SBFS022C June 2003 – October 2015 SRC4192 , SRC4193
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DB|28
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted) (1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply Voltage | VDD | –0.3 | 4 | V |
| VIO | –0.3 | 4 | ||
| Digital Input Voltage | –0.3 | 4 | ||
| Operating Temperature | –45 | 85 | °C | |
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±3000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±1500 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage | VDD | 3 | 3.3 | 3.6 | V |
| VIO 1.8 V | 1.65 | 1.8 | 1.95 | ||
| VIO 3.3 V | 3 | 3.3 | 3.6 | ||
| Operating temperature | –45 | 85 | °C | ||
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | SRC4192 SRC4193 |
UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DB (SSOP) | |||
| 28 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 78.6 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 38.1 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 39.3 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 7.1 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 38.9 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | N/A | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
All parameters specified with TA = 25°C, VDD = 3.3 V, and VIO = 3.3 V, unless otherwise noted.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE(1) | |||||||
| Resolution | 24 | Bits | |||||
| fSIN | Input sampling frequency | 4 | 212 | kHz | |||
| fSOUT | Output sampling frequency | 4 | 212 | kHz | |||
| Input: output sampling ratio | Upsampling | 1:16 | |||||
| Downsampling | 16:1 | ||||||
| Dynamic range | 44.1 kHz; 48 kHz | BW = 20 Hz to fSOUT/2, –60-dBFS Input fIN = 1 kHz, Unweighted (add 3 dB to spec for A-weighted result) |
140 | dB | |||
| 48 kHz; 44.1 kHz | 140 | ||||||
| 48 kHz; 96 kHz | 140 | ||||||
| 44.1 kHz; 192 kHz | 138 | ||||||
| 96 kHz; 48 kHz | 141 | ||||||
| 192 kHz; 12 kHz | 141 | ||||||
| 192 kHz; 32 kHz | 141 | ||||||
| 192 kHz; 48 kHz | 141 | ||||||
| 32 kHz; 48 kHz | 140 | ||||||
| 12 kHz; 192 kHz | 138 | ||||||
| Total harmonic distortion + noise | 44.1 kHz; 48 kHz | BW = 20 Hz to fSOUT/2, 0-dBFS Input fIN = 1 kHz, Unweighted | –140 | dB | |||
| 48 kHz; 44.1 kHz | –140 | ||||||
| 48 kHz; 96 kHz | –140 | ||||||
| 44.1 kHz; 192 kHz | –137 | ||||||
| 96 kHz; 48 kHz | –140 | ||||||
| 192 kHz; 12 kHz | –140 | ||||||
| 192 kHz; 32 kHz | –141 | ||||||
| 192 kHz; 48 kHz | –141 | ||||||
| 32 kHz; 48 kHz | –140 | ||||||
| 12 kHz; 192 kHz | –137 | ||||||
| Interchannel gain mismatch | 0 | dB | |||||
| Interchannel phase deviation | 0 | ° | |||||
