DLPS241 april 2023 DLP670RE
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 Storage Conditions
- 6.3 ESD Ratings
- 6.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.5 Thermal Information
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7 Timing Requirements
- 6.8 System Mounting Interface Loads
- 6.9 Micromirror Array Physical Characteristics
- 6.10 Micromirror Array Optical Characteristics
- 6.11 Window Characteristics
- 6.12 Chipset Component Usage Specification
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Requirements
- 10Device Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- FYE|350
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
6.7 Timing Requirements
Over Recommended Operating Conditions (Section 6.4) unless otherwise noted.(5)
| DESCRIPTION(1) | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCP INTERFACE(2) | |||||||
| tr | Rise time | 20% to 80% reference points | 200 | ns | |||
| tƒ | Fall time | 80% to 20% reference points | 200 | ns | |||
| LVDS INTERFACE(2) | |||||||
| tr | Rise time | 20% to 80% | 100 | 400 | ps | ||
| tƒ | Fall time | 80% to 20% | 100 | 400 | ps | ||
| LVDS CLOCKS(3) | |||||||
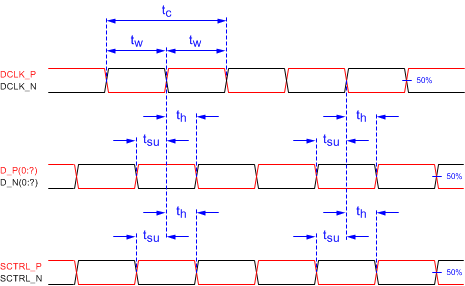
| tc | Cycle time | DCLK_A, 50% to 50% | 2.5 | ns | |||
| DCLK_B, 50% to 50% | 2.5 | ||||||
| tw | Pulse duration | DCLK_A, 50% to 50% | 1.19 | 1.25 | ns | ||
| DCLK_B, 50% to 50% | 1.19 | 1.25 | |||||
| LVDS INTERFACE(3) | |||||||
| tsu | Setup time | D_A(15:0) before rising or falling edge of DCLK_A | 0.17 | ns | |||
| D_B(15:0) before rising or falling edge of DCLK_B | 0.17 | ||||||
| tsu | Setup time | SCTRL_A before rising or falling edge of DCLK_A | 0.17 | ns | |||
| SCTRL_B before rising or falling edge of DCLK_B | 0.17 | ||||||
| th | Hold time | D_A(15:0) after rising or falling edge of DCLK_A | 0.47 | ns | |||
| D_B(15:0) after rising or falling edge of DCLK_B | 0.47 | ||||||
| th | Hold time | SCTRL_A after rising or falling edge of DCLK_A | 0.47 | ns | |||
| SCTRL_B after rising or falling edge of DCLK_B | 0.47 | ||||||
| LVDS INTERFACE(4) | |||||||
| tskew | Skew time | Channel B relative to Channel A(4) | Channel A includes the following
LVDS pairs: DCLK_AP and DCLK_AN SCTRL_AP and SCTRL_AN D_AP(15:0) and D_AN(15:0) |
–1.25 | 1.25 | ns | |
| Channel B includes the following
LVDS pairs: DCLK_BP and DCLK_BN SCTRL_BP and SCTRL_BN D_BP(15:0) and D_BN(15:0) |
|||||||
(1) Refer to Section 5 for pin details.
(2) Refer to Figure 6-6.
(3) Refer to Figure 6-8.
(4) Refer to Figure 6-9.
(5) Tested at the device pin. For output timing analysis, the
tester pin electronics and its transmission line effects must be
considered.
