SBOS374E November 2006 – September 2017 INA200 , INA201 , INA202
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage, Vs | 2.7 | 18 | V | |
| Current-shunt monitor analog inputs, VIN+, VIN– | Differential (VIN+) – (VIN–) | –18 | 18 | V |
| Common-mode(2) | –16 | 80 | V | |
| Comparator analog input and reset pins(2) | GND – 0.3 | (Vs) + 0.3 | V | |
| Analog output, OUT(2) | GND – 0.3 | (Vs) + 0.3 | V | |
| Comparator output, OUT(2) | GND – 0.3 | 18 | V | |
| Input current into any pin(2) | 5 | mA | ||
| Operating temperature | –55 | 150 | °C | |
| Junction temperature | –65 | 150 | °C | |
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) This voltage may exceed the ratings shown if the current at that pin is limited to 5 mA.
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001, all pins(1) | ±4000 | V | |
| Charged device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101, all pins(2) | ±1000 | ||||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCM | Common-mode input voltage | –16 | 12 | 80 | V |
| VS | Operating supply voltage | 2.7 | 12 | 18 | V |
| TA | Operating free-air temperature | –40 | 25 | 125 | °C |
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | INA20x | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D (SOIC) | DGK (SOIC) | |||
| 8 PINS | 8 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 110.5 | 162.2 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 50.4 | 37.7 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 52.7 | 82.9 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 7.8 | 1.3 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 51.9 | 81.4 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report.
6.5 Electrical Characteristics: Current-Shunt Monitor
at TA = 25°C, VS = 12 V, VCM = 12 V, VSENSE = 100 mV, RL = 10 kΩ to GND, RPULL-UP = 5.1 kΩ connected from CMPOUT to VS, and CMPIN = GND, (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INPUT | ||||||||
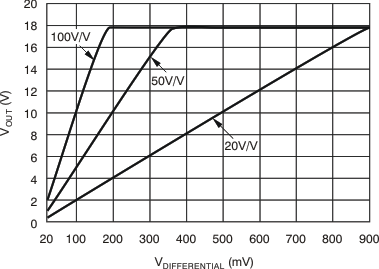
| VSENSE | Full-scale sense input voltage | VSENSE = VIN+ – VIN– | 0.15 | (VS – 0.25) / Gain | V | |||
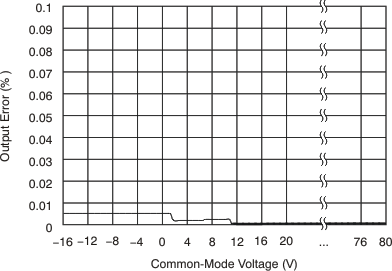
| VCM | Common-mode input range | TA = –40°C to 125°C | –16 | 80 | V | |||
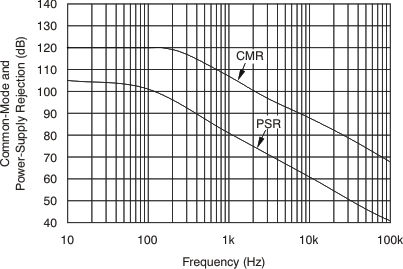
| CMR | Common-mode rejection | VIN+ = –16 V to 80 V | 80 | 100 | dB | |||
| VIN+ = 12 V to 80 V, TA = –40°C to 125°C | 100 | 123 | dB | |||||
| VOS | Offset voltage, RTI(1) | TA = 25°C | ±0.5 | ±2.5 | mV | |||
