SNLS420D July 2012 – July 2015 DS90UB913Q-Q1 , DS90UB914Q-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description continued
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
8 Specifications
- 8.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 8.2 ESD Ratings
- 8.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 8.4 Thermal Information
- 8.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 8.6 Timing Requirements: Recommended for Serializer PCLK
- 8.7 AC Timing Specifications (SCL, SDA) - I2C Compliant
- 8.8 Bidirectional Control Bus DC Timing Specifications (SCL, SDA) - I2C Compliant
- 8.9 Switching Characteristics: Serializer
- 8.10 Switching Characteristics: Deserializer
- 8.11 Typical Characteristics
- 9 Parameter Measurement Information
-
10Detailed Description
- 10.1 Overview
- 10.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 10.3
Feature Description
- 10.3.1 Serial Frame Format
- 10.3.2 Line Rate Calculations for the DS90UB91xQ
- 10.3.3 Deserializer Multiplexer Input
- 10.3.4 Error Detection
- 10.3.5 Description of Bidirectional Control Bus and I2C Modes
- 10.3.6 Slave Clock Stretching
- 10.3.7 I2C Pass-Through
- 10.3.8 ID[x] Address Decoder on the Serializer
- 10.3.9 ID[x] Address Decoder on the Deserializer
- 10.3.10 Programmable Controller
- 10.3.11 Synchronizing Multiple Cameras
- 10.3.12 General-Purpose I/O (GPIO) Descriptions
- 10.3.13 LVCMOS VDDIO Option
- 10.3.14 Deserializer - Adaptive Input Equalization (AEQ)
- 10.3.15 EMI Reduction
- 10.4
Device Functional Modes
- 10.4.1 DS90UB91xQ-Q1 Operation With External Oscillator as Reference Clock
- 10.4.2 DS90UB91xQ-Q1 Operation With Pixel Clock from Imager as Reference Clock
- 10.4.3 MODE Pin on Serializer
- 10.4.4 MODE Pin on Deserializer
- 10.4.5 Clock-Data Recovery Status Flag (LOCK), Output Enable (OEN) and Output State Select (OSS_SEL)
- 10.4.6 Multiple Device Addressing
- 10.4.7 Powerdown
- 10.4.8 Pixel Clock Edge Select (TRFB / RRFB)
- 10.4.9 Power-Up Requirements and PDB Pin
- 10.4.10 Built-In Self Test
- 10.4.11 BIST Configuration and Status
- 10.5 Register Maps
- 11Application and Implementation
- 12Power Supply Recommendations
- 13Layout
- 14Device and Documentation Support
- 15Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RTV|32
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RTV|32
Orderable Information
8 Specifications
8.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted) (1)(3)(2)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage – VDDn (1.8 V) | −0.3 | 2.5 | V | |
| Supply voltage – VDDIO | −0.3 | 4.0 | V | |
| LVCMOS input voltage | −0.3 | VDDIO + 0.3 | V | |
| CML driver I/O voltage (VDD) | −0.3 | VDD + 0.3 | V | |
| CML receiver I/O voltage (VDD) | −0.3 | VDD + 0.3 | V | |
| Junction temperature | 150 | °C | ||
| Maximum package power dissipation capacity package | 1/θJA above +25° | °C/W | ||
| Air discharge (DOUT+, DOUT–, RIN+, RIN–) | −25 | 25 | kV | |
| Contact discharge (DOUT+, DOUT–, RIN+, RIN–) | −7 | 7 | kV | |
| Storage temperature Tstg | −65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) For soldering specifications: see product folder at www.ti.com and SNOA549.
(3) If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required, contact the Texas Instruments Sales Office/ Distributors for availability and specifications.
8.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per AEC Q100-002(1) | ±8000 | V | ||
| Charged-device model (CDM), per AEC Q100-011 | ±1000 | |||||
| Machine model (MM) | ±250 | |||||
| IEC 61000-4-2(2) | Air Discharge (DOUT+, DOUT-, RIN+, RIN-) | ≥±25 000 | ||||
| Contact Discharge (DOUT+, DOUT-, RIN+, RIN-) | ≥±7000 | |||||
| ISO10605(3)(4) | Air Discharge | ≥±15 000 | ||||
| Contact Discharge | ≥±8000 | |||||
(1) AEC Q100-002 indicates HBM stressing is done in accordance with the ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001 specification.
