SLOS630C December 2010 – November 2014 TLV320AIC3256
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Simplified Block Diagram
- 5 Revision History
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
8 Specifications
- 8.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 8.2 Handling Ratings
- 8.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 8.4 Thermal Information
- 8.5 Electrical Characteristics, ADC
- 8.6 Electrical Characteristics, Bypass Outputs
- 8.7 Electrical Characteristics, Microphone Interface
- 8.8 Electrical Characteristics, Audio DAC Outputs
- 8.9 Electrical Characteristics, Misc.
- 8.10 Electrical Characteristics, Logic Levels
- 8.11 I2S/LJF/RJF Timing in Master Mode (see )
- 8.12 I2S/LJF/RJF Timing in Slave Mode (see )
- 8.13 DSP Timing in Master Mode (see )
- 8.14 DSP Timing in Slave Mode (see )
- 8.15 Digital Microphone PDM Timing (see )
- 8.16 I2C Interface Timing
- 8.17 SPI Interface Timing
- 8.18 Typical Characteristics
- 9 Parameter Measurement Information
- 10Detailed Description
- 11Application and Implementation
- 12Power Supply Recommendations
- 13Layout
- 14Device and Documentation Support
- 15Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RSB|40
Orderable Information
8 Specifications
8.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted) (1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVdd to AVss | –0.3 | 2.2 | V | |
| DVdd to DVss | –0.3 | 2.2 | V | |
| Vsys to DVss | –0.3 | 5.5 | V | |
| IOVdd to IOVss | –0.3 | 3.9 | V | |
| Digital Input voltage | IOVss | IOVdd + 0.3 | V | |
| Analog input voltage | AVss | AVdd + 0.3 | V | |
| Operating temperature range | –40 | 85 | °C | |
| Junction temperature (TJ Max) | 105 | °C | ||
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
8.2 Handling Ratings
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tstg | Storage temperature range | –55 | 125 | °C | |
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001, all pins(1) | –2 | 2 | kV |
| Charged device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101, all pins(2) | –750 | 750 | V | ||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
8.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVDD | Power Supply Voltage Range | Referenced to AVss(1) | 1.5 | 1.8 | 1.95 | V | |
| IOVDD | Referenced to IOVss(1) | 1.1 | 3.6 | ||||
| Vsys | Referenced to DVss(1) | 1.5 | 1.8 | 5.5 | |||
| DVdd(2) | Referenced to DVss(1) | 1.26 | 1.8 | 1.95 | |||
| DVDD_CP | Power Supply Voltage Range | Referenced to DVss(1) | 1.26 | 1.8 | 1.95 | V | |
| DRVDD_HP | Referenced to AVss(1) | Ground-centered config | 1.5 | 1.8 | 1.95 | ||
| Unipolar config | 1.5 | 3.6 | |||||
| PLL Input Frequency | Clock divider uses fractional divide (D > 0), P = 1, DVdd ≥ 1.65V (See table in SLAU306, Maximum TLV320AIC3256 Clock Frequencies) |
10 | 20 | MHz | |||
| Clock divider uses integer divide (D = 0), P = 1, DVdd ≥ 1.65V (See table in SLAU306, Maximum TLV320AIC3256 Clock Frequencies) |
0.512 | 20 | MHz | ||||
| MCLK | Master Clock Frequency | MCLK; Master Clock Frequency; DVdd ≥ 1.65V | 50 | MHz | |||
| MCLK; Master Clock Frequency; DVdd ≥ 1.26V | 25 | ||||||
| SCL | SCL Clock Frequency | 400 | kHz | ||||
| Audio input max ac signal swing (IN1_L, IN1_R, IN2_L, IN2_R, IN3_L, IN3_R) |
CM = 0.75 V | 0 | 0.530 | 0.75 or AVDD -0.75(3) | Vpeak | ||
| CM = 0.9 V | 0 | 0.707 | 0.9 or AVDD -0.9(3) | Vpeak | |||
| LOL, LOR | Stereo line output load resistance | 0.6 | 10 | kΩ | |||
| HPL, HPR | Stereo headphone output load resistance | Single-ended configuration | 14.4 | 16 | Ω | ||
| Headphone output load resistance | Differential configuration | 24.4 | 32 | Ω | |||
| CLout | Digital output load capacitance | 10 | pF | ||||
| TOPR | Operating Temperature Range | –40 | 85 | °C | |||
(1) All grounds on board are tied together; they must not differ in voltage by more than 0.2V max, for any combination of ground signals.
