SPRS825F October 2012 – June 2020 F28M36H33B2 , F28M36H53B2 , F28M36P53C2 , F28M36P63C2
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1Device Overview
- 2Revision History
- 3Device Comparison
- 4Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
5Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings – Commercial
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Power Consumption Summary
- 5.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 5.6 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for ZWT Package (Revision 0 Silicon)
- 5.7 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for ZWT Package (Revision A Silicon)
- 5.8 Thermal Design Considerations
- 5.9
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 5.9.1 Power Sequencing
- 5.9.2
Clock Specifications
- 5.9.2.1 Changing the Frequency of the Main PLL
- 5.9.2.2
Input Clock Frequency and Timing Requirements, PLL Lock Times
- Table 5-5 Input Clock Frequency
- Table 5-7 Crystal Oscillator Electrical Characteristics
- Table 5-8 X1 Timing Requirements - PLL Enabled
- Table 5-9 X1 Timing Requirements - PLL Disabled
- Table 5-10 XCLKIN Timing Requirements - PLL Enabled
- Table 5-11 XCLKIN Timing Requirements - PLL Disabled
- Table 5-12 PLL Lock Times
- 5.9.2.3 Output Clock Frequency and Switching Characteristics
- 5.9.2.4 Internal Clock Frequencies
- 5.9.3 Timing Parameter Symbology
- 5.9.4 Flash Timing – Master Subsystem
- 5.9.5 Flash Timing – Control Subsystem
- 5.9.6 GPIO Electrical Data and Timing
- 5.9.7 External Interrupt Electrical Data and Timing
- 5.10
Analog and Shared Peripherals
- 5.10.1 Analog-to-Digital Converter
- 5.10.2 Comparator + DAC Units
- 5.10.3 Interprocessor Communications
- 5.10.4
External Peripheral Interface
- 5.10.4.1 EPI General-Purpose Mode
- 5.10.4.2 EPI SDRAM Mode
- 5.10.4.3 EPI Host Bus Mode
- 5.10.4.4
EPI Electrical Data and Timing
- Table 5-52 EPI SDRAM Interface Switching Characteristics (see , , and )
- Table 5-53 EPI Host-Bus 8 and Host-Bus 16 Interface Switching Characteristics (see , , , and )
- Table 5-54 EPI Host-Bus 8 and Host-Bus 16 Interface Timing Requirements (see and )
- Table 5-55 EPI General-Purpose Interface Switching Characteristics (see )
- Table 5-56 EPI General-Purpose Interface Timing Requirements (see and )
- 5.11
Master Subsystem Peripherals
- 5.11.1 Synchronous Serial Interface
- 5.11.2 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter
- 5.11.3 Cortex-M3 Inter-Integrated Circuit
- 5.11.4 Cortex-M3 Controller Area Network
- 5.11.5 Cortex-M3 Universal Serial Bus Controller
- 5.11.6 Cortex-M3 Ethernet Media Access Controller
- 5.12
Control Subsystem Peripherals
- 5.12.1 High-Resolution PWM and Enhanced PWM Modules
- 5.12.2 Enhanced Capture Module
- 5.12.3 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse Module
- 5.12.4 C28x Inter-Integrated Circuit Module
- 5.12.5 C28x Serial Communications Interface
- 5.12.6 C28x Serial Peripheral Interface
- 5.12.7
C28x Multichannel Buffered Serial Port
- 5.12.7.1
McBSP Electrical Data and Timing
- 5.12.7.1.1 McBSP Transmit and Receive Timing
- 5.12.7.1.2
McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing
- Table 5-81 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing Requirements (CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 0)
- Table 5-82 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Switching Characteristics (CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 0)
- Table 5-83 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing Requirements (CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 0)
- Table 5-84 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Switching Characteristics (CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 0)
- Table 5-85 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing Requirements (CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 1)
- Table 5-86 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Switching Characteristics (CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 1)
- Table 5-87 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing Requirements (CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 1)
- Table 5-88 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Switching Characteristics (CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 1)
- 5.12.7.1
McBSP Electrical Data and Timing
-
6Detailed Description
- 6.1 Memory Maps
- 6.2 Identification
- 6.3 Master Subsystem
- 6.4 Control Subsystem
- 6.5 Analog Subsystem
- 6.6 Master Subsystem NMIs
- 6.7 Control Subsystem NMIs
- 6.8 Resets
- 6.9 Internal Voltage Regulation and Power-On-Reset Functionality
- 6.10 Input Clocks and PLLs
- 6.11 Master Subsystem Clocking
- 6.12 Control Subsystem Clocking
- 6.13 Analog Subsystem Clocking
- 6.14 Shared Resources Clocking
- 6.15 Loss of Input Clock (NMI Watchdog Function)
- 6.16 GPIOs and Other Pins
- 6.17 Emulation/JTAG
- 6.18 Code Security Module
- 6.19 µCRC Module
- 7Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 8Device and Documentation Support
- 9Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- ZWT|289
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6.10.5 USB PLL
The USB PLL uses the reference clock selectable between the input clock arriving at the XCLKIN pin, or the internal OSCCLK (originating from the external crystal or oscillator through the X1/X2 pins). An input mux selects the source of the USB PLL reference based on the UPLLCLKSRC bit of the UPLLCTL Register (see Figure 6-9). The input clock is multiplied by an integer multiplier and a fractional multiplier as selected by the UPLLIMULT and UPLLFMULT fields of the UPLLMULT register. For example, to achieve PLL multiply of 28.5, the integer multiplier should be set to 28, and the fractional multiplier to 0.5. The output clock from the USB PLL must always be 240 MHz. The PLL output clock is then divided by 4—resulting in 60 MHz that the USB needs—before entering a mux that selects between this clock and the PLL input clock (used in the PLL bypass mode). The PLL bypass mode is selected by setting the UPLLIMULT field of the UPLLMULT register to 0. The output clock from the mux becomes the USBPLLCLK (there is not another clock divider). Figure 6-9 shows the USB PLL function and configuration examples. Table 6-23 and Table 6-24 list the integer multiplier configuration values.