(2) RD = 330 Ω, CS = 150 pF
(3) RD = 330 Ω, CS = 150 / 330 pF
(4) RD = 2 KΩ, CS = 150 / 330 pF
8.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage (VDDn) | 1.71 | 1.8 | 1.89 | V | |
| LVCMOS supply voltage (VDDIO) OR | 1.71 | 1.8 | 1.89 | V | |
| LVCMOS supply voltage (VDDIO) OR | 3.0 | 3.3 | 3.6 | ||
| LVCMOS supply voltage (VDDIO) only serializer | 2.52 | 2.8 | 3.08 | ||
| Supply noise(1) | VDDn (1.8 V) | 25 | mVp-p | ||
| VDDIO (1.8 V) | 25 | ||||
| VDDIO (3.3 V) | 50 | ||||
| Operating free-air temperature (TA) | –40 | 25 | 105 | °C | |
| PCLK clock frequency | 10 | 100 | MHz | ||
(1) Supply noise testing was done with minimum capacitors (as shown on Figure 49 and Figure 48) on the PCB. A sinusoidal signal is AC coupled to the VDDn (1.8-V) supply with amplitude = 25 mVp-p measured at the device VDDn pins. Bit error rate testing of input to the serializer and output of the deserializer with 10 meter cable shows no error when the noise frequency on the serializer is less than
1 MHz. The deserializer on the other hand shows no error when the noise frequency is less than 750 kHz.
1 MHz. The deserializer on the other hand shows no error when the noise frequency is less than 750 kHz.
8.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | DS90UB913Q-Q1 | DS90UB914Q-Q1 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RTV (WQFN) | RHS (WQFN) | |||
| 32 PINS | 48 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 38.4 | 26.9 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 6.9 | 4.4 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
8.5 Electrical Characteristics
over recommended operating supply and temperature ranges unless otherwise specified.(1)(2)(3)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LVCMOS DC SPECIFICATIONS 3.3V I/O (SERIALIZER INPUTS, DESERIALIZER OUTPUTS, GPI, GPO, CONTROL INPUTS AND OUTPUTS) | |||||||
| VIH | High level input voltage | VIN = 3 V to 3.6 V | 2 | VIN | V | ||
| VIL | Low level input voltage | VIN = 3 V to 3.6 V | GND | 0.8 | V | ||
| IIN | Input current | VIN = 0 V or 3.6 V, VIN = 3 V to 3.6 V | −20 | ±1 | 20 | µA | |
| VOH | High level output voltage | VDDIO = 3 V to 3.6 V, IOH = −4 mA | 2.4 | VDDIO | V | ||
| VOL | Low level output voltage | VDDIO = 3 V to 3.6 V, IOL = +4 mA | GND | 0.4 | V | ||
| IOS | Output short circuit current | VOUT = 0 V | Serializer GPO outputs |
–15 | mA | ||
| Deserializer LVCMOS outputs | –35 | ||||||
| IOZ | TRI-STATE output current | PDB = 0 V, VOUT = 0 V or VDD |
LVCMOS outputs | –20 | 20 | µA | |
| LVCMOS DC SPECIFICATIONS 1.8V I/O (SERIALIZER INPUTS, DESERIALIZER OUTPUTS, GPI, GPO, CONTROL INPUTS AND OUTPUTS) | |||||||
| VIH | High level input voltage | VIN = 1.71 V to 1.89 V | 0.65 VIN | VIN | V | ||
| VIL | Low level input voltage | VIN = 1.71 V to 1.89 V | GND | 0.35 VIN | |||
| IIN | Input current | VIN = 0 V or 1.89 V, VIN = 1.71 V to 1.89 V | –20 | ±1 | 20 | µA | |
| VOH | High level output voltage | VDDIO = 1.71 V to 1.89 V, IOH = −4 mA | VDDIO – 0.45 | VDDIO | V | ||
| VOL | Low level output voltage | VDDIO = 1.71 V to 1.89 V IOL = 4 mA |
Deserializer LVCMOS outputs | GND | 0.45 | V | |
| IOS | Output short circuit current | VOUT = 0 V | Serializer GPO outputs |
–11 | mA | ||
| Deserializer LVCMOS outputs | –17 | ||||||