(2) At DVdd values lower than 1.65V, the PLL does not function. Please see table in SLAU306, Maximum TLV320AIC3256 Clock Frequencies for details on maximum clock frequencies.
(3) Whichever is smaller
8.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | TLV320AIC3256 | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSB (QFN) | YZF (DSGBA) | |||
| 48 PINS | 42 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 32.3 | 49.7 | °C/W |
| RθJCtop | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 22.5 | 0.1 | |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 6.1 | 7.7 | |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.3 | 0.1 | |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 6 | 7.7 | |
| RθJCbot | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 1.7 | – | |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
8.5 Electrical Characteristics, ADC
At 25°C, Vsys, AVdd, DVdd, IOVdd, DVdd_CP, DRVdd_HP = 1.8V, fS (Audio) = 48kHz, CREF = 1µF on REF PIN, PLL and Charge pump disabled unless otherwise noted.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUDIO ADC (CM = 0.9V) | ||||||
| Input signal level (for 0dB output) | Single-ended, CM = 0.9V | 0.5 | VRMS | |||
| Device Setup | 1kHz sine wave input Single-ended Configuration IN1_R to Right ADC and IN1_L to Left ADC, RIN = 20kΩ, fS = 48kHz, AOSR = 128, MCLK = 256 * fS, PLL Disabled; AGC = OFF, Channel Gain = 0dB, Processing Block = PRB_R1, Power Tune = PTM_R4 |
|||||
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio, A-weighted(1)(2) | Inputs ac-shorted to ground | 80 | 93 | dB | |
| IN2_R, IN3_R routed to Right ADC and ac-shorted to ground IN2_L, IN3_L routed to Left ADC and ac-shorted to ground |
93 | |||||
| DR | Dynamic range A-weighted(1)(2) | –60dB full-scale, 1kHz input signal | 93 | dB | ||
| THD+N | Total Harmonic Distortion plus Noise | –3dB full-scale, 1kHz input signal | –84 | –70 | dB | |
| IN2_R,IN3_R routed to Right ADC IN2_L, IN3_L routed to Left ADC –3dB full-scale, 1kHz input signal |
–84 | |||||
| AUDIO ADC (CM = 0.75V) | ||||||
| Input signal level (for 0dB output) | Single-ended, CM = 0.75V, AVdd = 1.5V | 0.375 | VRMS | |||
| Device Setup: | 1kHz sine wave input Single-ended Configuration INR, IN2_R, IN3_R routed to Right ADC INL, IN2_L, IN3_L routed to Left ADC RIN = 20kΩ, fS = 48kHz, AOSR = 128, MCLK = 256 * fS, PLL Disabled, AGC = OFF, Channel Gain = 0dB, Processing Block = PRB_R1 Power Tune = PTM_R4 |
|||||
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio, A-weighted (1)(2) | Inputs ac-shorted to ground | 90 | dB | ||
| DR | Dynamic range A-weighted(1)(2) | –60dB full-scale, 1kHz input signal | 90 | dB | ||
| THD+N | Total Harmonic Distortion plus Noise | –3dB full-scale, 1kHz input signal | –81 | dB | ||
| AUDIO ADC (Gain = 40dB) | ||||||
| Input signal level (for 0dB output) | Differential Input, CM = 0.9V, Channel Gain = 40dB | 10 | mVRMS | |||
| Device Setup | 1kHz sine wave input Differential configuration IN1_L and IN1_R routed to Right ADC IN2_L and IN2_R routed to Left ADC RIN = 10kΩ, fS = 48kHz, AOSR = 128 MCLK = 256 * fS PLL Disabled AGC = OFF Processing Block = PRB_R1, Power Tune = PTM_R4 |
|||||
| ICN | Idle-Channel Noise, A-weighted(1)(2) | Inputs ac-shorted to ground, input referred noise | 2.8 | μVRMS | ||
| AUDIO ADC | ||||||