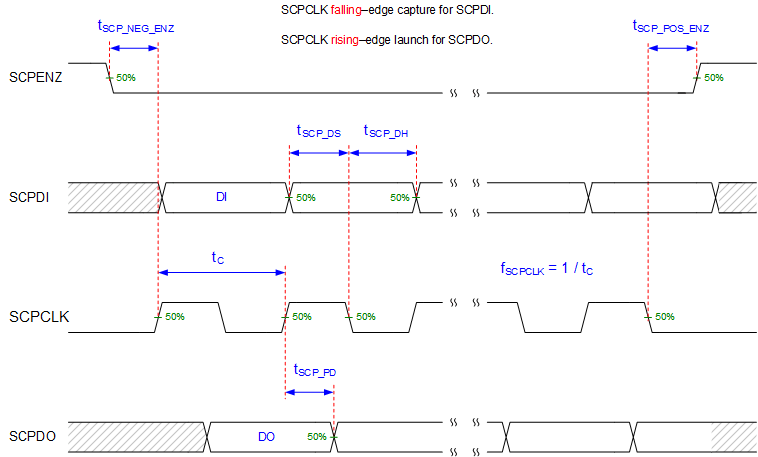
Not to
scale
Refer to the SCP
Interface section of the Recommended Operating ConditionsSection 6.4.
Figure 6-2 SCP
Timing Parameters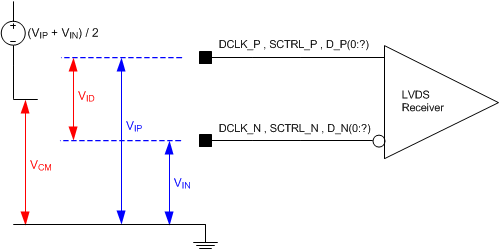
Refer to the LVDS
Interface section of the Recommended Operating Conditions (Section 6.4).
Refer to the Pin
Functions table for the list of LVDS pins.
Figure 6-3 LVDS
Voltage Definitions (References)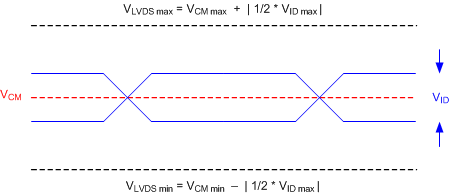
Not to
scale
Refer to the LVDS
Interface section of the Recommended Operating Conditions (Section 6.4).
Figure 6-4 LVDS
Voltage Parameters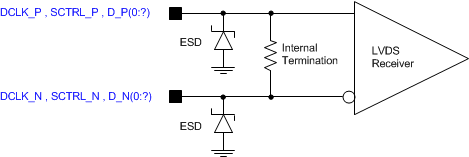
Refer to the LVDS
Interface section of the Recommended Operating Conditions (Section 6.4).
Refer to the Pin
Functions table for the list of LVDS pins.
Figure 6-5 LVDS
Equivalent Input Circuit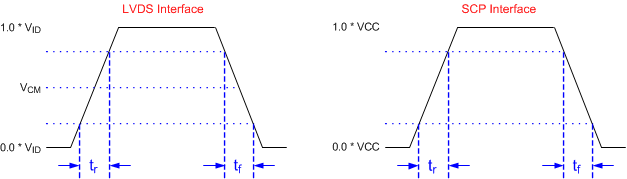
Not to
scale
Refer to the
timing requirements.
Refer to the Pin
Functions table for the list of LVDS pins and SCP pins.
Figure 6-6 Rise Time
and Fall Time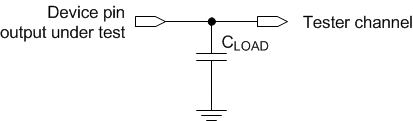 Figure 6-7 Test Load Circuit for Output
Propagation Measurement
Figure 6-7 Test Load Circuit for Output
Propagation MeasurementFor output timing analysis, the tester pin electronics and its transmission line effects must be considered. System design should use IBIS or other simulation tools to correlate the timing reference load to a system environment. See Figure 6-7.
Not to
scale
Refer to the LVDS
Interface section in the timing requirements.
Figure 6-8 Timing
Requirement Parameter Definitions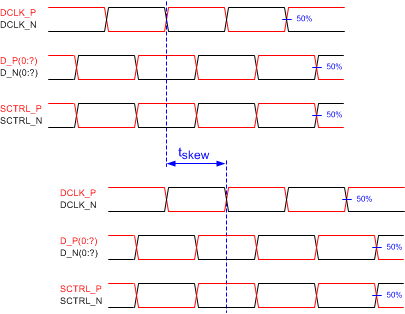
Not to
scale
Refer to the LVDS
Interface section in the timing requirements.
Figure 6-9 LVDS
Interface Channel Skew Definition