SNLS542C October 2016 – December 2020 DS280MB810
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- ZBL|135
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.2 Typical Application
The DS280MB810 with integrated cross-point is typically used in two main application scenarios:
- Backplane, mid-plane, and chip-to-chip reach extension
- Front-port eye opening for copper and optical applications
 Figure 9-1 Typical application block diagram
Figure 9-1 Typical application block diagramTI recommends to AC couple the DS280MB810's high-speed outputs. In some cases, ASIC or FPGA SerDes receivers support DC coupling, and it may be desirable to DC couple the DS280MB810 output with the ASIC/FPGA RX input to reduce the PCB area which would normally be consumed by AC coupling capacitors. To DC couple the DS280MB810 output with an ASIC RX input, the ASIC RX must support DC coupling and it must support an input common mode voltage of 1.05 V. To determine if the ASIC RX supports DC coupling, here are some items to consider based on Figure 9-2:
- The ASIC RX must be AC coupled on-chip.
- The ASIC RX should not force a DC bias on the RX pins.
- System designers should ensure that when the PCB powers on, the power supply rails are appropriately sequenced to prevent the DS280MB810's output common mode voltage from forward-biasing the ESD structure of the ASIC or violating the absolute maximum input voltage specifications of the ASIC.
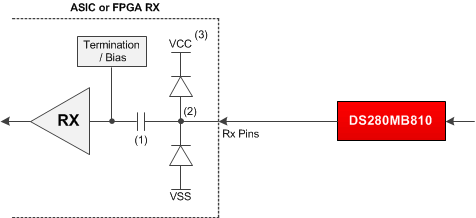 Figure 9-2 Considerations for DC coupling to ASIC RX
Figure 9-2 Considerations for DC coupling to ASIC RX