SLIS183 June 2017 LM193-MIL
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC | Supply voltage(2) | 36 | V | |||
| VID | Differential input voltage(3) | ±36 | V | |||
| VI | Input voltage (either input) | –0.3 | 36 | V | ||
| IIK | Input current(5) | -50 | mA | |||
| VO | Output voltage | 36 | V | |||
| IO | Output current | 20 | mA | |||
| Duration of output short circuit to ground(4) | Unlimited | |||||
| TJ | Operating virtual-junction temperature | 150 | °C | |||
| Case temperature for 60 s | FK package | 260 | °C | |||
| Lead temperature 1.6 mm (1/16 in) from case for 60 s | JG package | 300 | °C | |||
| Tstg | Storage temperature | –65 | 150 | °C | ||
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) All voltage values, except differential voltages, are with respect to network ground.
(3) Differential voltages are at IN+ with respect to IN–.
(4) Short circuits from outputs to VCC can cause excessive heating and eventual destruction.
(5) Input current flows thorough parasitic diode to ground and will turn on parasitic transistors that will increase ICC and may cause output to be incorrect. Normal operation resumes when input current is removed.
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±1000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±750 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC | Supply voltage | non-V devices | 2 | 30 | V |
| V devices | 2 | 32 | V | ||
| TA | Operating temperature | LM193 | –55 | 125 | °C |
| LM293, LM293A | –25 | 85 | °C | ||
| LM393, LM393A | 0 | 70 | °C | ||
| LM2903, LM2903V, LM2903AV | –40 | 125 | °C | ||
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | LM193-MIL | UNIT | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JG (CDIP) | FK (LCCC) | ||||||||
| 8 PINS | 20 PINS | ||||||||
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 14.5 | 5.61 | °C/W | |||||
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report.
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
at specified free-air temperature, VCC = 5 V (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | TA(1) | LM193-MIL | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | TYP | MAX | ||||||
| VIO | Input offset voltage | VCC = 5 V to 30 V, VIC = VICR min, VO = 1.4 V |
25°C | 2 | 5 | mV | ||
| Full range | 9 | |||||||
| IIO | Input offset current | VO = 1.4 V | 25°C | 3 | 25 | nA | ||
| Full range | 100 | |||||||
| IIB | Input bias current | VO = 1.4 V | 25°C | –25 | –100 | nA | ||
| Full range | –300 | |||||||
| VICR | Common-mode input-voltage range(2) | 25°C | 0 to VCC – 1.5 |
V | ||||
| Full range | 0 to VCC – 2 |
|||||||
| AVD | Large-signal differential-voltage amplification | VCC = 15 V, VO = 1.4 V to 11.4 V, RL ≥ 15 kΩ to VCC |
25°C | 50 | 200 | V/mV | ||
| IOH | High-level output current | VOH = 5 V | VID = 1 V | 25°C | 0.1 | nA | ||
| VOH = 30 V | VID = 1 V | Full range | 1 | µA | ||||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage | IOL = 4 mA, | VID = –1 V | 25°C | 150 | 400 | mV | |
| Full range | 700 | |||||||
| IOL | Low-level output current | VOL = 1.5 V, | VID = –1 V | 25°C | 6 | mA | ||
| ICC | Supply current | RL = ∞ | VCC = 5 V | 25°C | 0.8 | 1 | mA | |
| VCC = 30 V | Full range | 2.5 | ||||||
(1) Full range (minimum or maximum) for LM193-MIL is –55°C to 125°C. All characteristics are measured with zero common-mode input voltage, unless otherwise specified.
(2) The voltage at either input should not be allowed to go negative by more than 0.3 V otherwise output may be incorrect and excessive input current can flow. The upper end of the common-mode voltage range is limited by VCC – 2 V. However only one input needs to be in the valid common mode range, the other input can go up the maximum VCC level and the comparator provides a proper output state. Either or both inputs can go to maximum VCC level without damage.
6.6 Switching Characteristics
VCC = 5 V, TA = 25°C| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | TYP | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Response time | RL connected to 5 V through 5.1 kΩ, CL = 15 pF(1)(2) |
100-mV input step with 5-mV overdrive | 1.3 | µs |
| TTL-level input step | 0.3 | |||
(1) CL includes probe and jig capacitance.
