SBOS427F June 2017 – March 2021 OPA145 , OPA2145
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.8 EMIRR +IN Test Configuration
Figure 7-6 shows the circuit configuration for testing the EMIRR IN+. An RF source is connected to the op amp noninverting input terminal using a transmission line. The op amp is configured in a unity-gain buffer topology with the output connected to a low-pass filter (LPF) and a digital multimeter (DMM). A large impedance mismatch at the op amp input causes a voltage reflection; however, this effect is characterized and accounted for when determining the EMIRR IN+. The resulting DC offset voltage is sampled and measured by the multimeter. The LPF isolates the multimeter from residual RF signals that may interfere with multimeter accuracy.
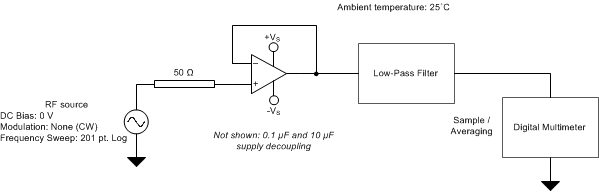 Figure 7-6 EMIRR +IN Test Configuration
Figure 7-6 EMIRR +IN Test Configuration