SNVSC09 March 2022 LM5143
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Input Voltage Range (VIN)
- 9.3.2 High-Voltage Bias Supply Regulator (VCC, VCCX, VDDA)
- 9.3.3 Enable (EN1, EN2)
- 9.3.4 Power-Good Monitor (PG1, PG2)
- 9.3.5 Switching Frequency (RT)
- 9.3.6 Clock Synchronization (DEMB)
- 9.3.7 Synchronization Out (SYNCOUT)
- 9.3.8 Spread Spectrum Frequency Modulation (DITH)
- 9.3.9 Configurable Soft Start (SS1, SS2)
- 9.3.10 Output Voltage Setpoint (FB1, FB2)
- 9.3.11 Minimum Controllable On Time
- 9.3.12 Error Amplifier and PWM Comparator (FB1, FB2, COMP1, COMP2)
- 9.3.13 Slope Compensation
- 9.3.14 Inductor Current Sense (CS1, VOUT1, CS2, VOUT2)
- 9.3.15 Hiccup Mode Current Limiting (RES)
- 9.3.16 High-Side and Low-Side Gate Drivers (HO1/2, LO1/2, HOL1/2, LOL1/2)
- 9.3.17 Output Configurations (MODE, FB2)
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2
Typical Applications
- 10.2.1 Design 1 – 5-V and 3.3-V Dual-Output Buck Regulator for Computing Applications
- 10.2.2 Design 2 – Two-Phase, 15-A, 2.1-MHz Single-Output Buck Regulator for Server Applications
- 10.2.3 Design 3 – Two-Phase, 50-A, 300-kHz Single-Output Buck Regulator for ASIC Power Applications
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHA|40
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RHA|40
Orderable Information
10.2.2.3 Application Curves
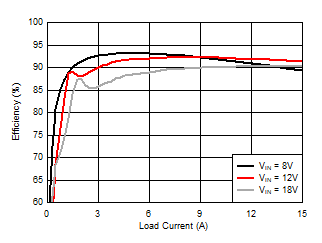
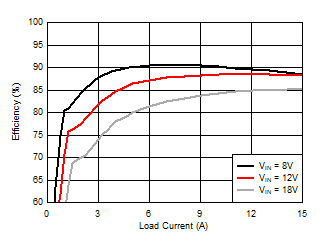
| Configure the regulator as a 3.3-V output by tying FB1 to VDDA. |