| Gain Error | 1kHz sine wave input Single-ended configuration RIN = 20kΩ, fS = 48kHz, AOSR = 128, MCLK = 256 * fS, PLL Disabled AGC = OFF, Channel Gain = 0dB Processing Block = PRB_R1, Power Tune = PTM_R4, CM = 0.9V |
0.1 | dB | |||
| Input Channel Separation | 1kHz sine wave input at -3dBFS Single-ended configuration IN1_L routed to Left ADC IN1_R routed to Right ADC, RIN = 20kΩ AGC = OFF, AOSR = 128, Channel Gain = 0dB, CM = 0.9V |
109 | dB | |||
| Input Pin Crosstalk | 1kHz sine wave input at –3dBFS on IN2_L, IN2_L internally not routed. IN1_L routed to Left ADC ac-coupled to ground |
108 | dB | |||
| 1kHz sine wave input at –3dBFS on IN2_R, IN2_R internally not routed. IN1_R routed to Right ADC ac-coupled to ground |
||||||
| Single-ended configuration RIN = 20kΩ, AOSR = 128 Channel, Gain = 0dB, CM = 0.9V |
||||||
| PSRR | 217Hz, 100mVpp signal on AVdd, Single-ended configuration, RIN= 20kΩ, Channel Gain = 0dB; CM = 0.9V |
55 | dB | |||
| ADC programmable gain amplifier gain | Single-Ended, RIN = 10kΩ, PGA gain set to 0dB | 0 | dB | |||
| Single-Ended, RIN = 10kΩ, PGA gain set to 47.5dB | 47.5 | dB | ||||
| Single-Ended, RIN = 20kΩ, PGA gain set to 0dB | –6 | dB | ||||
| Single-Ended, RIN = 20kΩ, PGA gain set to 47.5dB | 41.5 | dB | ||||
| Single-Ended, RIN = 40kΩ, PGA gain set to 0dB | –12 | dB | ||||
| Single-Ended, RIN = 40kΩ, PGA gain set to 47.5dB | 35.5 | dB | ||||
| ADC programmable gain amplifier step size | 1kHz tone | 0.5 | dB | |||
(1) Ratio of output level with 1kHz full-scale sine wave input, to the output level with the inputs short circuited, measured A-weighted over a 20Hz to 20kHz bandwidth using an audio analyzer.
(2) All performance measurements done with 20kHz low-pass filter and, where noted, A-weighted filter. Failure to use such a filter may result in higher THD+N and lower SNR and dynamic range readings than shown in the Electrical Characteristics. The low-pass filter removes out-of-band noise, which, although not audible, may affect dynamic specification values
8.6 Electrical Characteristics, Bypass Outputs
At 25°C, Vsys, AVdd, DVdd, IOVdd, DVdd_CP, DRVdd_HP = 1.8V, fS (Audio) = 48kHz, CREF = 1µF on REF PIN, PLL and Charge pump disabled unless otherwise noted.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANALOG BYPASS TO HEADPHONE AMPLIFIER, DIRECT MODE | ||||||
| Device Setup | Load = 16Ω (single-ended), 50pF; Input and Output CM = 0.9V; Headphone Output on DRVdd_HP Supply; IN1_L routed to HPL and IN1_R routed to HPR; Channel Gain = 0dB |
|||||
| Gain Error | 0.8 | dB | ||||
| Noise, A-weighted(1) | Idle Channel, IN1_L and IN1_R ac-shorted to ground | 3.3 | μVRMS | |||
| THD | Total Harmonic Distortion | 446mVrms, 1kHz input signal | –81 | dB | ||
| ANALOG BYPASS TO LINE-OUT AMPLIFIER, PGA MODE | ||||||
| Device Setup | Load = 10kΩ (single-ended), 50pF; Input and Output CM = 0.9V; LINE Output on DRVDD_HP Supply; IN1_L, IN1_R routed to line out Channel Gain = 0dB |
|||||
| Gain Error Gain Error | 0.8 | dB | ||||
| Noise, A-weighted(1) | Idle Channel, IN1_L and IN1_R ac-shorted to ground |
6.7 | μVRMS | |||
| Channel Gain = 40dB, Input Signal (0dB) = 5mVRMS Inputs ac-shorted to ground, Input Referred |
3 | μVRMS | ||||
(1) All performance measurements done with 20kHz low-pass filter and, where noted, A-weighted filter. Failure to use such a filter may result in higher THD+N and lower SNR and dynamic range readings than shown in the Electrical Characteristics. The low-pass filter removes out-of-band noise, which, although not audible, may affect dynamic specification values