| Digital attenuation | Minimum | SRC4193 Only | 0 | dB | |||
| Maximum | –127.5 | ||||||
| Step Size | 0.5 | ||||||
| Mute attenuation | 24-Bit Word Length, A-weighted | –144 | dB | ||||
| DIGITAL INTERPOLATION FILTER CHARACTERISTICS | |||||||
| Passband | 0.4535 × fSIN | Hz | |||||
| Passband ripple | ±0.007 | dB | |||||
| Transition band | 0.4535 × fSIN | 0.5465 × fSIN | Hz | ||||
| Stop band | 0.5465 × fSIN | Hz | |||||
| Stop band attenuation | –144 | dB | |||||
| Normal group delay (LGRP = 0) | Decimation Filter On (DFLT = 0) | 102.53125/fSIN | s | ||||
| Decimation Filter Off (DFLT = 1) | 102/fSIN | ||||||
| Low group delay (LGRP = 1) | Decimation Filter On (DFLT = 0) | 70.53125/fSIN | s | ||||
| Decimation Filter Off (DFLT = 1) | 70/fSIN | ||||||
| DIGITAL DECIMATION FILTER CHARACTERISTICS | |||||||
| Passband | 0.4535 × fSOUT | Hz | |||||
| Passband ripple | ±0.008 | dB | |||||
| Transition band | 0.4535 × fSOUT | 0.5465 × fSOUT | Hz | ||||
| Stop band | 0.5465 × fSOUT | Hz | |||||
| Stop band attenuation | –143 | dB | |||||
| Group delay – decimation filter | DFLT = 0 for SRC4193 | 36.46875/fSOUT | s | ||||
| Direct downsampling | SRC4193 only, DFLT = 1 | 0 | s | ||||
| DIGITAL I/O CHARACTERISTICS | |||||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 0.7 × VIO | VIO | V | |||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | 0 | 0.3 × VIO | V | |||