| TA = 25°C to 125°C | ±3 | mV | ||||||
| TA = –40°C to 25°C | ±3.5 | mV | ||||||
| dVOS/dT | Offset voltage, RTI, vs temperature | TMIN to TMAX, TA = –40°C to 125°C | 5 | μV/°C | ||||
| PSR | Offset voltage, RTI, vs power supply | VOUT = 2 V, VIN+ = 18 V, 2.7 V, TA = –40°C to 125°C | 2.5 | 100 | μV/V | |||
| IB | Input bias current, VIN– pin | TA = –40°C to 125°C | ±9 | ±16 | μA | |||
| OUTPUT (VSENSE ≥ 20 mV) | ||||||||
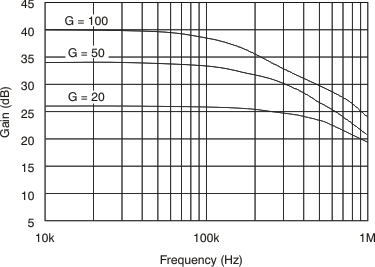
| G | Gain | INA200 | 20 | V/V | ||||
| INA201 | 50 | V/V | ||||||
| INA202 | 100 | V/V | ||||||
| Gain error | VSENSE = 20 mV to 100 mV | ±0.2% | ±1% | |||||
| VSENSE = 20 mV to 100 mV, TA = –40°C to 125°C | ±2% | |||||||
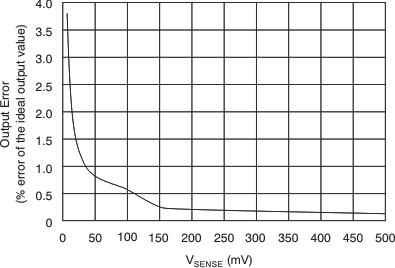
| Total output error(2) | VSENSE = 120 mV, VS = 16 V | ±0.75% | ±2.2% | |||||
| VSENSE = 120 mV, VS = 16 V, TA = –40°C to 125°C | ±3.5% | |||||||
| Nonlinearity error(3) | VSENSE = 20 mV to 100 mV | ±0.002% | ||||||
| RO | Output impedance | 1.5 | Ω | |||||
| Maximum capacitive load | No sustained oscillation | 10 | nF | |||||
| OUTPUT (VSENSE < 20 mV)(4) | ||||||||
| Output | INA200, INA201, INA202 | –16 V ≤ VCM < 0 V | 300 | mV | ||||
| INA200 | 0 V ≤ VCM ≤ VS, VS = 5 V | 0.4 | V | |||||
| INA201 | 0 V ≤ VCM ≤ VS, VS = 5 V | 1 | V | |||||
| INA202 | 0 V ≤ VCM ≤ VS, VS = 5 V | 2 | V | |||||
| INA200, INA201, INA202 | VS < VCM ≤ 80 V | 300 | mV | |||||
| VOLTAGE OUTPUT(5) | ||||||||
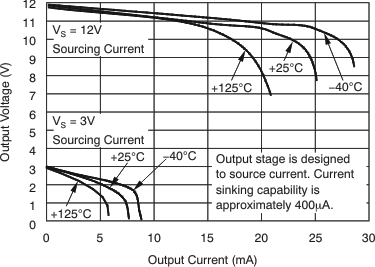
| Output swing to the positive rail | VIN– = 11 V, VIN+ = 12 V, TA = –40°C to 125°C | (Vs) – 0.15 | (Vs) – 0.25 | V | ||||
| Output swing to GND(6) | VIN– = 0 V, VIN+ = –0.5 V, TA = –40°C to 125°C | (GND) + 0.004 | (GND) + 0.05 | V | ||||
| FREQUENCY RESPONSE | ||||||||
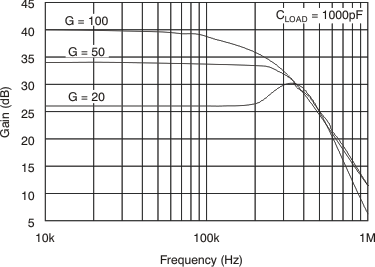
| BW | Bandwidth | INA200 | CLOAD = 5 pF | 500 | kHz | |||
| INA201 | CLOAD = 5 pF | 300 | kHz | |||||
| INA202 | CLOAD = 5 pF | 200 | kHz | |||||
| Phase margin | CLOAD < 10 nF | 40 | °C | |||||
| SR | Slew rate | 1 | V/μs | |||||
| Settling time (1%) | VSENSE = 10 mVPP to 100 mVPP, CLOAD = 5 pF |
2 | μs | |||||
| NOISE, RTI | ||||||||
| Voltage noise density | 40 | nV/√Hz | ||||||
(1) Offset is extrapolated from measurements of the output at 20-mV and 100-mV VSENSE.
(2) Total output error includes effects of gain error and VOS.
(3) Linearity is best fit to a straight line.
(4) For details on this region of operation, see Accuracy Variations section in Device Functional Modes.
(5) See Figure 8.
(6) Specified by design.