| IOZ | TRI-STATE output current | PDB = 0 V, VOUT = 0 V or VDD |
LVCMOS outputs | –20 | 20 | µA | |
| LVCMOS DC SPECIFICATIONS 2.8-V I/O (SERIALIZER INPUTS, GPI, GPO, CONTROL INPUTS AND OUTPUTS) | |||||||
| VIH | High level input voltage | VIN = 2.52 V to 3.08 V | 0.7 VIN | VIN | V | ||
| VIL | Low level input voltage | VIN = 2.52 V to 3.08 V | GND | 0.3 VIN | |||
| IIN | Input current | VIN = 0 V or 3.08 V, VIN = 2.52 V to 3.08 V | −20 | ±1 | 20 | µA | |
| VOH | High level output voltage | VDDIO = 2.52 V to 3.08 V, IOH = −4 mA | VDDIO – 0.4 | VDDIO | V | ||
| VOL | Low level output voltage | VDDIO =2.52 V to 3.08 V IOL = 4 mA |
Deserializer LVCMOS outputs | GND | 0.4 | V | |
| IOS | Output short circuit current | VOUT = 0 V | Serializer GPO outputs |
−11 | mA | ||
| Deserializer LVCMOS outputs | −20 | ||||||
| IOZ | TRI-STATE output current | PDB = 0 V, VOUT = 0 V or VDD |
LVCMOS outputs | −20 | 20 | µA | |
| CML DRIVER DC SPECIFICATIONS (DOUT+, DOUT–) | |||||||
| |VOD| | Output differential voltage | RL = 100 Ω (see Figure 9) | 268 | 340 | 412 | mV | |
| ΔVOD | Output differential voltage unbalance | RL = 100 Ω | 1 | 50 | mV | ||
| VOS | Output differential offset voltage |
RL = 100 Ω (see Figure 9) | VDD – VOD/2 | V | |||
| ΔVOS | Offset voltage unbalance | RL = 100 Ω | 1 | 50 | mV | ||
| IOS | Output short circuit current |
DOUT± = 0 V | –26 | mA | |||
| RT | Differential internal termination resistance | Differential across DOUT+ and DOUT– | 80 | 100 | 120 | Ω | |
| CML RECEIVER DC SPECIFICATIONS (RIN0+, RIN0–, RIN1+, RIN1– ) | |||||||
| IIN | Input current | VIN = VDD or 0 V, VDD = 1.89 V | −20 | 1 | 20 | µA | |
| RT | Differential internal termination resistance | Differential across RIN+ and RIN- | 80 | 100 | 120 | Ω | |
| CML RECEIVER AC SPECIFICATIONS (RIN0+, RIN0–, RIN1+, RIN1– ) | |||||||
| |Vswing| | Minimum allowable swing for 1010 pattern(4) | Line rate = 1.4 Gbps (see Figure 11) | 135 | mV | |||
| CML MONITOR OUTPUT DRIVER SPECIFICATIONS (CMLOUTP, CMLOUTN) | |||||||
| Ew | Differential output eye opening |
RL = 100 Ω Jitter frequency > f / 40 (see Figure 20) |
0.45 | UI | |||
| EH | Differential output eye height |
200 | mV | ||||
| SERIALIZER AND DESERIALIZER SUPPLY CURRENT *DIGITAL, PLL, AND ANALOG VDD | |||||||
| IDDT | Serializer (TX) VDDn supply current (includes load current) |
RL = 100 Ω WORST CASE pattern (see Figure 6) |
VDDn = 1.89 V VDDIO = 3.6 V f = 100 MHz, 10-bit mode default registers |
61 | 80 | mA | |
| VDDn = 1.89 V VDDIO = 3.6 V f = 75 MHz, 12-bit high-frequency mode default registers |
61 | 80 | mA | ||||
| VDDn = 1.89 V VDDIO = 3.6 V f = 50 MHz, 12-bit low-frequency mode default registers |
61 | 80 | |||||
| RL = 100 Ω RANDOM PRBS-7 pattern |
VDDn = 1.89 V VDDIO = 3.6 V f = 100 MHz, 10-bit mode default registers |
54 | mA | ||||
| VDDn = 1.89 V VDDIO = 3.6 V f = 75 MHz, 12-bit high-frequency mode default registers |
54 | ||||||
| VDD = 1.89 V VDDIO = 3.6 V f = 50 MHz, 12-bit low-frequency mode default registers |
54 | ||||||
| IDDIOT | Serializer (TX) VDDIO supply current (includes load current) |
RL = 100 Ω WORST CASE pattern (see Figure 6) |
VDDIO = 1.89 V f = 75 MHz, 12-bit high-freq mode default registers |
1.5 | 3 | mA | |