| IIH | High-level input current | 0.5 | 10 | µA | |||
| IIL | Low-level input current | 0.5 | 10 | µA | |||
| VOH | High-level output voltage | IO = –4 mA | 0.8 × VIO | VIO | V | ||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage | IO = +4 mA | 0 | 0.2 × VIO | V | ||
| CIN | Input Capacitance | 3 | pF | ||||
| POWER SUPPLIES | |||||||
| Operating voltage, VDD | 3 | 3.3 | 3.6 | V | |||
| Operating voltage, VIO | 1.65 | 3.3 | 3.6 | ||||
| Supply current, IDD, power down | VDD = 3.3 V, VIO = 3.3 V, RST = 0, No Clocks | 100 | µA | ||||
| SRC4193 only, VDD = 3.3 V, VIO = 3.3 V, PDN Bit = 0, No Clocks |
5 | mA | |||||
| Supply current, IDD, dynamic | VDD = 3.3 V, VIO = 3.3 V, fSIN = fSOUT = 192 kHz | 66 | mA | ||||
| Supply current, IIO, power down | VDD = 3.3 V, VIO = 3.3 V, RST = 0, No Clocks | 100 | µA | ||||
| SRC4193 only, VDD = 3.3 V, VIO = 3.3 V, PDN Bit = 0, No Clocks |
21 | ||||||
| Supply current, IIO, dynamic | VDD = 3.3 V, VIO = 3.3 V, fSIN = fSOUT = 192 kHz | 2 | mA | ||||
| Total power dissipation, PD, power down | VDD = 3.3 V, VIO = 3.3 V, RST = 0, No Clocks | 660 | µW | ||||
| SRC4193 only, VDD = 3.3 V, VIO = 3.3 V, PDN Bit = 0, No Clocks |
16.6 | mW | |||||
| Total power dissipation, PD, dynamic | VDD = 3.3 V, VIO = 3.3 V, fSIN = fSOUT = 192 kHz | 225 | mW | ||||
