SCPS285A november 2022 – august 2023 TCAL9539-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RTW|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RTW|24
Orderable Information
8.5.1 I2C Interface
The bidirectional I2C bus consists of the serial clock (SCL) and serial data (SDA) lines. Both lines must be connected to a positive supply through a pull-up resistor when connected to the output stages of a device. Data transfer may be initiated only when the bus is not busy.
I2C communication with this device is initiated by a controller sending a Start condition, a high-to-low transition on the SDA input/output, while the SCL input is high (see Figure 8-4). After the Start condition, the device address byte is sent, most significant bit (MSB) first, including the data direction bit (R/ W).
After receiving the valid address byte, this device responds with an acknowledge (ACK), a low on the SDA input/output during the high of the ACK-related clock pulse. The address input of the target device must not be changed between the Start and the Stop conditions.
On the I2C bus, only one data bit is transferred during each clock pulse. The data on the SDA line must remain stable during the high pulse of the clock period, as changes in the data line at this time are interpreted as control commands (Start or Stop) (see Figure 8-5).
A Stop condition, a low-to-high transition on the SDA input/output while the SCL input is high, is sent by the controller (see Figure 8-4).
Any number of data bytes can be transferred from the transmitter to receiver between the Start and the Stop conditions. Each byte of eight bits is followed by one ACK bit. The transmitter must release the SDA line before the receiver can send an ACK bit. The device that acknowledges must pull down the SDA line during the ACK clock pulse, so that the SDA line is stable low during the high pulse of the ACK-related clock period (see Figure 8-6). When a target receiver is addressed, it must generate an ACK after each byte is received. Similarly, the controller must generate an ACK after each byte that it receives from the target transmitter. Setup and hold times must be met for proper operation.
A controller receiver signals an end of data to the target transmitter by not generating an acknowledge (NACK) after the last byte has been clocked out of the target. This is done by the controller receiver by holding the SDA line high. In this event, the transmitter must release the data line to enable the controller to generate a Stop condition.
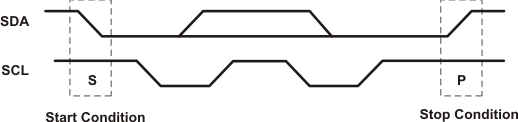 Figure 8-4 Definition of Start and Stop Conditions
Figure 8-4 Definition of Start and Stop Conditions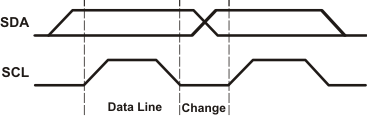 Figure 8-5 Bit Transfer
Figure 8-5 Bit Transfer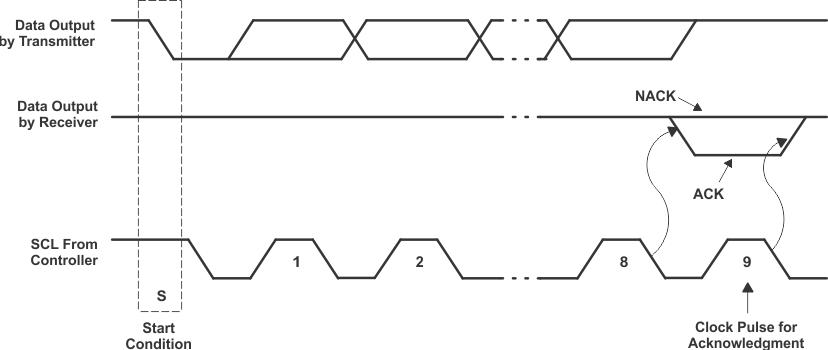 Figure 8-6 Acknowledgment on the I2C Bus
Figure 8-6 Acknowledgment on the I2C Bus| BYTE | BIT | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 (MSB) | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 (LSB) | |
| Device I2C address | H | H | H | L | H | A1 | A0 | R/ W |
| I/O data bus | P07 | P06 | P05 | P04 | P03 | P02 | P01 | P00 |
| P17 | P16 | P15 | P14 | P13 | P12 | P11 | P10 | |