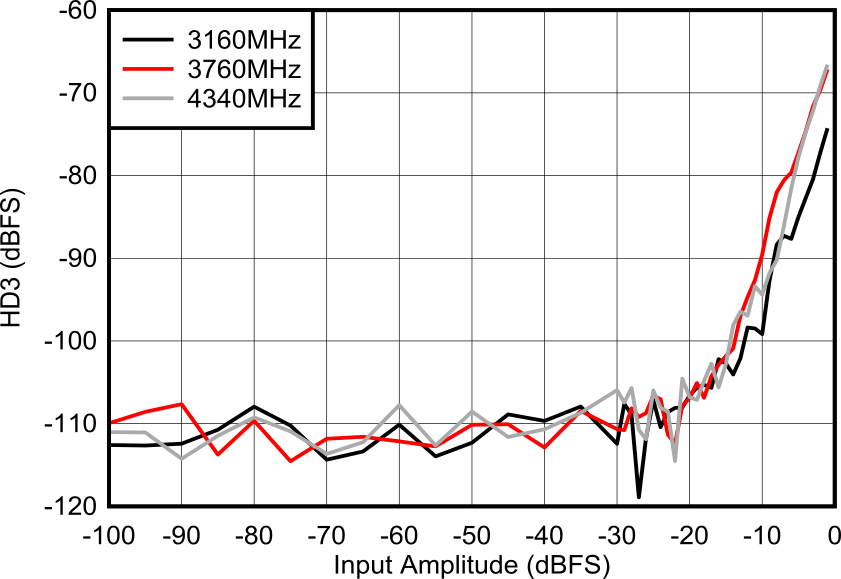
Figure 6-163 RX HD3 vs Input
Level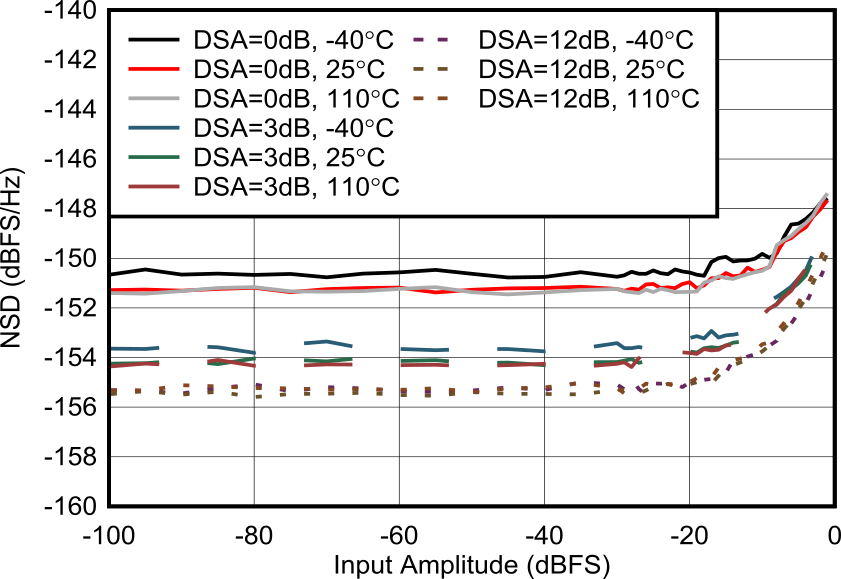
| External clock mode, 25°C, 2x
Decimation |
Figure 6-165 RX Noise Spectral
Density vs Input Level at 3.76GHz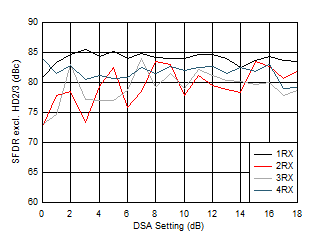 Figure 6-167 RX SFDR Excluding HD2/3 vs DSA Setting and Channel at 3.6 GHz
Figure 6-167 RX SFDR Excluding HD2/3 vs DSA Setting and Channel at 3.6 GHz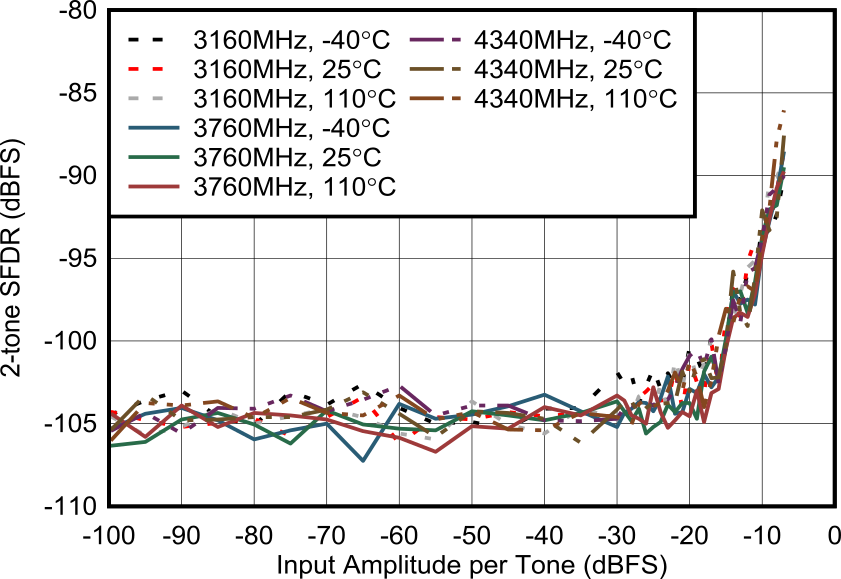
| External clock mode, 20MHz tone
spacing, excluding 3rd order
distortion |
Figure 6-169 RX 2-tone SFDR vs
Input Amplitude and Frequency at 3.7 GHz
| With 3.6 GHz matching, –7 dBFS each
tone, 20-MHz tone spacing, all supplies at MIN,
TYP, or MAX recommended operating voltages |
Figure 6-171 RX
IMD5 vs Supply Voltage and Channel at 3.6
GHz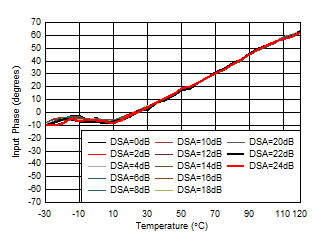