| VDDIO = 3.6 V f = 75 MHz, 12-bit high-frequency mode default registers |
5 | 8 | |||||
| IDDTZ | Serializer (TX) supply current power-down | PDB = 0 V; all other LVCMOS inputs = 0 V | VDDIO = 1.89 V Default registers |
300 | 900 | µA | |
| VDDIO = 3.6 V Default registers |
300 | 900 | µA | ||||
| IDDIOTZ | Serializer (TX) VDDIO supply current power-down | PDB = 0 V; All other LVCMOS Inputs = 0 V | VDDIO = 1.89 V Default registers |
15 | 100 | µA | |
| VDDIO = 3.6 V Default registers |
15 | 100 | µA | ||||
| IDDIOR | Deserializer (RX) total supply current (includes load current) | VDDIO = 1.89 V CL = 8 pF WORST CASE pattern |
f = 100 MHz, 10-bit mode | 22 | 42 | mA | |
| f = 75 MHz, 12-bit high-freq mode | 19 | 39 | |||||
| f = 50 MHz, 12-bit low-freq mode | 21 | 32 | |||||
| VDDIO = 1.89 V CL=8pF Random pattern |
f = 100 MHz, 10–bit mode | 15 | mA | ||||
| f = 75 MHz, 12-bit high-freq mode | 12 | ||||||
| f = 50 MHz, 12-bit low-freq mode | 14 | ||||||
| VDDIO = 3.6 V CL = 8 pF WORST CASE pattern |
f = 100 MHz, 10-bit mode | 42 | 55 | mA | |||
| f = 75 MHz, 12-bit high-freq mode | 37 | 50 | |||||
| f = 50 MHz, 12-bit low-freq mode | 25 | 38 | |||||
| VDDIO = 3.6 V CL = 8 pF Random pattern |
f = 100 MHz, 10-bit mode | 35 | mA | ||||
| f = 75 MHz, 12-bit high-freq mode | 30 | ||||||
| f = 50 MHz, 12-bit low-freq mode | 18 | ||||||
| VDDIO = 1.89 V CL = 4 pF WORST CASE pattern |
f = 100 MHz, 10-bit mode | 15 | mA | ||||
| f = 75 MHz, 12-bit high-freq mode | 11 | ||||||
| f = 50 MHz, 12-bit low-freq mode | 16 | ||||||
| VDDIO = 1.89 V CL = 4 pF Random pattern |
f = 100 MHz, 10-bit mode | 8 | mA | ||||
| f = 75 MHz, 12-bit high-freq mode | 4 | ||||||
| f = 50 MHz, 12-bit low-freq mode | 9 | ||||||
| VDDIO = 3.6 V CL = 4 pF WORST CASE pattern |
f = 100 MHz, 10-bit mode | 36 | mA | ||||
| f = 75 MHz, 12-bit high-freq mode | 29 | ||||||
| f = 50 MHz, 12-bit low-freq mode | 20 | ||||||
| VDDIO = 3.6 V CL = 4 pF Random pattern |
f = 100 MHz, 10-bit mode | 29 | mA | ||||
| f = 75 MHz, 12-bit high-freq mode | 22 | ||||||
| f = 50 MHz, 12-bit low-freq mode | 13 | ||||||
| IDDR | Deserializer (RX) VDDn supply current (includes load current) | VDDn = 1.89 V CL = 4 pF WORST CASE pattern |
f = 100 MHz, 10-bit mode |
64 | 110 | mA | |
| f = 75 MHz, 12-bit high-frequency mode |
67 | 114 | |||||
| f = 50 MHz, 12-bit low-frequency mode |
63 | 96 | |||||
| VDDn = 1.89 V CL = 4 pF Random pattern |
f = 100 MHz, 10-bit mode |
57 | |||||
| f = 75 MHz, 12–bit high-frequency mode |
60 | ||||||
| f = 50 MHz, 12-bit low-frequency mode |
56 | ||||||
| IDDRZ | Deserializer (RX) supply current power-down | PBB = 0 V, all other LVCMOS Inputs=0 V | VDDIO = 1.89 V Default registers |
42 | 400 | µA | |
| PBB = 0 V, all other LVCMOS Inputs=0 V | VDDIO = 3.6 V Default registers |
42 | 400 | ||||
| IDDIORZ | Deserializer (RX) VDD supply current power-down |
PDB = 0 V, all other LVCMOS Inputs = 0 V | VDDIO = 1.89 V | 8 | 40 | µA | |
| VDDIO = 3.6 V | 360 | 800 | |||||
(1) The Electrical Characteristics tables list ensured specifications under the listed Recommended Operating Conditions except as otherwise modified or specified by the Electrical Characteristics Conditions and/or Notes. Typical specifications are estimations only and are not ensured.
