SLLSFG3 May 2020 THVD1428
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.3.3 Surge Protection
Surge transients often result from lightning strikes (direct strike or an indirect strike which induce voltages and currents), or the switching of power systems, including load changes and short circuit switching. These transients are often encountered in industrial environments, such as factory automation and power-grid systems.
Figure 18 compares the pulse-power of the EFT and surge transients with the power caused by an IEC ESD transient. The left hand diagram shows the relative pulse-power for a 0.5-kV surge transient and 4-kV EFT transient, both of which dwarf the 10-kV ESD transient visible in the lower-left corner. 500-V surge transients are representative of events that may occur in factory environments in industrial and process automation.
The right hand diagram shows the pulse-power of a 6-kV surge transient, relative to the same 0.5-kV surge transient. 6-kV surge transients are most likely to occur in power generation and power-grid systems.
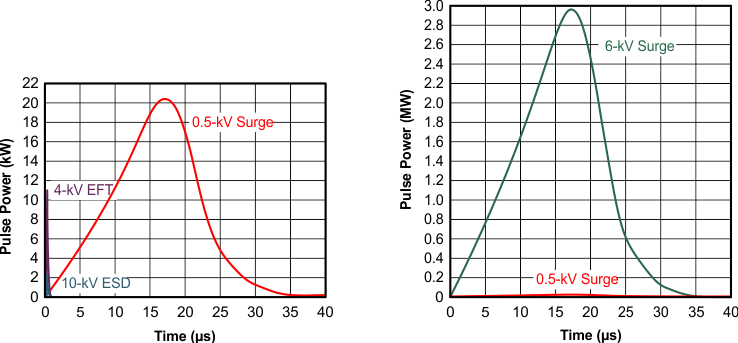 Figure 18. Power Comparison of ESD, EFT, and Surge Transients
Figure 18. Power Comparison of ESD, EFT, and Surge Transients Figure 19 shows the test setup used to validate THVD1428 surge performance according to the IEC 61000-4-5 1.2/50-μs surge pulse.
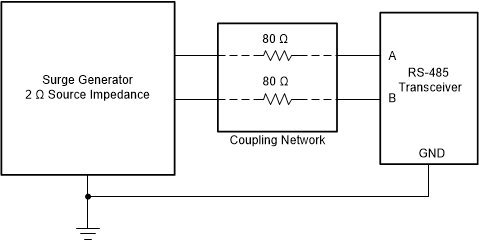 Figure 19. THVD1428 Surge Test Setup
Figure 19. THVD1428 Surge Test Setup THVD1428 is robust to ±3-kV surge transients without the need for any external components.