SNAS744B July 2017 – March 2018 LMS3655
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Applications
- 9.2.1 General Application
- 9.2.2 Adjustable 5-V Output
- 9.2.3 Adjustable 3.3-V Output
- 9.2.4 6-V Adjustable Output
- 9.3 Do's and Don't's
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RNL|22
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RNL|22
Orderable Information
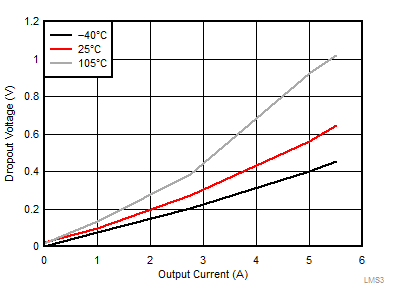
9.2.3.3 Application Curves
The following characteristics apply only to the circuit of Figure 35. These parameters are not tested and represent typical performance only. Unless otherwise stated, the following conditions apply: VIN = 12 V, TA = 25°C. For the purpose of offering more information to the designer, information for the application with FPWM pin high (FPWM mode) and FPWM pin low (AUTO mode) is included, although the schematic shows the application running specifically in AUTO mode. The mode is specified under each of the following graphs.

| VOUT = 3.3 V | AUTO |

| VOUT = 3.3 V | AUTO |

| VOUT = 3.3 V |

| VOUT = 3.3 V |

| VOUT = 3.3 V | L = 10 µH |

| FPWM | VOUT = 3.3 V | L = 10 µH, |
| COUT = 190 µF | IOUT = 0 A to 3.5 A | TR = TF = 1 µs |

| VOUT = 3.3 V | FPWM |

| VOUT = 3.3 V | FPWM |
| VOUT = 3.3 V |

| VOUT = 3.3 V | AUTO |

| AUTO | VOUT = 3.3 V | L = 10 µH, |
| COUT = 190 µF | IOUT = 0 A to 3.5 A | TR = TF = 1 µs |

| VOUT = 3.3 V | IOUT = 10 mA |