(2) Current into device pins is defined as positive. Current out of a device pin is defined as negative. Voltages are referenced to ground except VOD, ΔVOD, VTH and VTL which are differential voltages.
(3) Typical values represent most likely parametric norms at 1.8 V or 3.3 V, TA = 25°C, and at the Recommended Operation Conditions at the time of product characterization and are not specified.
(4) Specification is ensured by characterization and is not tested in production.
8.6 Timing Requirements: Recommended for Serializer PCLK
over recommended operating supply and temperature ranges unless otherwise specified.(1)| TEST CONDITIONS | PIN/FREQ | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tTCP | Transmit clock period | 10-bit mode | 10 | T | 50 | ns | |
| 12-bit high-frequency mode | 13.33 | T | 66.66 | ||||
| 12-bit low-frequency mode | 20 | T | 100 | ||||
| tTCIH | Transmit clock input high time |
0.4T | 0.5T | 0.6T | ns | ||
| tTCIL | Transmit clock input low time |
0.4T | 0.5T | 0.6T | ns | ||
| tCLKT | PCLK input transition time (Figure 12) | 20 MHz–100 MHz, 10-bit mode |
0.5T | 2.5T | 0.3T | ns | |
| 15 MHz to 75 MHz, 12-bit high-frequency mode | 0.5T | 2.5T | 0.3T | ||||
| 10 MHz to 50 MHz, 12-bit low-frequency mode | 0.5T | 2.5T | 0.3T | ||||
| tJIT0 | PCLK input jitter (PCLK from imager mode) |
Refer to jitter freq > f / 40 | f = 10 to 100 MHz | 0.1T | ns | ||
| tJIT1 | PCLK input jitter (external oscillator mode) | Refer to jitter freq > f / 40 | f = 10 to 100 MHz | 1T | ns | ||
| tJIT2 | External oscillator jitter | 0.1 | UI | ||||
(1) Recommended input timing requirements are input specifications and not tested in production.
8.7 AC Timing Specifications (SCL, SDA) - I2C Compliant
over recommended supply and temperature ranges unless otherwise specified. (See Figure 5)| TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RECOMMENDED INPUT TIMING REQUIREMENTS | ||||||
| fSCL | SCL clock frequency | Standard mode | >0 | 100 | kHz | |
| Fast mode | >0 | 400 | ||||
| tLOW | SCL low period | Standard mode | 4.7 | µs | ||
| Fast mode | 1.3 | |||||
| tHIGH | SCL high period | Standard mode | 4.0 | µs | ||
| Fast mode | 0.6 | |||||
| tHD:STA | Hold time for a start or a repeated start condition | Standard mode | 4 | µs | ||
| Fast mode | 0.6 | |||||
| tSU:STA | Setup time for a start or a repeated start condition | Standard mode | 4.7 | µs | ||
| Fast mode | 0.6 | |||||
| tHD:DAT | Data hold time | Standard mode | 0 | 3.45 | µs | |
| Fast mode | 0 | 900 | ||||
| tSU:DAT | Data setup time | Standard mode | 250 | ns | ||
| Fast mode | 100 | |||||
| tSU:STO | Setup time for STOP condition | Standard mode | 4 | µs | ||
| Fast mode | 0.6 | |||||
| tBUF | Bus free time between stop and start | Standard mode | 4.7 | µs | ||
| Fast mode | 1.3 | |||||
| tr | SCL and SDA rise time | Standard mode | 1000 | ns | ||
| Fast mode | 300 | |||||
| tf | SCL and SDA fall time | Standard mode | 300 | ns | ||
| Fast mode | 300 | |||||
8.8 Bidirectional Control Bus DC Timing Specifications (SCL, SDA) - I2C Compliant