6.6 Electrical Characteristics: Comparator
at TA = 25°C, VS = 12 V, VCM = 12 V, VSENSE = 100 mV, RL = 10 kΩ to GND, and RPULL-UP = 5.1 kΩ connected from CMPOUT to VS, (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OFFSET VOLTAGE | |||||||
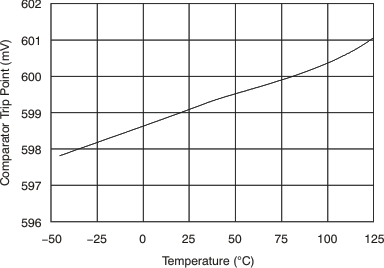
| Threshold | TA = 25°C | 590 | 608 | 620 | mV | ||
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 586 | 625 | mV | ||||
| Hysteresis(1) | TA = –40°C to 85°C | –8 | mV | ||||
| INPUT BIAS CURRENT(2) | |||||||
| Input bias current, CMPin PIN | 0.005 | 10 | nA | ||||
| Input bias current, CMPin PIN, vs temperature | TA = –40°C to 125°C | 15 | nA | ||||
| INPUT VOLTAGE RANGE | |||||||
| Input voltage range, CMPin PIN | 0 V to VS – 1.5 V | V | |||||
| OUTPUT (OPEN-DRAIN) | |||||||
| Large-signal differential voltage gain | CMP VOUT 1 V to 4 V, RL ≥ 15 kΩ connected to 5 V |
200 | V/mV | ||||
| ILKG | High-level leakage current(3)(4) | VID = 0.4 V, VOH = VS | 0.0001 | 1 | μA | ||
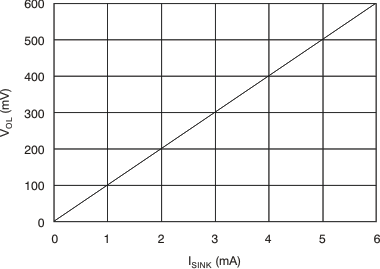
| VOL | Low-level output voltage(3) | VID = –0.6 V, IOL = 2.35 mA | 220 | 300 | mV | ||
| RESPONSE TIME | |||||||
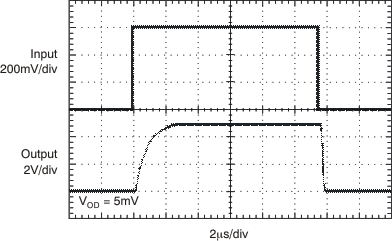
| Response time(5) | RL to 5 V, CL = 15 pF, 100-mV Input Step with 5-mV overdrive | 1.3 | μs | ||||
| RESET | |||||||
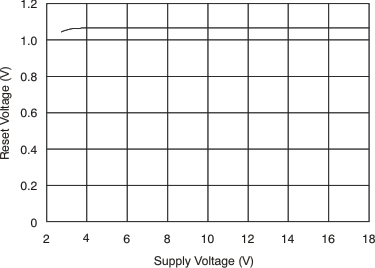
| RESET threshold(6) | 1.1 | V | |||||
| Logic input impedance | 2 | MΩ | |||||
| Minimum RESET pulse width | 1.5 | μs | |||||
| RESET propagation delay | 3 | μs | |||||
(1) Hysteresis refers to the threshold (the threshold specification applies to a rising edge of a noninverting input) of a falling edge on the noninverting input of the comparator; refer to Figure 1.
(2) Specified by design.
(3) VID refers to the differential voltage at the comparator inputs.
(4) Open-drain output can be pulled to the range of 2.7 to 18 V, regardless of VS.
(5) The comparator response time specified is the interval between the input step function and the instant when the output crosses 1.4 V.
(6) The RESET input has an internal 2 MΩ (typical) pull-down. Leaving RESET open results in a LOW state, with transparent comparator operation.
6.7 Electrical Characteristics: General
at TA = 25°C, VS = 12 V, VCM = 12 V, VSENSE = 100 mV, RL = 10 kΩ to GND, RPULL-UP = 5.1 kΩ connected from CMPOUT to VS, and CMPIN = 1 V, unless otherwise noted.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POWER SUPPLY | |||||||
| VS | Operating power supply | TA = –40°C to 125°C | 2.7 | 18 | V | ||
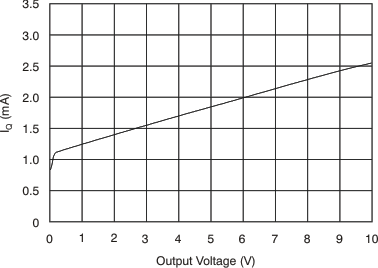
| IQ | Quiescent current | VOUT = 2 V | 1350 | 1800 | μA | ||
| VSENSE = 0 mV, TA = –40°C to 125°C | 1850 | μA | |||||
| Comparator power-on reset threshold(1) | 1.5 | V | |||||
| TEMPERATURE | |||||||
| Specified temperature | –40 | 125 | °C | ||||
| Operating temperature | –55 | 150 | °C | ||||
| Storage temperature | –65 | 150 | °C | ||||
| θJA | Thermal resistance | VSSOP-8 Surface-Mount | 200 | °C/W | |||
| SOIC-8 | 150 | °C/W | |||||
(1) The INA200, INA201, and INA202 are designed to power-up with the comparator in a defined reset state as long as RESET is open or grounded. The comparator is in reset as long as the power supply is below the voltage shown here. The comparator assumes a state based on the comparator input above this supply voltage. If RESET is high at power-up, the comparator output comes up high and requires a reset to assume a low state, if appropriate.