(1) Dynamic performance measured with an Audio Precision System Two Cascade or Cascade Plus.
6.6 Switching Characteristics
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REFERENCE CLOCK TIMING | ||||||
| RCKI frequency | fSMIN = min (fSIN, fSOUT), fSMAX = max (fSIN, fSOUT) |
128 × fSMIN | 50 | MHz | ||
| tRCKIP | RCKI period | 20 | 1/(128 ×fSMIN) | ns | ||
| tRCKIH | RCKI pulsewidth high | 0.4 × tRCKIP | ns | |||
| tRCKIL | RCKI pulsewidth low | 0.4 × tRCKIP | ns | |||
| RESET TIMING | ||||||
| tRSTL | RST pulse width low | 500 | ns | |||
| Delay following RST rising edge | SRC4193 only | 500 | µs | |||
| INPUT SERIAL PORT TIMING | ||||||
| tLRIS | LRCKI to BCKI setup time | 10 | ns | |||
| tSIH | BCKI pulsewidth high | 10 | ns | |||
| tSIL | BCKI pulsewidth low | 10 | ns | |||
| tLDIS | SDIN data setup time | 10 | ns | |||
| tLDIH | SDIN data hold time | 10 | ns | |||
| OUTPUT SERIAL PORT TIMING | ||||||
| tDOPD | SDOUT data delay time | 10 | ns | |||
| tDOH | SDOUT data hold time | 2 | ns | |||
| tSOH | BCKO pulsewidth high | 10 | ns | |||
| tSOL | BCKO pulsewidth low | 5 | ns | |||
| TDM MODE TIMING | ||||||
| tLROS | LRCKO setup time | 10 | ns | |||
| tLROH | LRCKO hold time | 10 | ns | |||
| tTDMS | TDMI data setup time | 10 | ns | |||
| tTDMH | TDMI data hold time | 10 | ns | |||