over recommended supply and temperature ranges unless otherwise specified(1)| TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RECOMMENDED INPUT TIMING REQUIREMENTS | ||||||
| VIH | Input high level | SDA and SCL | 0.7 × VDDIO | VDDIO | V | |
| VIL | Input low level | SDA and SCL | GND | 0.3 × VDDIO | V | |
| VHY | Input hysteresis | >50 | mV | |||
| VOL | Output low level | SDA, IOL = 0.5 mA | 0 | 0.4 | V | |
| IIN | Input current | SDA or SCL, VIN = VDDOP OR GND | −10 | 10 | µA | |
| tR | SDA rise time-READ | SDA, RPU = 10 kΩ, Cb ≤ 400 pF (see Figure 5) | 430 | ns | ||
| tF | SDA fall time-READ | 20 | ns | |||
| tSU;DAT | See Figure 5 | 560 | ns | |||
| tHD;DAT | See Figure 5 | 615 | ns | |||
| tSP | 50 | ns | ||||
| CIN | SDA or SCL | <5 | pF | |||
(1) Specification is ensured by design.
8.9 Switching Characteristics: Serializer
over recommended operating supply and temperature ranges unless otherwise specified.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tLHT | CML low-to-high transition time | RL = 100 Ω (see Figure 7) | 150 | 330 | ps | |
| tHLT | CML high-to-low transition time | RL = 100 Ω (see Figure 7) | 150 | 330 | ps | |
| tDIS | Data input setup to PCLK | Serializer data inputs (see Figure 13) | 2 | ns | ||
| tDIH | Data input hold from PCLK | 2 | ns | |||
| tPLD | Serializer PLL lock time | RL = 100 Ω(1)(2), (see Figure 14) | 1 | 2 | ms | |
| tSD | Serializer delay(2) | RT = 100 Ω, 10-bit mode Register 0x03h b[0] (TRFB = 1) (see Figure 15) |
32.5T | 38T | 44T | ns |
| RT = 100 Ω, 12-bit mode Register 0x03h b[0] (TRFB = 1) (see Figure 15) |
11.75T | 13T | 15T | |||
| tJIND | Serializer output deterministic jitter | Serializer output intrinsic deterministic jitter. Measured (cycle-cycle) with PRBS-7 test pattern(3)(4) | 0.13 | UI | ||
| tJINR | Serializer output random jitter |
Serializer output intrinsic random jitter (cycle-cycle). Alternating-1,0 pattern.(3)(4) | 0.04 | UI | ||
| tJINT | Peak-to-peak serializer output jitter | Serializer output peak-to-peak jitter includes deterministic jitter, random jitter, and jitter transfer from serializer input. Measured (cycle-cycle) with PRBS-7 test pattern.(3)(4) | 0.396 | UI | ||
| λSTXBW | Serializer jitter transfer function –3-dB bandwidth(5) |
PCLK = 100 MHz 10-bit mode. Default registers |
2.2 | MHz | ||
| PCLK = 75 MHz 12-bit high-frequency mode. Default registers |
2.2 | |||||
| PCLK = 50 MHz 12-bit low-frequency mode. Default registers |
2.2 | |||||
| δSTX | Serializer jitter transfer function (peaking)(5) |
PCLK = 100 MHz 10-bit mode. Default Registers |
1.06 | dB | ||
| PCLK = 75 MHz 12-bit high-frequency mode. Default registers |
1.09 | |||||
| PCLK = 50 MHz 12-bit low-frequency mode. Default registers |
1.16 | |||||
| δSTXf | Serializer jitter transfer function (peaking frequency)(5) |
PCLK = 100 MHz 10-bit mode. Default registers |
400 | kHz | ||
| PCLK = 75 MHz 12-bit high-frequency mode. Default registers |
500 | |||||
| PCLK = 50 MHz 12-bit low-frequency mode. Default registers |
600 | |||||
(1) tPLD and tDDLT is the time required by the serializer and deserializer to obtain lock when exiting power-down state with an active PCLK
(2) Specification is ensured by design.