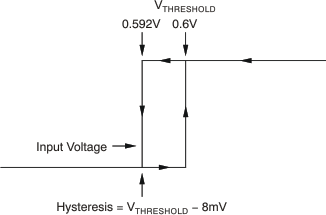 Figure 1. Typical Comparator Hysteresis
Figure 1. Typical Comparator Hysteresis
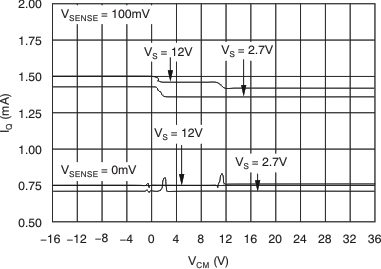
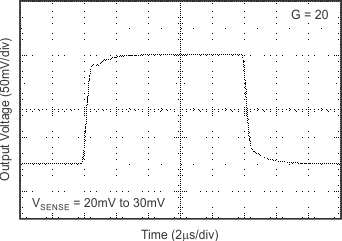
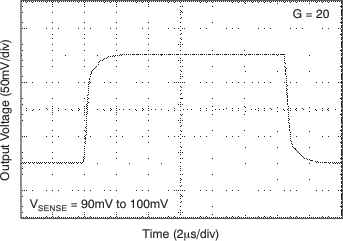
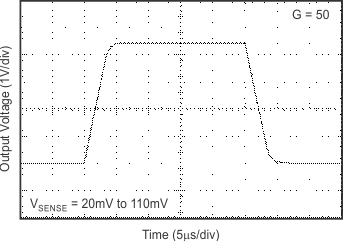
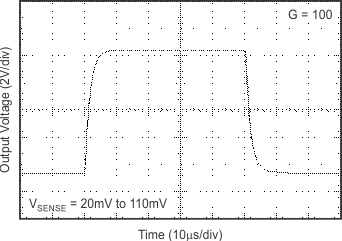
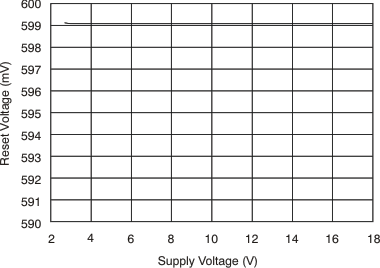
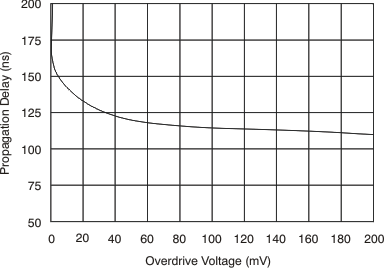
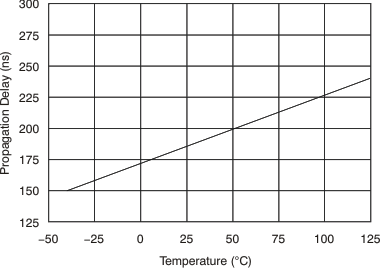
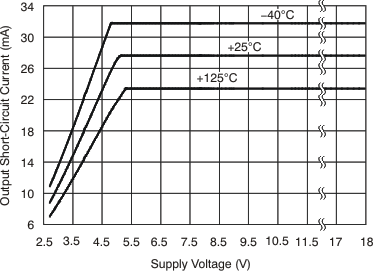
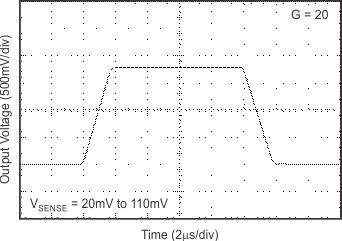
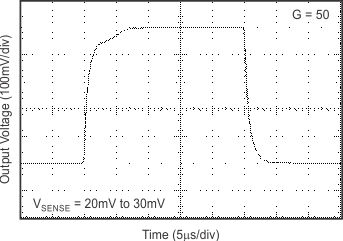
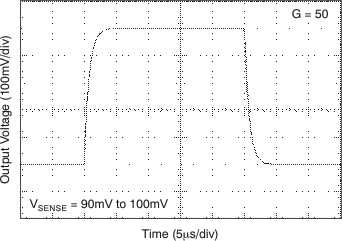
6.8 Typical Characteristics
at TA = 25°C, VS = 12 V, VIN+ = 12 V, and VSENSE = 100 mV, (unless otherwise noted)