SNVSAJ8D February 2016 – March 2018 LM36273
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Features Description
- 7.3.1 Enabling the LM36273
- 7.3.2 Backlight
- 7.3.3 LCM Bias
- 7.3.4 Software Reset
- 7.3.5 HWEN Input
- 7.3.6 Thermal Shutdown (TSD)
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Maps
- 7.6.1 Revision Register (Address = 0x01)[Reset = 0x01]
- 7.6.2 Backlight Configuration1 Register (Address = 0x02)[Reset = 0x28]
- 7.6.3 Backlight Configuration 2 Register (Address = 0x03)[Reset = 0x8D]
- 7.6.4 Backlight Brightness LSB Register (Address = 0x04)[Reset = 0x07]
- 7.6.5 Backlight Brightness MSB Register (Address = 0x05)[Reset = 0xFF]
- 7.6.6 Backlight Auto-Frequency Low Threshold Register (Address = 0x06)[Reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.7 Backlight Auto-Frequency High Threshold Register (Address = 0x07)[Reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.8 Backlight Enable Register (Address = 0x08)[Reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.9 Bias Configuration 1 Register (Address = 0x09)[Reset = 0x18]
- 7.6.10 Bias Configuration 2 register (Address = 0x0A)[Reset = 0x11]
- 7.6.11 Bias Configuration 3 Register (Address = 0x0B)[Reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.12 LCM Boost Bias Register (Address = 0x0C)[Reset = 0x28]
- 7.6.13 VPOS Bias Register (Address = 0x0D)[Reset = 0x1E]
- 7.6.14 VNEG Bias Register (Address = 0x0E)[Reset = 0x1C]
- 7.6.15 Flags Register (Address = 0x0F)[Reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.16 Option 1 Register (Address = 0x10)[Reset = 0x06]
- 7.6.17 Option 2 Register (Address = 0x11)[Reset = 0x35]
- 7.6.18 PWM-to-Digital Code Readback LSB Register (Address = 0x12)[Reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.19 PWM-to-Digital Code Readback MSB Register (Address = 0x13)[Reset = 0x00]
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- YFF|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
YFF Package
24-Pin DSBGA
Top View
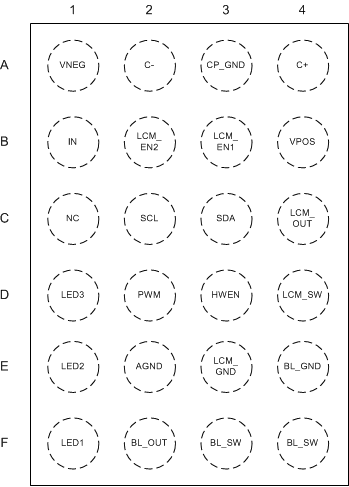
Pin Functions
| PIN | TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NUMBER | NAME | ||
| A1 | VNEG | O | Inverting charge pump output. Bypass VNEG with a 10-µF ceramic capacitor to CP_GND. |
| A2 | C- | O | Inverting charge-pump flying capacitor negative connection |
| A3 | CP_GND | — | Charge pump GND. Connect the CNEG capacitor negative terminal to this pin. |
| A4 | C+ | O | Inverting charge-pump flying capacitor positive connection |
| B1 | IN | I | Input voltage connection. Bypass IN with a 10-µF ceramic capacitor to GND. |
| B2 | LCM_EN2 | I | Enable for LCD bias negative output; 300-kΩ internal pulldown resistor between LCM_EN2 and GND. |
| B3 | LCM_EN1 | I | Enable for LCD bias positive output; 300-kΩ internal pulldown resistor between LCM_EN1 and GND. |
| B4 | VPOS | O | Positive LCD bias output. Bypass VPOS with a 10-µF ceramic capacitor to GND. |
| C1 | NC | — | No connect; leave this pin disconnected |
| C2 | SCL | I | Serial clock connection for I2C-compatible interface |
| C3 | SDA | I/O | Serial clock connection for I2C-compatible interface |
| C4 | LCM_OUT | O | LCD bias boost output voltage. Bypass LCM_OUT with a 10-µF ceramic capacitor to LCM_GND. |
| D1 | LED3 | I | Current sink 3 input. Connect the cathode of LED string 3 to this pin. Leave this pin disconnected if not used. |
| D2 | PWM | I | PWM input for duty cycle current control; 300-kΩ internal pulldown resistor between PWM and GND. |
| D3 | HWEN | I | Active high chip enable; 300-kΩ internal pulldown resistor between HWEN and GND. |
| D4 | LCM_SW | O | LCD bias boost inductor connection |
| E1 | LED2 | I | Current sink 2 input. Connect the cathode of LED string 2 to this pin. Leave this pin disconnected if not used. |
| E2 | AGND | — | Analog ground connection. Connect AGND directly to GND on the PCB. |
| E3 | LCM_GND | — | LCD bias boost GND connection. Connect LCM_GND to the negative terminal of the LCD bias output capacitor. |
| E4 | BL_GND | — | Backlight boost output capacitor GND connection |
| F1 | LED1 | I | Current sink 1 input. Connect the cathode of LED string 1 to this pin. Leave this pin disconnected if not used. |
| F2 | BL_OUT | O | Backlight boost output voltage sense connection. Connect to the positive terminal of backlight boost output capacitor. |
| F3 | BL_SW | O | Backlight boost inductor connection |
| F4 | BL_SW | O | Backlight boost inductor connection |