(3) Typical values represent most likely parametric norms at 1.8 V or 3.3 V, TA = 25°C, and at the recommended operation conditions at the time of product characterization and are not specified.
(4) UI – Unit Interval is equivalent to one ideal serialized data bit width. The UI scales with PCLK frequency.
(5) Specification is ensured by characterization and is not tested in production.
8.10 Switching Characteristics: Deserializer
over recommended operating supply and temperature ranges unless otherwise specified.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | PIN/FREQ | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tRCP | Receiver output clock period |
10-bit mode | PCLK (see Figure 19) | 10 | 50 | ns | |
| 12-bit high-frequency mode | 13.33 | 66.66 | |||||
| 12-bit low-frequency mode | 10 | 100 | |||||
| tPDC | PCLK duty cycle | 10-bit mode | PCLK | 45% | 50% | 55% | |
| 12-bit high-frequency mode | 40% | 50% | 60% | ||||
| 12-bit low-frequency mode | 40% | 50% | 60% | ||||
| tCLH | LVCMOS low-to-high transition time | VDDIO: 1.71 V to 1.89 V or 3.0 V to 3.6 V, CL = 8 pF (lumped load) Default registers (see Figure 17)(1) |
PCLK | 1.3 | 2 | 2.8 | ns |
| tCHL | LVCMOS high-to-low transition time | 1.3 | 2 | 2.8 | ns | ||
| tCLH | LVCMOS low-to-high transition time | VDDIO: 1.71 V to 1.89 V or 3.0 V to 3.6 V, CL = 8 pF (lumped load) Default registers (see Figure 17)(1) |
ROUT[11:0], HS, VS | 1 | 2.5 | 4 | ns |
| tCHL | LVCMOS high-to-low transition time | 1 | 2.5 | 4 | ns | ||
| tROS | ROUT setup data to PCLK |
VDDIO: 1.71 V to 1.89 V or 3.0 V to 3.6 V, CL = 8 pF (lumped load) Default registers (see Figure 19) |
ROUT[11:0], HS, VS | 0.38T | 0.5T | ns | |
| tROH | ROUT hold data to PCLK | 0.38T | 0.5T | ns | |||
| tDD | Deserializer delay | Default registers Register 0x03h b[0] (RRFB = 1) (see Figure 18)(1) |
10-bit mode | 154T | 158T | ns | |
| 12-bit low-frequency mode | 109T | 112T | |||||
| 12-bit high-frequency mode | 73T | 75T | |||||
| tDDLT | Deserializer data lock time | With Adaptive Equalization (see Figure 16) | 10-bit mode | 15 | 22 | ms | |
| 12-bit low-frequency mode | 15 | 22 | |||||
| 12-bit high-frequency mode | 15 | 22 | |||||
| tRCJ | Receiver clock jitter | PCLK SSCG[3:0] = OFF(1) |
10-bit mode PCLK = 100 MHz |
20 | 30 | ps | |
| 12-bit low-frequency mode PCLK = 50 MHz |
22 | 35 | |||||
| 12-bit high-frequency mode PCLK = 75 MHz |
45 | 90 | |||||
| tDPJ | Deserializer period jitter | PCLK SSCG[3:0] = OFF(1)(2) |
10-bit mode PCLK = 100 MHz |
170 | 815 | ps | |
| 12-bit low-frequency mode PCLK= 50 MHz |
180 | 330 | |||||
| 12-bit high-frequency mode PCLK= 75 MHz |
300 | 515 | |||||
| tDCCJ | Deserializer cycle-to-cycle clock jitter | PCLK SSCG[3:0] = OFF(1)(3) |
10-bit mode PCLK = 100 MHz |
440 | 1760 | ps | |
| 12-bit low-frequency mode PCLK = 50 MHz |
460 | 730 | |||||
| 12-bit high-frequency mode PCLK = 75 MHz |
565 | 985 | |||||
| fdev | Spread spectrum clocking deviation frequency | LVCMOS output bus SSC[3:0] = ON (see Figure 24)(1) |
10 MHz–100 MHz | ±0.5 to ±1.5% | |||
| fmod | Spread spectrum clocking modulation frequency | 10 MHz–100 MHz | 5 to 50 | kHz | |||
(1) Specification is ensured by characterization and is not tested in production.
