SLOS861C March 2015 – January 2023 DRV2700
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
AC-Coupled DAC Input Application
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1 Piezo Load Selection
- 8.2.1.2.2 Programming The Boost Voltage
- 8.2.1.2.3 Inductor and Transformer Selection
- 8.2.1.2.4 Programing the Boost and Flyback Current-Limit
- 8.2.1.2.5 Boost Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.6 Pulldown FET and Resistors
- 8.2.1.2.7 Low-Voltage Operation
- 8.2.1.2.8 Current Consumption Calculation
- 8.2.1.2.9 Input Filter Considerations
- 8.2.1.2.10 Output Limiting Factors
- 8.2.1.2.11 Startup and Shutdown Sequencing
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.2 Filtered AC Coupled Single-Ended PWM Input Application
- 8.2.3 DC-Coupled DAC Input Application
- 8.2.4 DC-Coupled Reference Input Application
- 8.2.5 Flyback Circuit
- 8.2.1
AC-Coupled DAC Input Application
- 8.3 System Example
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGP|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGP|20
Orderable Information
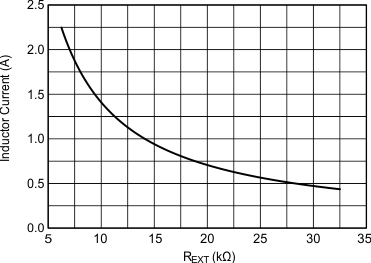
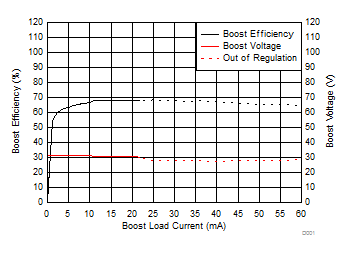
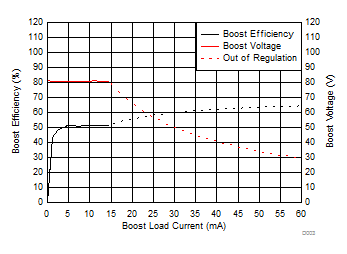
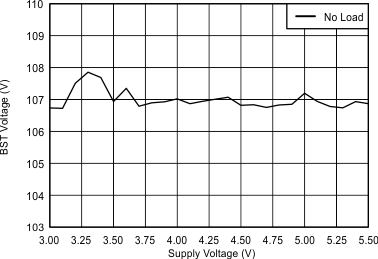
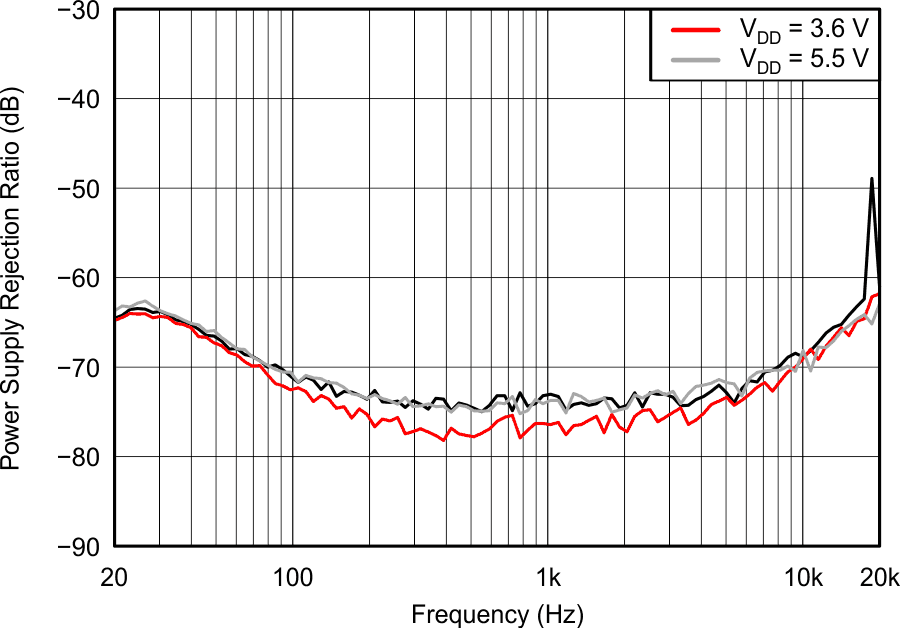
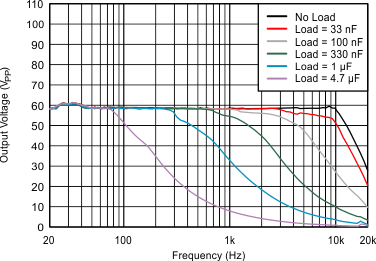
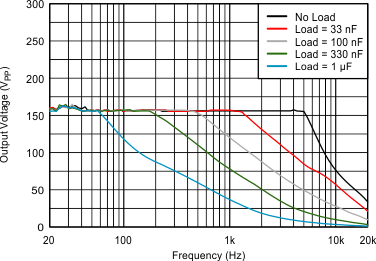
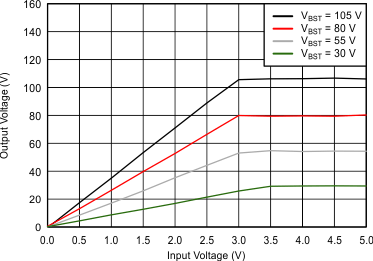
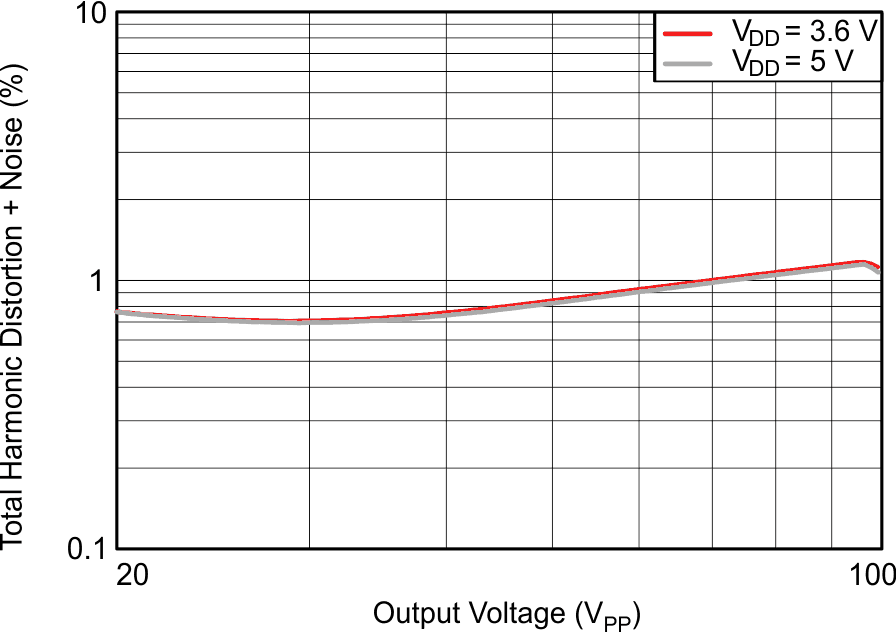
6.7 Typical characteristics
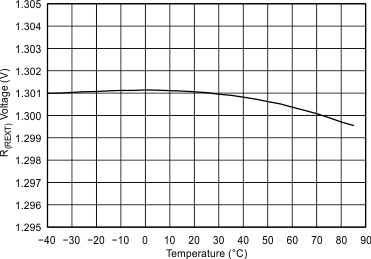
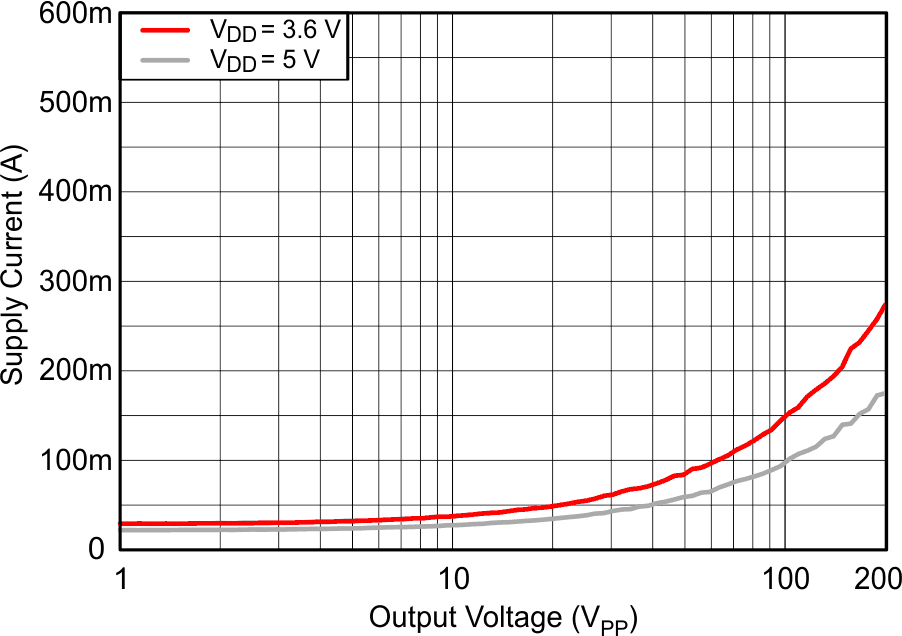
VDD = 3.6 V, R(REXT) = 7.5 kΩ, L = 4.7 µH, differential input, 100-nF DC blocking capacitors on IN±