| SPI TIMING | ||||||
| CCLK frequency | 25 | MHz | ||||
| tCDS | CDATA setup time | 12 | ns | |||
| tCDH | CDATA hold time | 8 | ns | |||
| tCSCR | CS falling to CCLK rising | 15 | ns | |||
| tCFCS | CCLK falling to CS rising | 12 | ns | |||
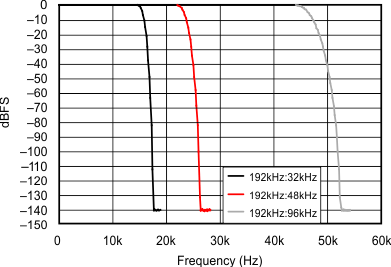
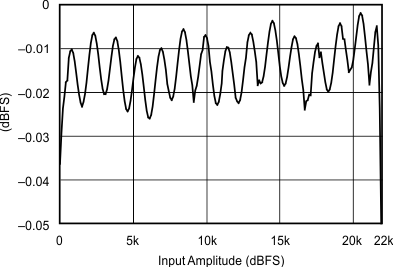
6.7 Typical Characteristics
At TA = 25°C, VDD = 3.3 V, and VIO = 3.3 V, unless otherwise noted.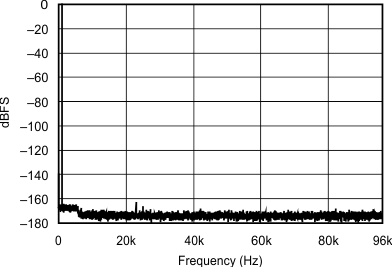
| 12 kHz:192 kHz |
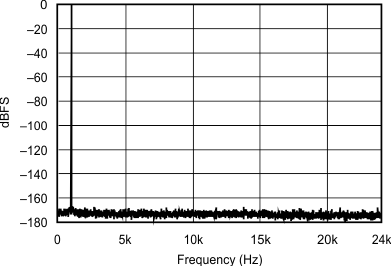
| 32 kHz:48 kHz |
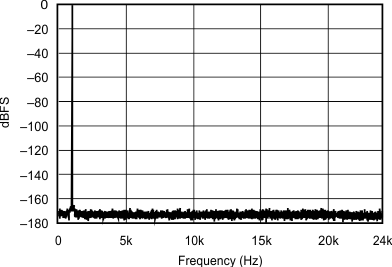
| 44.1 kHz:48 kHz | ||
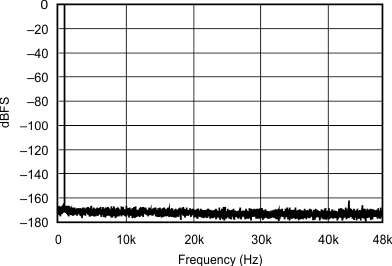
| 44.1 kHz:96 kHz | ||
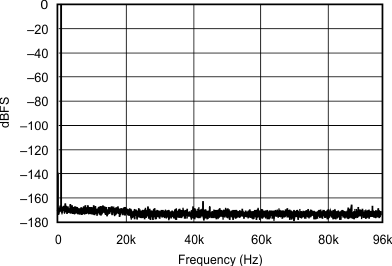
| 44.1 kHz:192 kHz | ||
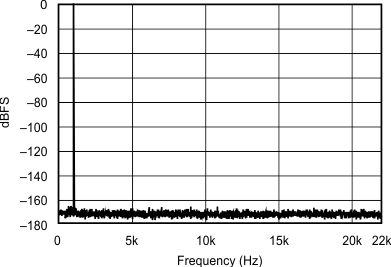
| 48 kHz:44.1 kHz | ||
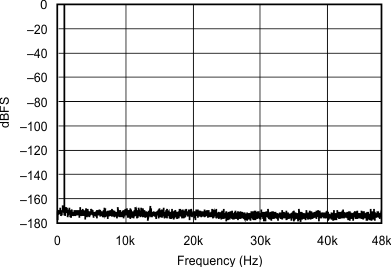
| 48 kHz:96 kHz | ||
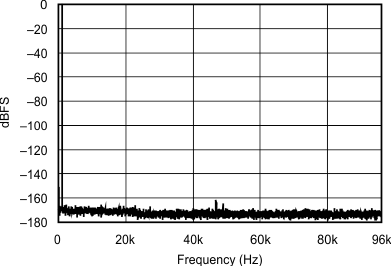
| 48 kHz:192 kHz | ||
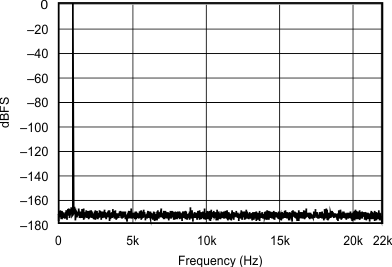
| 96 kHz:44.1 kHz | ||
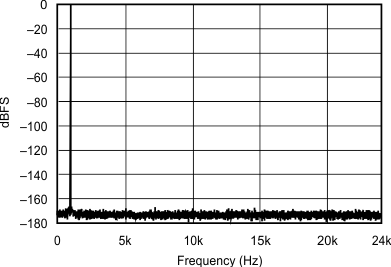
| 96 kHz:48 kHz | ||
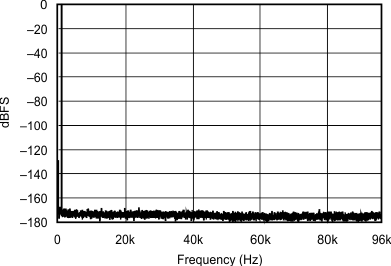
| 96 kHz:192 kHz | ||
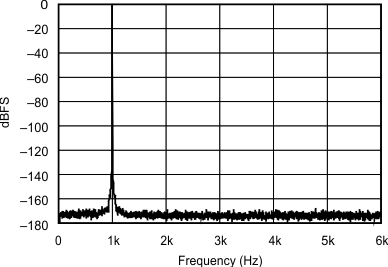
| 192 kHz:12 kHz | ||
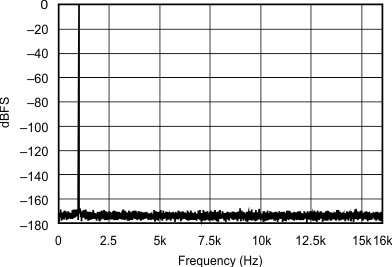
| 192 kHz:32 kHz | ||
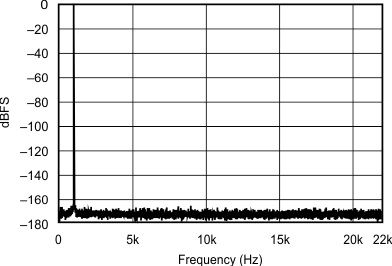
| 192 kHz:44.1 kHz | ||
