SNVS953G December 2012 – May 2021 LM25018
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Control Overview
- 7.3.2 VCC Regulator
- 7.3.3 Regulation Comparator
- 7.3.4 Overvoltage Comparator
- 7.3.5 On-Time Generator
- 7.3.6 Current Limit
- 7.3.7 N-Channel Buck Switch and Driver
- 7.3.8 Synchronous Rectifier
- 7.3.9 Undervoltage Detector
- 7.3.10 Thermal Protection
- 7.3.11 Ripple Configuration
- 7.3.12 Soft Start
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1 Application Circuit: 12.5-V to 48-V Input and 10-V, 325-mA Output Buck Converter
- 8.2.2 Application Curves
- 8.2.3
Typical Isolated DC-DC Converter Using LM25018
- 8.2.3.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.3.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.3.2.1 Transformer Turns Ratio
- 8.2.3.2.2 Total IOUT
- 8.2.3.2.3 RFB1, RFB2
- 8.2.3.2.4 Frequency Selection
- 8.2.3.2.5 Transformer Selection
- 8.2.3.2.6 Primary Output Capacitor
- 8.2.3.2.7 Secondary Output Capacitor
- 8.2.3.2.8 Type III Feedback Ripple Circuit
- 8.2.3.2.9 Secondary Diode
- 8.2.3.2.10 VCC and Bootstrap Capacitor
- 8.2.3.2.11 Input Capacitor
- 8.2.3.2.12 UVLO Resistors
- 8.2.3.2.13 VCC Diode
- 8.2.3.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2.1.2.4 Inductor Selection
The minimum inductance is selected to limit the output ripple to 30 to 40 percent of the maximum load current. In addition, the peak inductor current at maximum load must be smaller than the minimum current limit threshold as given in Equation 13. The inductor current ripple is calculated using Equation 13.
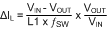
The maximum ripple is observed at maximum input voltage. To achieve the required output current of 300 mA without exceeding the peak current limit threshold, lower ripple current is required. Substituting VIN = 48 V and ΔIL = 30 percent × IOUT (max) results in L1 = 200 μH. The higher standard value of 220 μH is chosen. With this inductor value, the peak-to-peak minimum and maximum inductor current ripple are 21 mA and 82 mA at minimum and maximum input voltages, respectively. The peak inductor and switch current is shown in Equation 14.
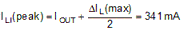
The calculated peak current of 341 mA is smaller than the minimum current limit threshold, which is 390 mA. In addition, the selected inductor must be able to operate at the maximum current limit threshold of 750 mA during startup and overload conditions without saturating.