SLASF99 December 2023 TAS5827
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3 Feature Description
- 6.4
Device Functional Modes
- 6.4.1 Software Control
- 6.4.2 Speaker Amplifier Operating Modes
- 6.4.3 Low EMI Modes
- 6.4.4 Thermal Foldback
- 6.4.5 Device State Control
- 6.4.6 Device Modulation
- 6.4.7 Programming and Control
- 6.5 Register Maps
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHB|32
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RHB|32
Orderable Information
6.4.7.3.1 Random Write
As shown in Figure 6-12, a single-byte data-write transfer begins with the controller device transmitting a start condition followed by the I2C device address and the read/write bit. The read/write bit determines the direction of the data transfer. For a write data transfer, the read/write bit is a 0. After receiving the correct I2C device address and the read/write bit, the device responds with an acknowledge bit. Next, the controller transmits the address byte corresponding to the internal memory address being accessed. After receiving the address byte, the device again responds with an acknowledge bit. Next, the controller device transmits the data byte to be written to the memory address being accessed. After receiving the data byte, the device again responds with an acknowledge bit. Finally, the controller device transmits a stop condition to complete the single-byte data-write transfer.
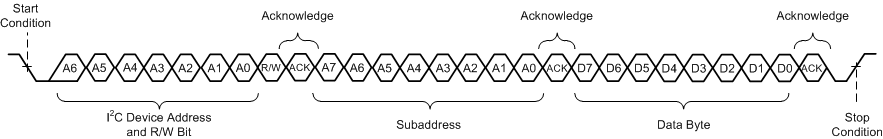 Figure 6-12 Random Write Transfer
Figure 6-12 Random Write Transfer