| VDD = 3.6 V | C(LOAD) = Open | VPVDD = 30 V |
| G = 28.8 dB |
| VDD = 3.6 V | C(LOAD) = Open | VPVDD = 80 V |
| G = 38.4 dB |
| G = 40.7 dB | C(LOAD) = Open | VPVDD = 105 V |
| G = 40.7 dB | C(LOAD) = Open | VPVDD = 105 V |
| VDD = 3.6 V | G = 28.8 dB | VPVDD = 30 V |
| VDD = 3.6 V | G = 38.4 dB | VPVDD = 80 V |
| VDD = 3.6 V | G = 40.7 dB | C(LOAD) = Open |
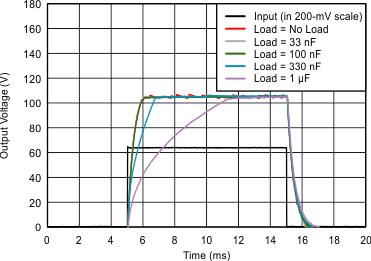
| VDD = 3.6 V | C(LOAD) = Open | VPVDD = 105 V |
| G = 40.7 dB |
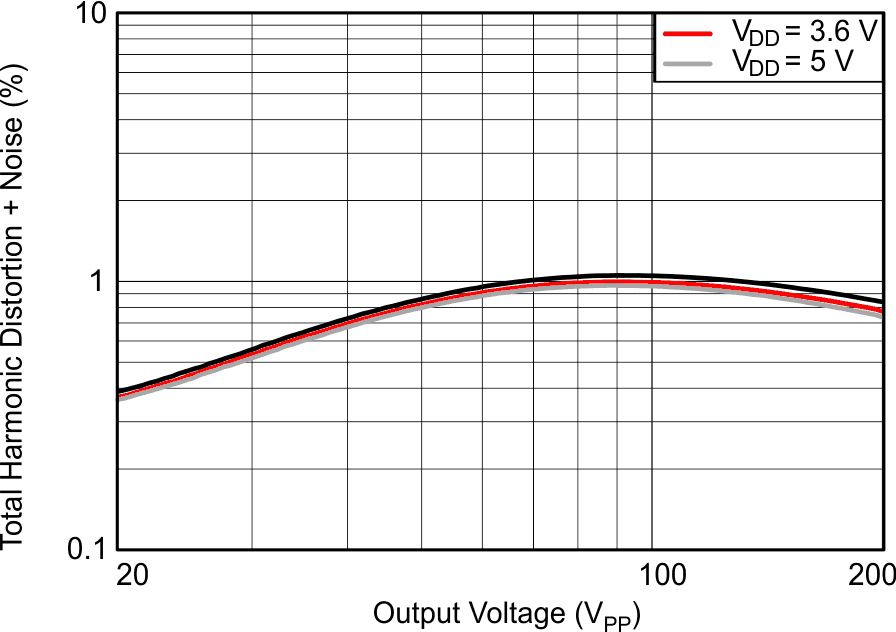
| ƒ = 200 Hz | C(LOAD) = 47 nF | VPVDD = 105 V |
| G = 40 dB |
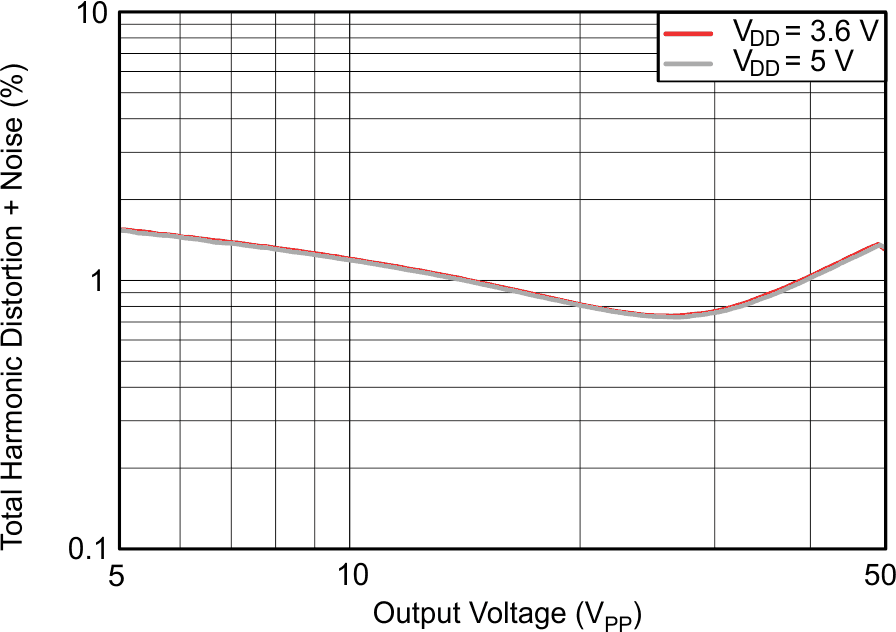
| ƒ = 200 Hz | C(LOAD) = 680 nF | VPVDD = 30 V |
| G = 28 dB |
| VDD = 3.6 V | C(LOAD) = Open | VPVDD = 105 V | ||
| G = 40.7 dB |
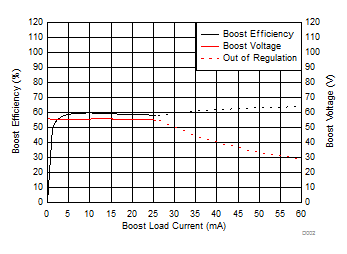
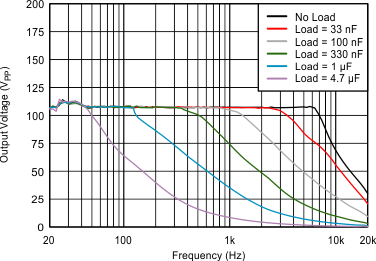