| With 3.6 GHz matching, normalized to phase at 25°C |
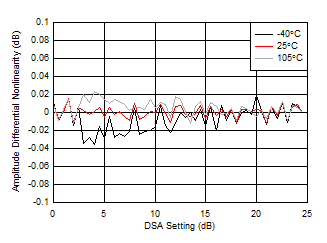
| With 3.6 GHz matching |
| Differential Amplitude Error = PIN(DSA Setting – 1) – PIN(DSA Setting) + 1 |
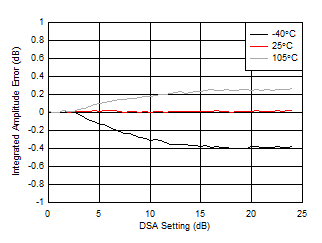
| With 3.6 GHz matching |
| Integrated Amplitude Error = PIN(DSA Setting) – PIN(DSA Setting = 0) + (DSA Setting) |
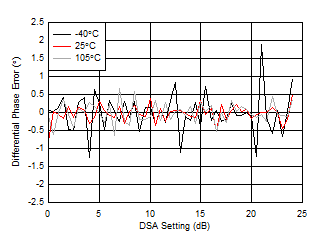
| With 3.6 GHz matching |
| Differential Phase Error = PhaseIN(DSA Setting – 1) – PhaseIN(DSA Setting) |
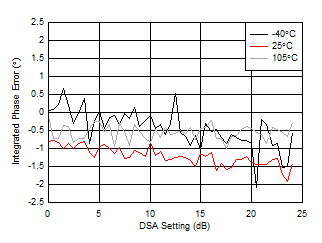
| With 3.6 GHz matching |
| Integrated Phase Error = Phase(DSA Setting) – Phase(DSA Setting = 0) |
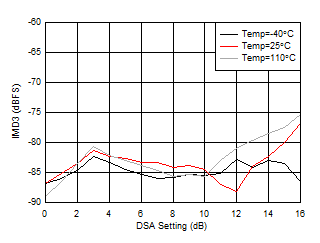
| With 3.5 GHz matching, each tone at –7 dBFS, 20-MHz tone spacing |
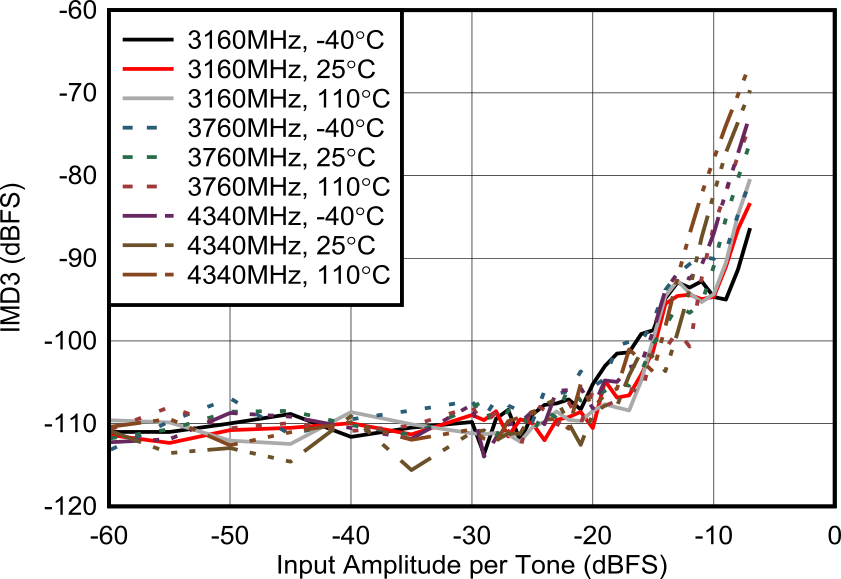
| External clock mode, 20-MHz tone
spacing, 2x Decimation |
|
