DLPS241 april 2023 DLP670RE
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 Storage Conditions
- 6.3 ESD Ratings
- 6.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.5 Thermal Information
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7 Timing Requirements
- 6.8 System Mounting Interface Loads
- 6.9 Micromirror Array Physical Characteristics
- 6.10 Micromirror Array Optical Characteristics
- 6.11 Window Characteristics
- 6.12 Chipset Component Usage Specification
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Requirements
- 10Device Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- FYE|350
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
9.3 DMD Power Supply Power-Down Procedure
- During power-down, VCC and VCCI must be supplied until after VBIAS, VRESET, and VOFFSET are discharged to within the specified limit of ground. Refer to Table 9-1.
- During power-down, it is a strict requirement that the change between VBIAS and VOFFSET must be within the specified limit shown in the Recommended Operating Conditions table. During power-down, it is not mandatory to stop driving VBIAS prior to VOFFSET.
- During power-down, there is no requirement for the relative timing of VRESET with respect to VOFFSET and VBIAS.
- Power supply slew rates during power-down are flexible, provided that the transient voltage levels follow the requirements listed in Absolute Maximum Ratings, in Recommended Operating Conditions, and in Figure 9-1.
- During power-down, LVCMOS input pins must be less than specified in the Recommended Operating Conditions table.
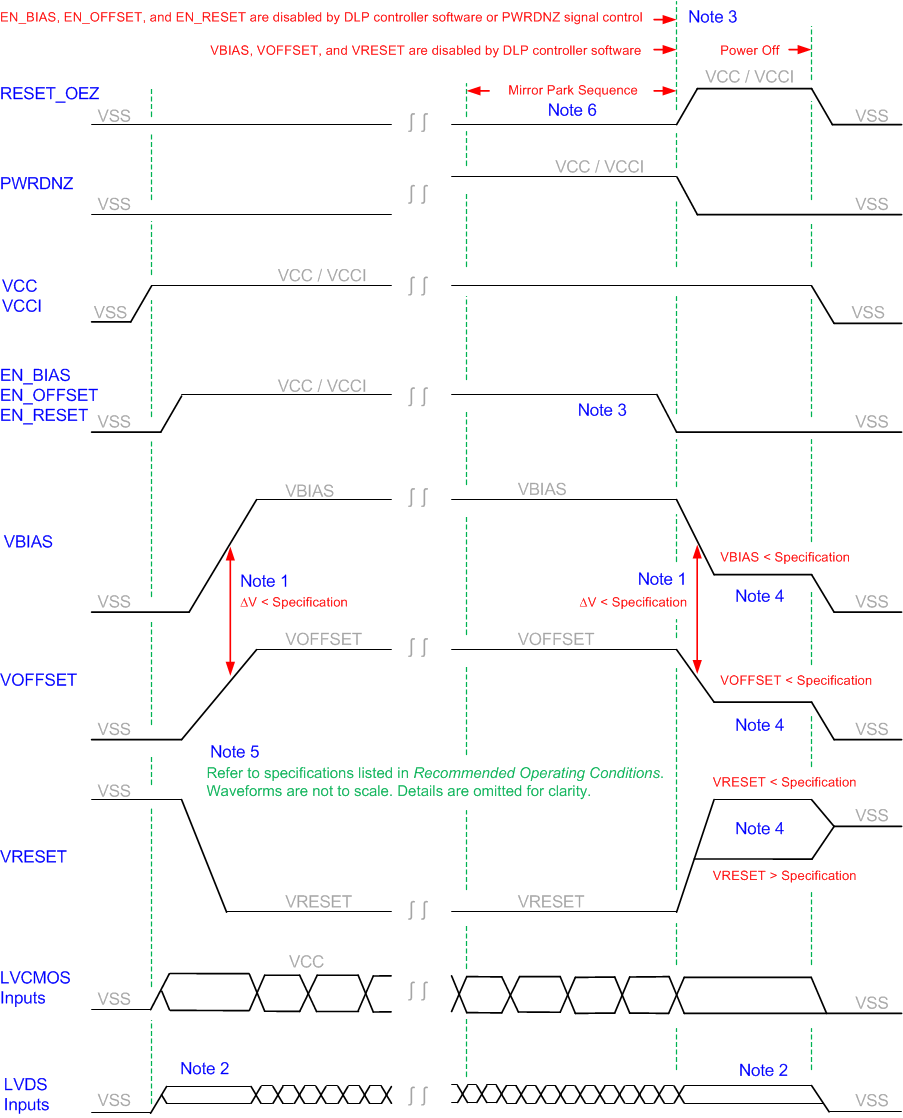 Figure 9-1 DMD Power Supply Sequencing Requirements
Figure 9-1 DMD Power Supply Sequencing RequirementsA. To prevent excess current, the supply voltage change |VBIAS – VOFFSET| must be less than specified in the Recommended Operating Conditions table. OEMs may find that the most reliable way to ensure this is to power VOFFSET prior to VBIAS during power-up and to remove VBIAS prior to VOFFSET during power-down.
B. LVDS signals are less than the input differential voltage (VID) maximum specified in the Recommended Operating Conditions table. During power-down, LVDS signals are less than the high level input voltage (VIH) maximum specified in the Recommended Operating Conditions table.
C. When system power is interrupted, the DLP DLPC4430 initiates a hardware power-down that activates PWRDNZ and disables VBIAS, VRESET and VOFFSET after the micromirror park sequence. Software power-down disables VBIAS, VRESET, and VOFFSET after the micromirror park sequence through software control. For either case, enable signals EN_BIAS, EN_OFFSET, and EN_RESET are used to disable VBIAS, VOFFSET, and VRESET, respectfully.
D. Refer to Table 9-1.
E. Figure not to scale. Details have been omitted for clarity. Refer to the Recommended Operating Conditions table.
F. EN_BIAS, EN_OFFSET, and EN_RESET are disabled by DLP controller software or PWRDNZ signal control.
G. VBIAS, VOFFSET, and VRESET are disabled by DLP controller software
Table 9-1 DMD Power-Down Sequence Requirements
| PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VBIAS | Supply voltage level during power–down sequence | 4.0 | V | |
| VOFFSET | 4.0 | V | ||
| VRESET | –4.0 | 0.5 | V | |