SLVSGD5 July 2021 LP5890
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Independent and Stackable Mode
- 8.3.2 Current Setting
- 8.3.3 Frequency Multiplier
- 8.3.4 Line Transitioning Sequence
- 8.3.5 Protections and Diagnostics
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Continuous Clock Series Interface
- 8.6 PWM Grayscale Control
- 8.7 Register Maps
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.6.1.1 Memory Structure Overview
The LP5890 implements a display memory unit to achieve high refresh rate and high contrast ratio in LED display products. The internal display memory unit is divided into two BANKs: BANK A and BANK B. During the normal operation, one BANK is selected to display the data of current frame, another is used to restore the data of next frame. The BANK switcher is controlled by the BANK_SEL bit, which is an internal flag register bit.
After power on, BANK_SEL is initialized to 0, and BANK A is selected to restore the data of next frame. Meanwhile, the data in BANK B is read out for display. When one frame has elapsed, the controller sends the vertical synchronization (VSYNC) command to start the next frame. The BANK_SEL bit value is toggled and the selection of the two BANKs reverses. Repeat this operation until all the frame images are displayed.
With this method, the LP5890 device can display the current frame image at a very high refresh rate. See Figure 8-22 for more details about the BANK-selection exchange operation.
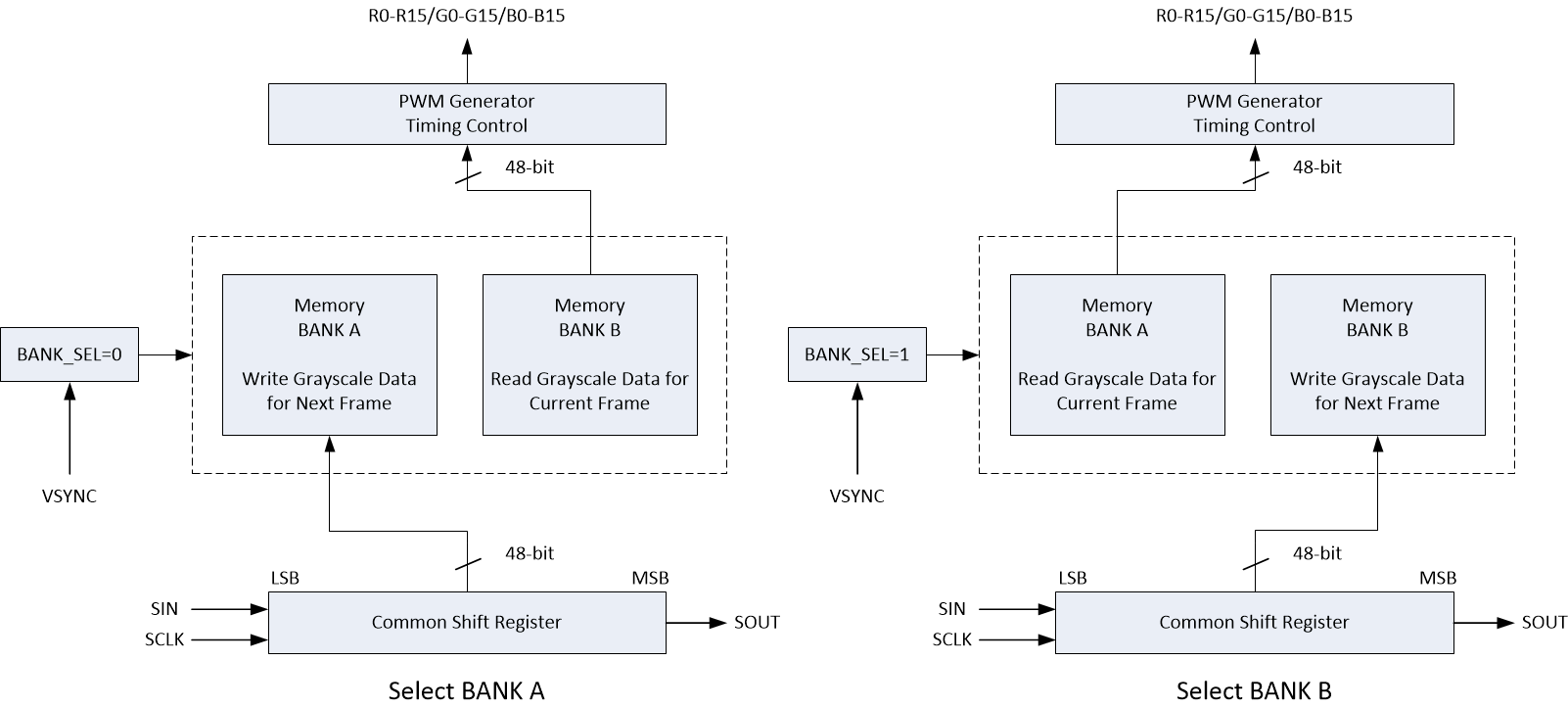 Figure 8-22 Bank Selection Exchange Operation
Figure 8-22 Bank Selection Exchange Operation