SNVS056J May 2000 – June 2015 LP3961 , LP3964
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configurations and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 External Capacitors
- 8.2.2.2 Selecting a Capacitor
- 8.2.2.3 Capacitor Characteristics
- 8.2.2.4 RFI and EMI Susceptibility
- 8.2.2.5 Output Adjustment
- 8.2.2.6 Turnon Characteristics for Output Voltages Programmed to 2.0 V or Below
- 8.2.2.7 Output Noise
- 8.2.2.8 Shutdown Operation
- 8.2.2.9 Maximum Output Current Capability
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- KTT|5
Orderable Information
10 Layout
10.1 Layout Guidelines
Good PC layout practices must be used or instability can be induced because of ground loops and voltage drops. The input and output capacitors must be directly connected to the IN, OUT, and GND pins of the LP396x using traces which do not have other currents flowing in them (Kelvin connect).
The best way to do this is to lay out CIN and COUT near the device with short traces to the IN, OUT, and GND pins. The regulator ground pin should be connected to the external circuit ground so that the regulator and its capacitors have a single-point ground.
It should be noted that stability problems have been seen in applications where vias to an internal ground plane were used at the ground points of the LP396x IC and the input and output capacitors. This was caused by varying ground potentials at these nodes resulting from current flowing through the ground plane. Using a single-point ground technique for the regulator and its capacitors fixed the problem.
Because high current flows through the traces going into the IN pin and coming from the OUT pin, Kelvin connect the capacitor leads to these pins so there is no voltage drop in series with the input and output capacitors.
10.2 Layout Example
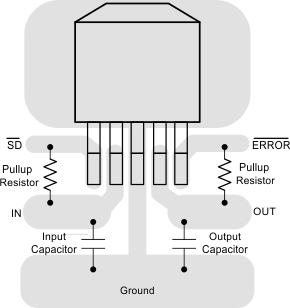 Figure 26. LP3961 TO-263 Package Typical Layout
Figure 26. LP3961 TO-263 Package Typical Layout
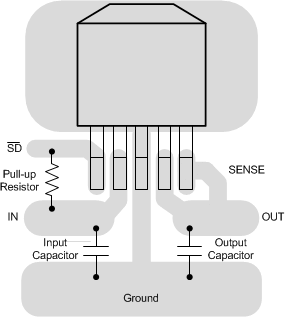 Figure 27. LP3964 TO-263 Package Typical Layout
Figure 27. LP3964 TO-263 Package Typical Layout
10.3 Heatsinking TO-220 Packages
The thermal resistance of a TO-220 package can be reduced by attaching it to a heatsink or a copper plane on a PC board.
The heatsink to be used in the application should have a heatsink-to-ambient thermal resistance,
In this equation, RθCH is the thermal resistance from the junction to the surface of the heatsink and RθJC is the thermal resistance from the junction to the surface of the case.