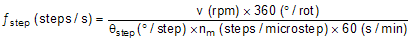SLOSE51A June 2020 – December 2020 DRV8428E
ADVANCE INFORMATION
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.3.2.1.1 Stepper Motor Speed
Next, the driving waveform needs to be planned. In order to command the correct speed, determine the frequency of the input waveform.If the target motor speed is too high, the motor will not spin. Make sure that the motor can support the target speed.For a desired motor speed (v), microstepping level (nm), and motor full step angle (θstep),