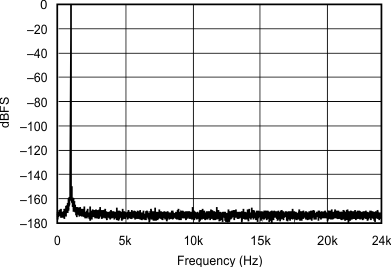
| 192 kHz:48 kHz | ||
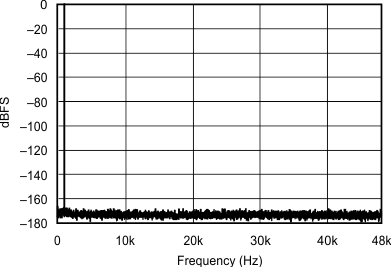
| 192 kHz:96 kHz | ||
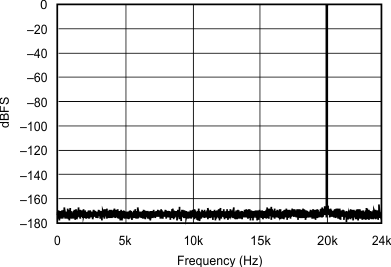
| 44.1 kHz:48 kHz | ||
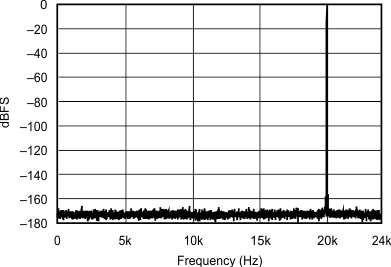
| 48 kHz:48 kHz | ||
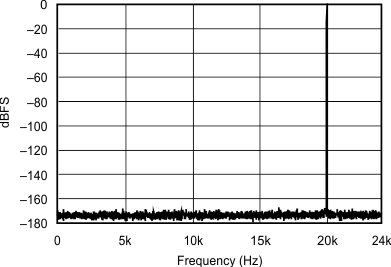
| 96 kHz:48 kHz | ||
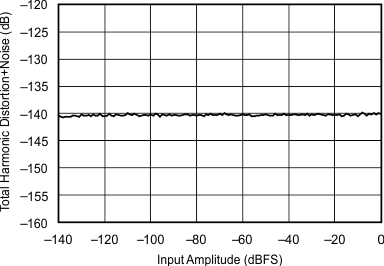
| 44.1 kHz:48 kHz | ||
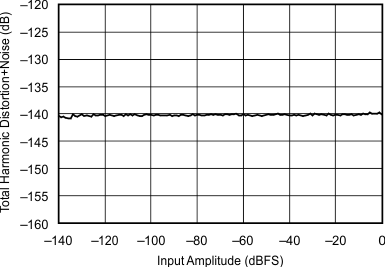
| 48 kHz:96 kHz | ||
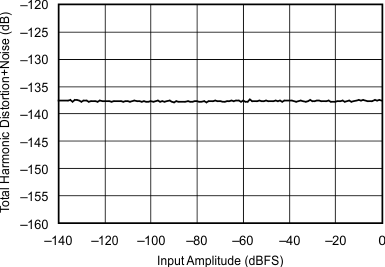
| 44.1 kHz:192 kHz | ||
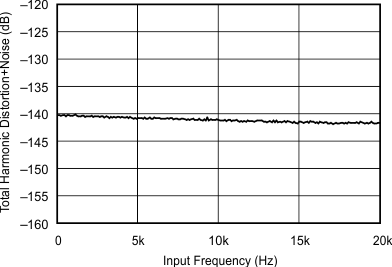
| 44.1 kHz:48 kHz | ||
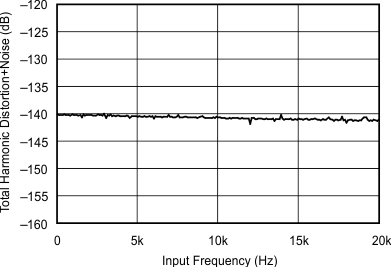
| 48 kHz:96 kHz | ||
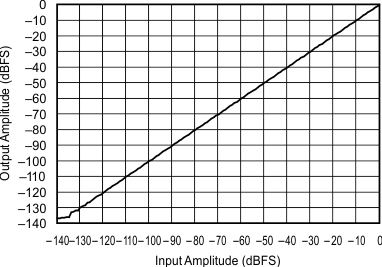
| 44.1 kHz:48 kHz | ||
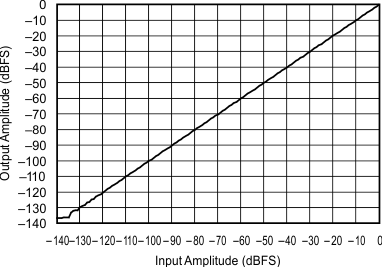
| 48 kHz:48 kHz | ||
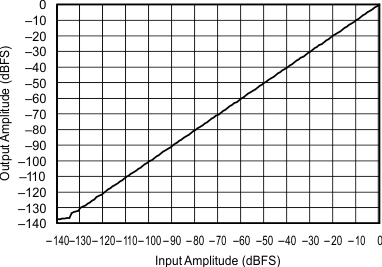
| 96 kHz:48 kHz | ||
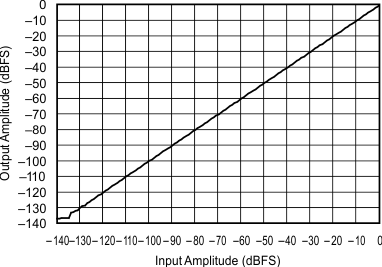
| 192 kHz:44.1 kHz | ||
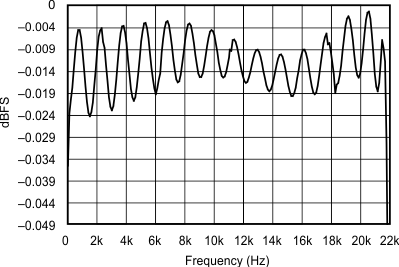
| 48k:48k | ||
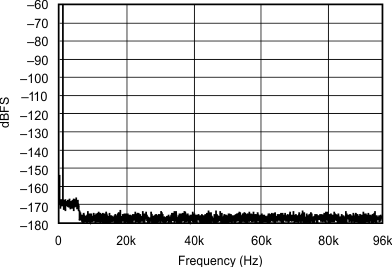
| 12 kHz:192 kHz |
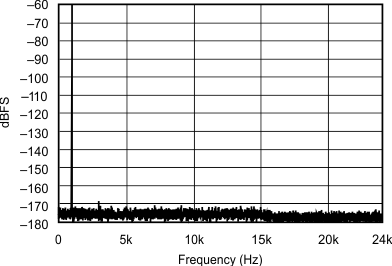
| 32 kHz:48 kHz |
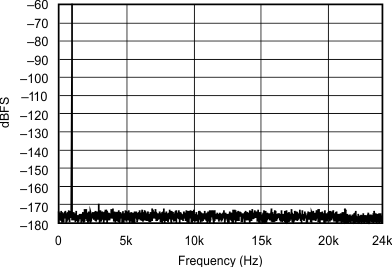
| 44.1 kHz:48 kHz | ||
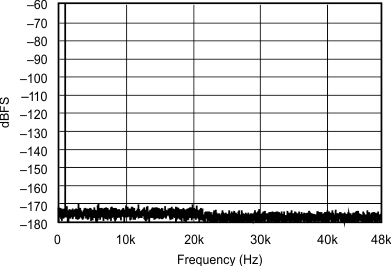
| 44.1 kHz:96 kHz | ||
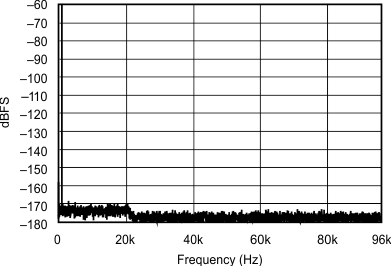
| 44.1 kHz:192 kHz | ||
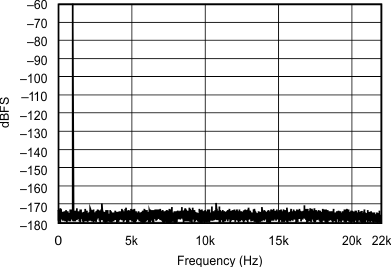
| 48 kHz:44.1 kHz | ||