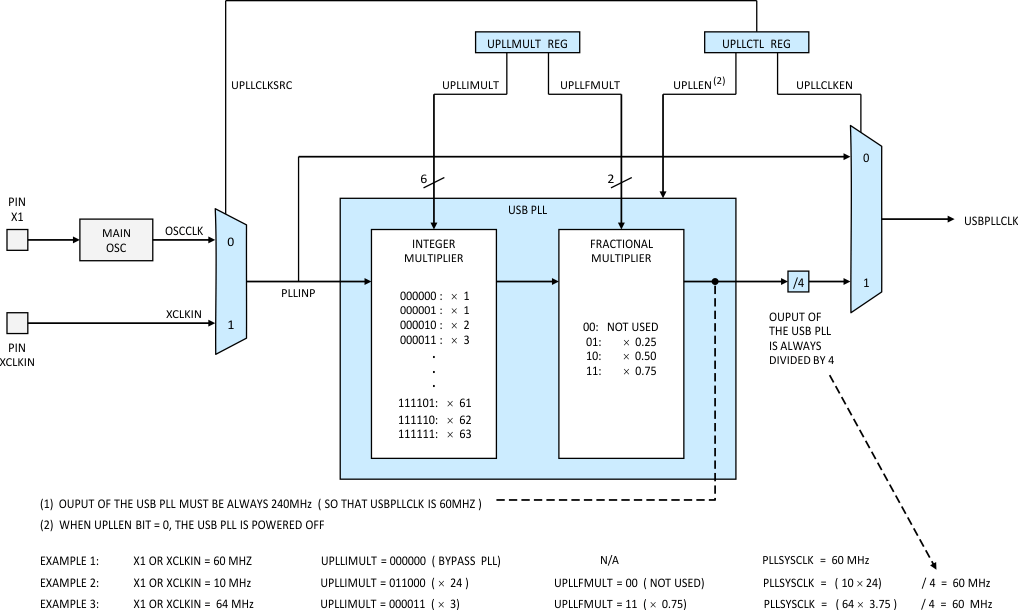 Figure 6-9 USB PLL
Figure 6-9 USB PLL Table 6-23 USB PLL Integer Multiplier Configuration
(Bypass PLL to × 31)
| SPLLIMULT(5:0) | MULT VALUE |
|---|---|
| 000000 b | Bypass PLL |
| 000001 b | × 1 |
| 000010 b | × 2 |
| 000011 b | × 3 |
| 000100 b | × 4 |
| 000101 b | × 5 |
| 000110 b | × 6 |
| 000111 b | × 7 |
| 001000 b | × 8 |
| 001001 b | × 9 |
| 001010 b | × 10 |
| 001011 b | × 11 |
| 001100 b | × 12 |
| 001101 b | × 13 |
| 001110 b | × 14 |
| 001111 b | × 15 |
| 010000 b | × 16 |
| 010001 b | × 17 |
| 010010 b | × 18 |
| 010011 b | × 19 |
| 010100 b | × 20 |
| 010101 b | × 21 |
| 010110 b | × 22 |
| 010111 b | × 23 |
| 011000 b | × 24 |
| 011001 b | × 25 |
| 011010 b | × 26 |
| 011011 b | × 27 |
| 011100 b | × 28 |
| 011101 b | × 29 |
| 011110 b | × 30 |
| 011111 b | × 31 |
Table 6-24 USB PLL Integer Multiplier Configuration
(× 32 to × 63)
| SPLLIMULT(5:0) | MULT VALUE |
|---|---|
| 100000 b | × 32 |
| 100001 b | × 33 |
| 100010 b | × 34 |
| 100011 b | × 35 |
| 100100 b | × 36 |
| 100101 b | × 37 |
| 100110 b | × 38 |
| 100111 b | × 39 |
| 101000 b | × 40 |
| 101001 b | × 41 |
| 101010 b | × 42 |
| 101011 b | × 43 |
| 101100 b | × 44 |
| 101101 b | × 45 |
| 101110 b | × 46 |
| 101111 b | × 47 |
| 110000 b | × 48 |
| 110001 b | × 49 |
| 110010 b | × 50 |
| 110011 b | × 51 |
| 110100 b | × 52 |
| 110101 b | × 53 |
| 110110 b | × 54 |
| 110111 b | × 55 |
| 111000 b | × 56 |
| 111001 b | × 57 |
| 111010 b | × 58 |
| 111011 b | × 59 |
| 111100 b | × 60 |
| 111101 b | × 61 |
| 111110 b | × 62 |
| 111111 b | × 63 |