Figure 6-150 RX IMD3 vs Input
Level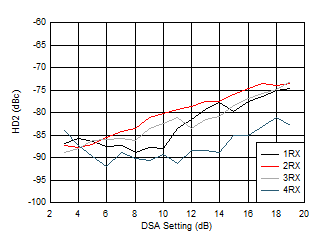
| With 3.5 GHz matching, DDC bypass mode (TI only mode for characterization) |
| With 3.5 GHz matching, DDC bypass mode (TI only mode for characterization) |
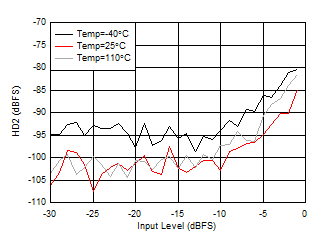
| External clock mode, 2x
Decimation |
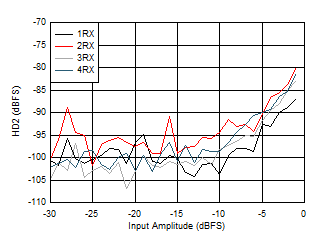
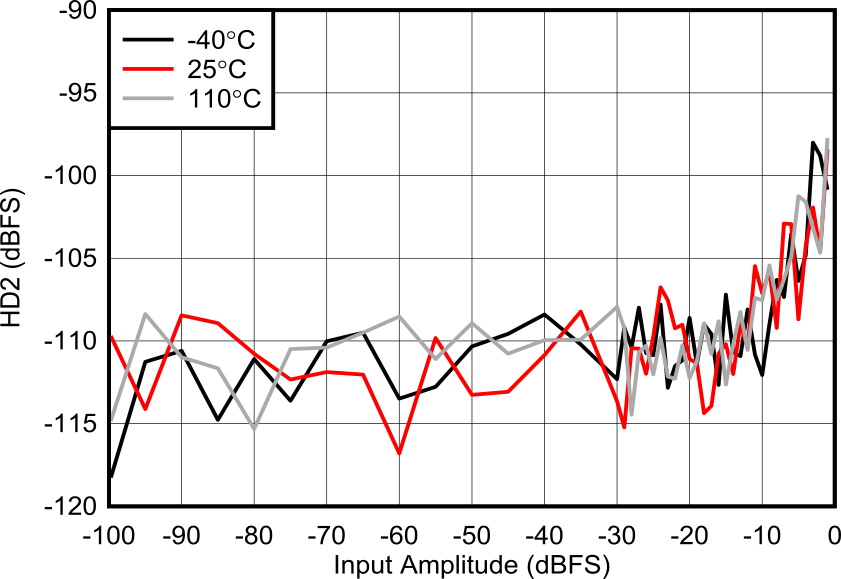
Figure 6-156 RX HD2 vs Input Level
at 3.76 GHz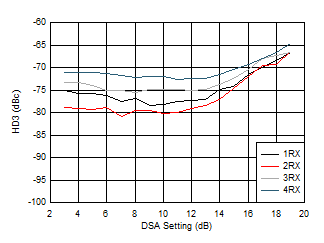
| With 3.5 GHz matching, DDC bypass mode (TI only mode for characterization) |
| With 3.5 GHz matching, DDC bypass mode (TI only mode for characterization) |

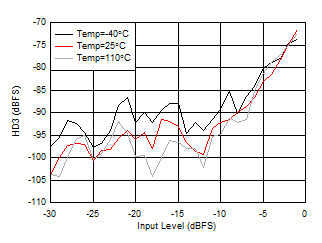
| External clock mode, 2x
Decimation |
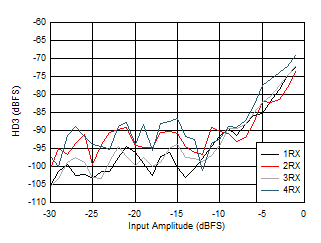
Figure 6-162 RX HD3 vs Input Level
at 3.76GHz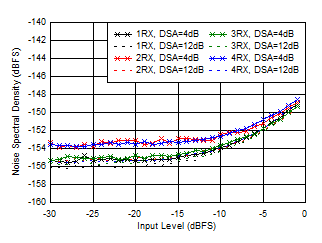