(2) The response time specified is the interval between the input step function and the instant when the output crosses 1.4 V.
6.7 Typical Characteristics
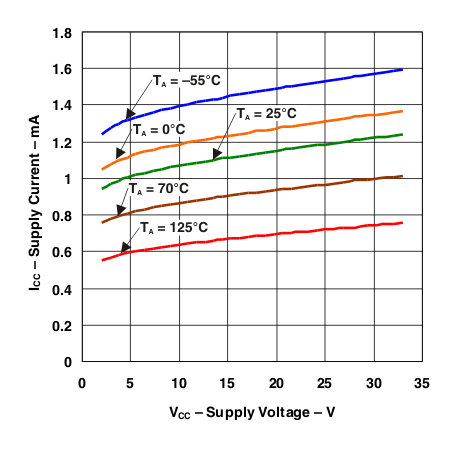 Figure 1. Supply Current vs Supply Voltage
Figure 1. Supply Current vs Supply Voltage
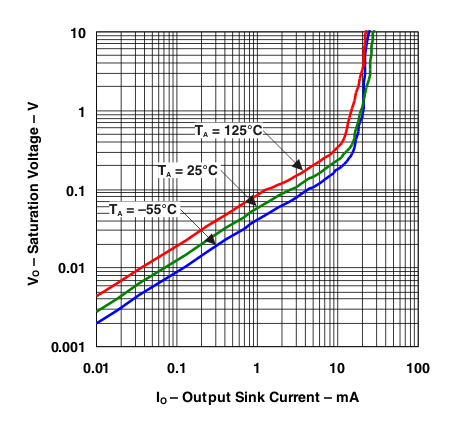 Figure 3. Output Saturation Voltage
Figure 3. Output Saturation Voltage
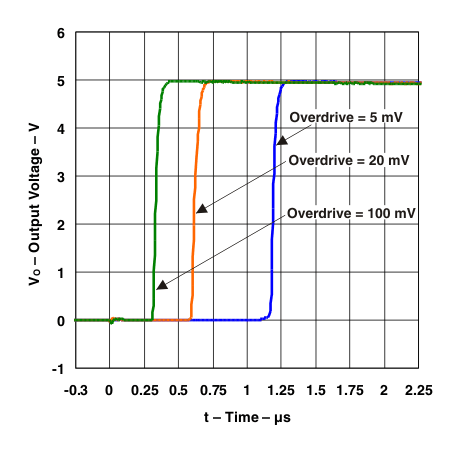 Figure 5. Response Time for Various Overdrives
Figure 5. Response Time for Various Overdrives Positive Transition
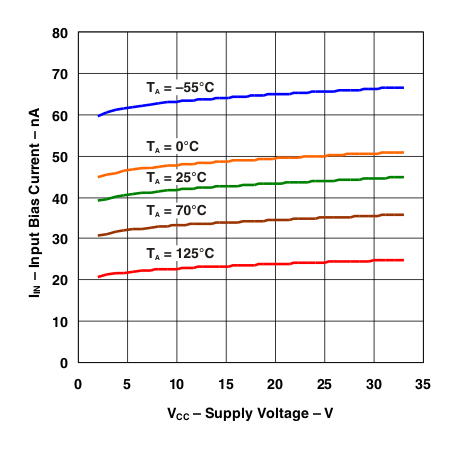 Figure 2. Input Bias Current vs Supply Voltage
Figure 2. Input Bias Current vs Supply Voltage
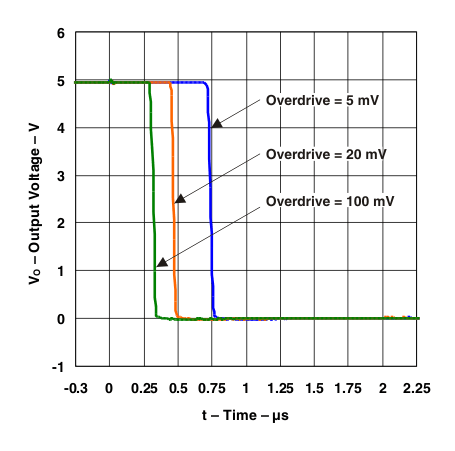 Figure 4. Response Time for Various Overdrives
Figure 4. Response Time for Various OverdrivesNegative Transition