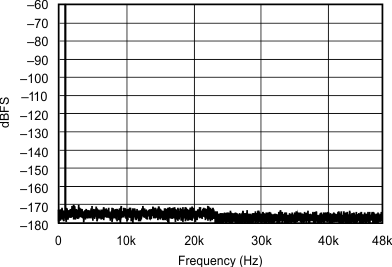
| 48 kHz:96 kHz | ||
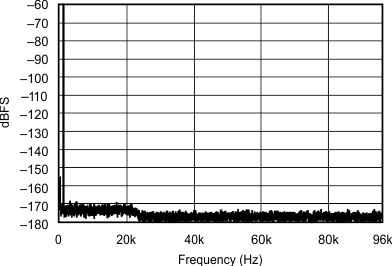
| 48 kHz:192 kHz | ||
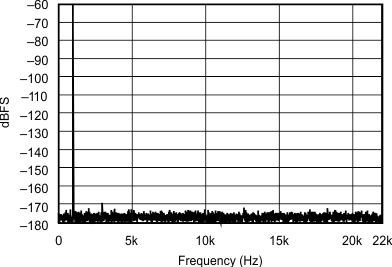
| 96 kHz:44.1 kHz | ||
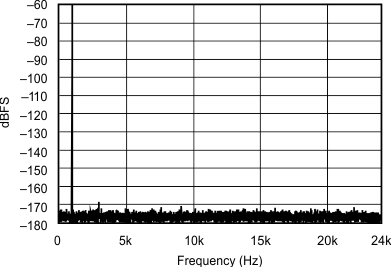
| 96 kHz:48 kHz | ||
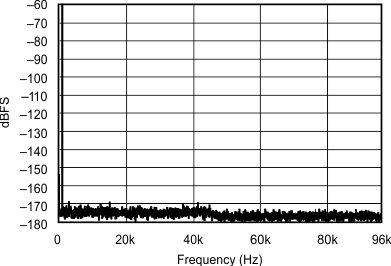
| 96 kHz:192 kHz | ||
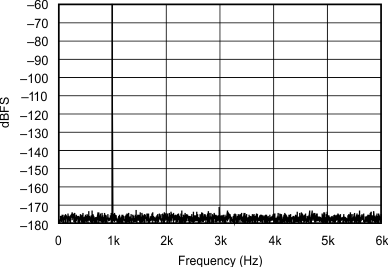
| 192 kHz:12 kHz | ||
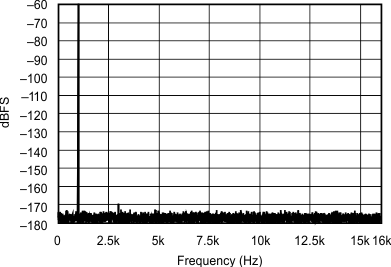
| 192 kHz:32 kHz | ||
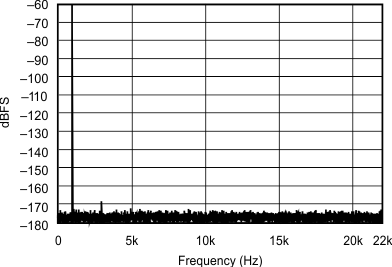
| 192 kHz:44.1 kHz | ||
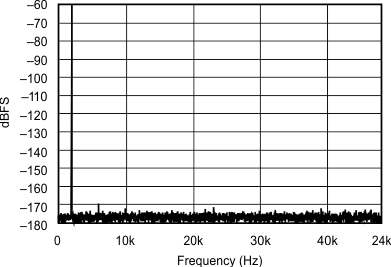
| 192 kHz:48 kHz | ||
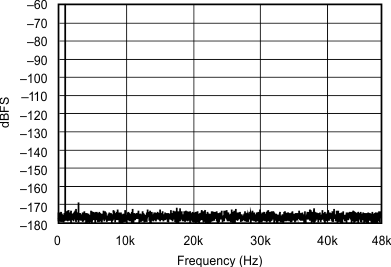
| 192 kHz:96 kHz | ||
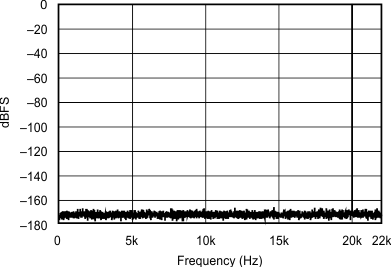
| 48 kHz:44.1 kHz | ||
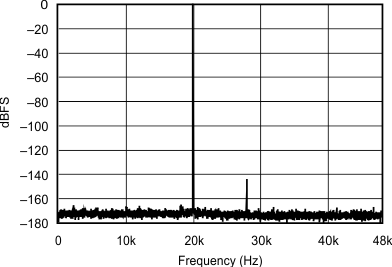
| 48 kHz:96 kHz | ||
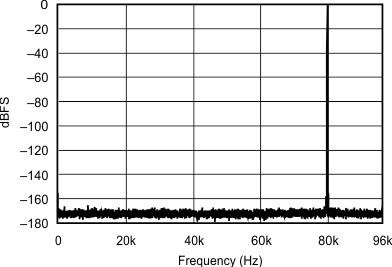
| 192 kHz:192 kHz | ||
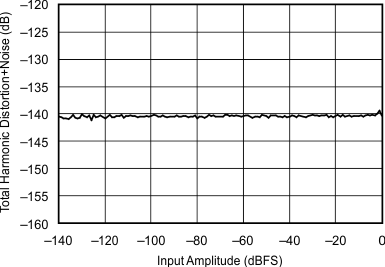
| 48 kHz:44.1 kHz | ||
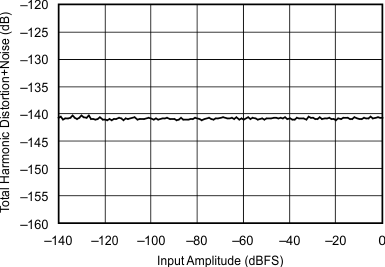
| 96 kHz:48 kHz | ||
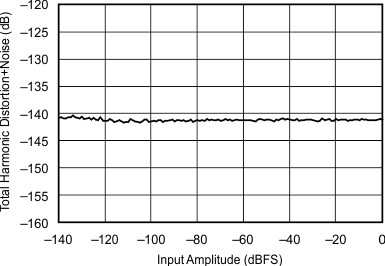
| 192 kHz:48 kHz | ||
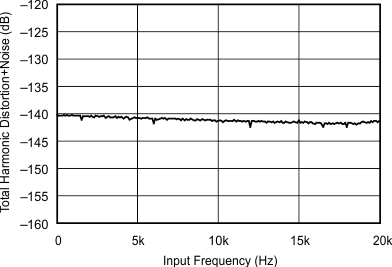
| 48 kHz:44.1 kHz | ||
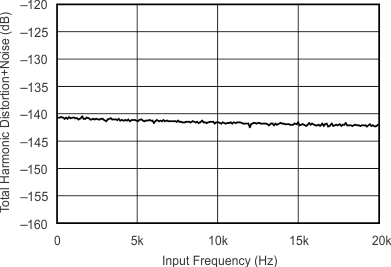
| 96 kHz:48 kHz | ||
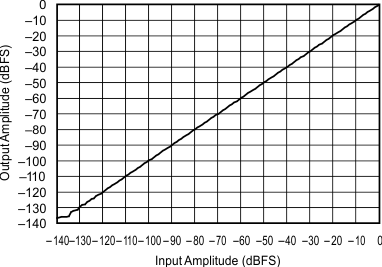
| 48 kHz:44.1 kHz | ||
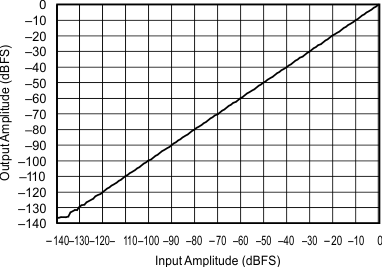
| 48 kHz:96 kHz | ||
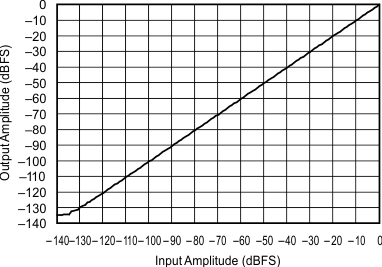
| 44.1 kHz:192 kHz | ||
| 192k:48k | ||