SNVS569C May 2009 – October 2016 LM3550
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 Register Maps
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- NHU|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
10 Layout
10.1 Layout Guidelines
The UQFN is a leadless package with very good thermal properties. This package has an exposed DAP (die attach pad) at the underside center of the package measuring 1.86 mm × 2.2 mm. The main advantage of this exposed DAP is to offer low thermal resistance when soldered to the thermal ground pad on the PCB. For good PCB layout TI recommends a 1:1 ratio between the package and the PCB thermal land. To further enhance thermal conductivity, the PCB thermal ground pad may include vias to a 2nd layer ground plane. For more detailed instructions on mounting UQFN packages, refer to AN-1187 Leadless Leadframe Package (LLP).
The proceeding steps must be followed to ensure stable operation and proper current source regulation.
- Bypass VIN with at least a 4.7-µF ceramic capacitor. Connect the positive terminal of this capacitor as close as possible to VIN.
- Connect COUT as close as possible to the VOUT pin with at least a 2.2-µF capacitor.
- Connect the return terminals of the input capacitor and the output capacitor as close as possible to the exposed DAP and GND pins through low impedance traces.
- Place the two 1-µF flying capacitors (C1 and C2) as close as possible to the LM3550 C1+, C1− and C2+, C2− pins.
- To minimize losses during the flash pulse, TI recommends that the flash LEDs, the current source NFET, and current-setting resistor be placed as close as possible to the super capacitor.
10.2 Layout Example
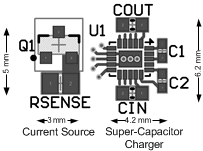 Figure 72. LM3550 Layout
Figure 72. LM3550 Layout