(2) tDPJ is the maximum amount the period is allowed to deviate measured over 30,000 samples.
(3) tDCCJ is the maximum amount of jitter between adjacent clock cycles measured over 30,000 samples.
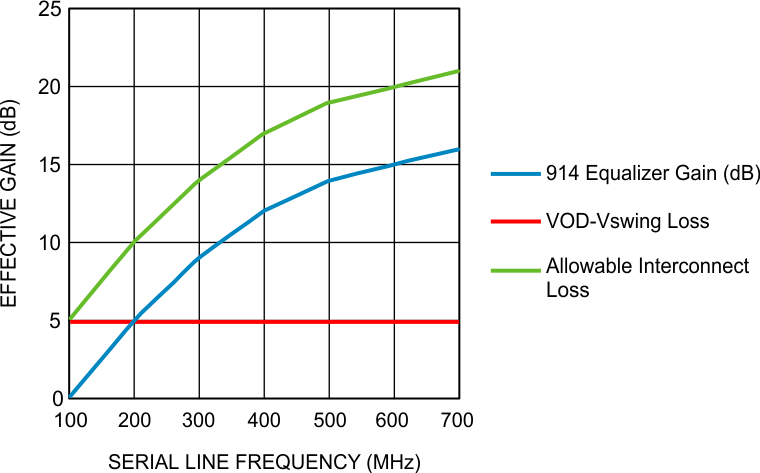
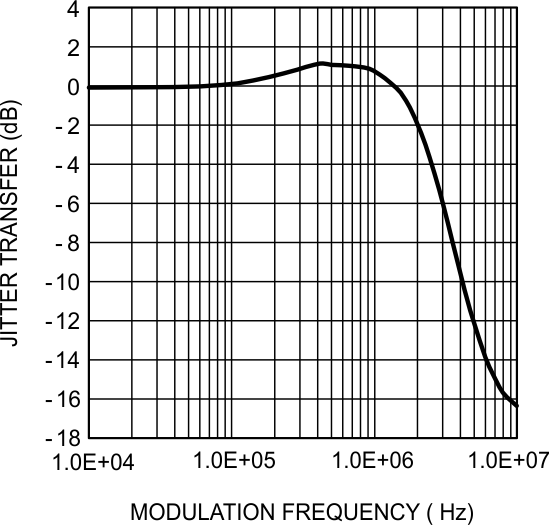
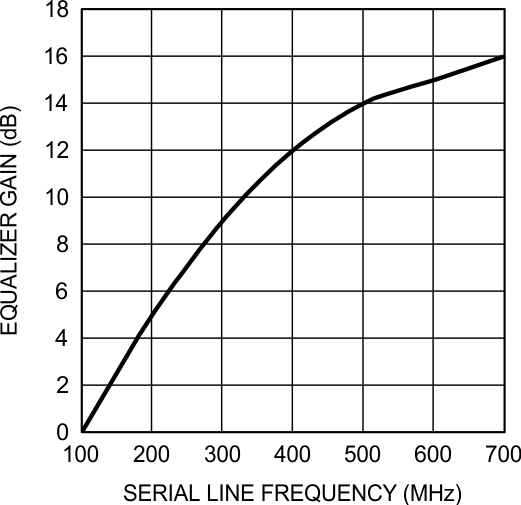
8.11 Typical Characteristics
at 100 MHz
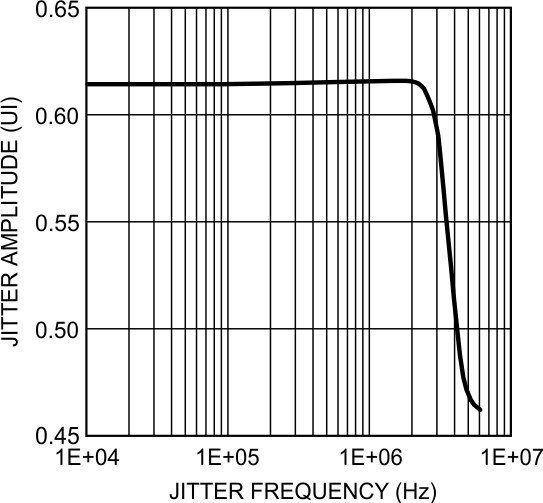
at 1.4-Gbps Line Rate