SNOSDD8 December 2022 LM7480
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
-
10Applications and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2 Typical 12-V Reverse Battery Protection Application
- 10.3 200-V Unsuppressed Load Dump Protection Application
- 10.4 Do's and Don'ts
- 10.5 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10.6 Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DRR|12
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DRR|12
Orderable Information
10.2.5 MOSFET Selection: Hot-Swap MOSFET Q2
The VDS rating of the MOSFET Q2 should be sufficient to handle the maximum system voltage along with the input transient voltage. For this 12-V design, transient overvoltage events are during suppressed load dump 35 V 400 ms and ISO 7637-2 pulse 2 A 50 V for 50 µs. Further, ISO 7637-2 Pulse 3B is a very fast repetitive pulse of 100 V 100 ns that is usually absorbed by the input and output ceramic capacitors and the maximum voltage on the 12-V battery can be limited to < 40 V the minimum recommended input capacitance of 0.1 µF. The 50-V SO 7637-2 Pulse 2 A can also be absorbed by input and output capacitors and its amplitude could be reduced to 40-V peak by placing sufficient amount of capacitance at input and output. However for this 12-V design, maximum system voltage is 50 V and a 60-V VDS rated MOSFET is selected.
The VGS rating of the MOSFET Q2 should be higher than that maximum HGATE-OUT voltage 15 V.
Inrush current through the MOSFET during input hot-plug into the 12-V battery is determined by output capacitance. External capacitor on HGATE, CDVDT is used to limit the inrush current during input hot-plug or startup. The value of inrush current determined by Equation 2 need to be selected to ensure that the MOSFET Q2 is operating well within its safe operating area (SOA). To limit inrush current to 250 mA, value of CDVDT is 10.43 nF, closest standard value of 10.0 nF is chosen.
Duration of inrush current is calculated by
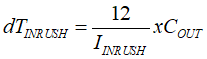
Calculated inrush current duration is 2.36 ms with 250-mA inrush current.
MOSFET BUK7Y4R8-60E having 60-V VDS and ±20-V VGS rating is selected for Q2. Power dissipation during inrush is well within the MOSFET's safe operating area (SOA).