| With 3.5 GHz matching, 12.5-MHz offset from tone |
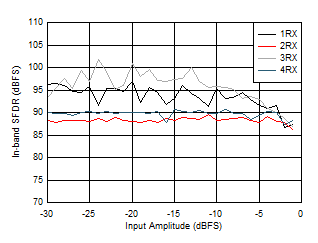 Figure 6-166 RX In-Band SFDR (±200 MHz) vs Input Level and Channel at 3.6 GHz
Figure 6-166 RX In-Band SFDR (±200 MHz) vs Input Level and Channel at 3.6 GHz
| External clock mode, 20MHz tone
spacing, excluding 3rd order
distortion |
Figure 6-168 RX 2-tone SFDR vs
Input Amplitude and DSA Setting at 3.7 GHz
| With 3.6 GHz matching, –7 dBFS each
tone, 20-MHz tone spacing, all supplies at MIN,
TYP, or MAX recommended operating voltages |
Figure 6-170 RX
IMD3 vs Supply Voltage and Channel at 3.6
GHz
| With 3.6 GHz matching, tone at –20
dBFS, 12.5-MHz offset frequency, all supplies at
MIN, TYP, or MAX recommended operating
voltages |
Figure 6-172 RX
Noise Spectral Density vs Supply Voltage and
Channel at 3.6 GHz


