| VDD = 3.6 V | C(LOAD) = Open | VPVDD = 55 V |
| G = 34.8 dB |
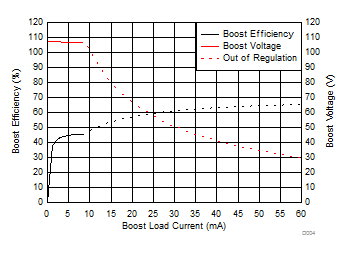
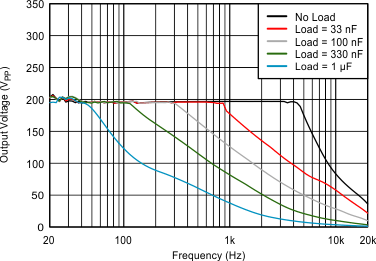
| VDD = 3.6 V | C(LOAD) = Open | VPVDD = 105 V |
| G = 40.7 dB |
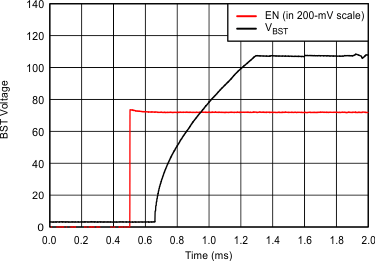
| VDD = 3.6 V | C(LOAD) = Open | VPVDD = 105 V |
| G = 40.7 dB |
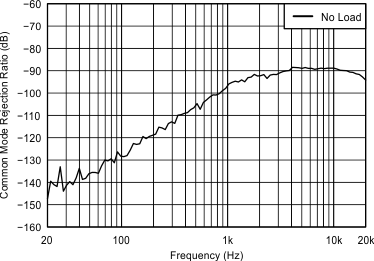
| G = 40.7 dB | C(LOAD) = Open | VPVDD = 105 V |
| VDD = 3.6 V | G = 34.8 dB | VPVDD = 55 V |
| VDD = 3.6 V | G = 40.7 dB | VPVDD = 105 V |
| VDD = 3.6 V | C(LOAD) = Open |
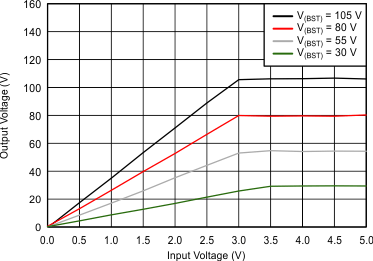
| G = 28.8 dB at VPVDD = 30 V | G = 34.8 dB at VPVDD = 55 V |
| G = 38.4 dB at VPVDD = 80 V | G = 40.7 dB at VPVDD = 105 V |
| ƒ = 200 Hz | C(LOAD) = 47 nF | VPVDD = 105 V |
| G = 40 dB |
| ƒ = 200 Hz | C(LOAD) = 330 nF | VPVDD = 55 V |
| G = 34 dB |