8.7 Electrical Characteristics, Microphone Interface
At 25°C, Vsys, AVdd, DVdd, IOVdd, DVdd_CP, DRVdd_HP = 1.8V, fS (Audio) = 48kHz, CREF = 1µF on REF PIN, PLL and Charge pump disabled unless otherwise noted.8.8 Electrical Characteristics, Audio DAC Outputs
At 25°C, Vsys, AVdd, DVdd, IOVdd, DVdd_CP, DRVdd_HP = 1.8V, fS (Audio) = 48kHz, CREF = 1µF on REF PIN, PLL and Charge pump disabled unless otherwise noted.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUDIO DAC – STEREO SINGLE-ENDED LINE OUTPUT (CM = 0.9V) | ||||||
| Device Setup | Load = 10kΩ (single-ended), 56pF Line Output on AVdd Supply Input and Output CM=0.9V DOSR = 128, MCLK = 256 x fS, Channel Gain = 0dB, word length = 16 bits, Processing Block = PRB_P1, Power Tune = PTM_P3 |
|||||
| Full scale output voltage (0dB) | 0.5 | VRMS | ||||
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio A-weighted(1)(2) | All zeros fed to DAC input | 87 | 100 | dB | |
| DR | Dynamic range, A-weighted (1)(2) | –60dB 1kHz input full-scale signal, Word length = 20 bits | 100 | dB | ||
| THD+N | Total Harmonic Distortion plus Noise | –3dB full-scale, 1kHz input signal | –81 | –70 | dB | |
| DAC Gain Error | 0dB, 1kHz input full scale signal | 0.5 | dB | |||
| DAC Mute Attenuation | Mute | 121 | dB | |||
| DAC channel separation | –1dB, 1kHz signal, between left and right HP out | 108 | dB | |||
| DAC PSRR | 100mVpp, 1kHz signal applied to AVdd | 72 | dB | |||
| 100mVpp, 217Hz signal applied to AVdd | 80 | dB | ||||
| AUDIO DAC – STEREO SINGLE-ENDED LINE OUTPUT (CM = 0.75V) | ||||||
| Device Setup | Load = 10kΩ (single-ended), 56pF Line Output on AVdd Supply Input and Output CM = 0.75V; AVdd = 1.5V DOSR = 128 MCLK=256 x fS Channel Gain = 0dB word length = 20-bits Processing Block = PRB_P1 Power Tune = PTM_P4 |
|||||
| Full scale output voltage (0dB) | 0.375 | VRMS | ||||
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio, A-weighted (1)(2) | All zeros fed to DAC input | 99 | dB | ||
| DR | Dynamic range, A-weighted (1)(2) | –60dB 1kHz input full-scale signal | 98 | dB | ||
| THD+N | Total Harmonic Distortion plus Noise | –1dB full-scale, 1kHz input signal | –77 | dB | ||
| AUDIO DAC – STEREO SINGLE-ENDED HEADPHONE OUTPUT (GROUND-CENTERED CIRCUIT CONFIGURATION) | ||||||
| Device Setup | Load = 16Ω (single-ended), 56pF Input CM = 0.9V, Output CM = 0V DOSR = 128, MCLK = 256x* fS, Channel Gain = 0dB word length = 16 bits; Processing Block = PRB_P1 Power Tune = PTM_P3 |
|||||
| FS1 | Full scale output voltage (for THD ≤ –40dB) |
0.65 | VRMS | |||
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio, A-weighted(1)(2) | All zeros fed to DAC input | 85 | 95 | dB | |
| DR | Dynamic range, A-weighted (1)(2) | –60dB 1kHz input full-scale signal, Word Length = 20 bits, Power Tune = PTM_P4 | 93 | dB | ||
| THD+N | Total Harmonic Distortion plus Noise | 500mVRMS output (corresponds to FS1 – 2.3dB), 1-kHz input signal |
–70 | –55 | dB | |
| DAC Gain Error | 500mVRMS output, 1kHz input full scale signal | 0.5 | dB | |||
| DAC Mute Attenuation | Mute | 118 | dB | |||
| DAC channel separation | –3dB, 1kHz signal, between left and right HP out | 102 | dB | |||
| DAC PSRR | 100mVpp, 1kHz signal applied to AVdd | 66 | dB | |||
| 100mVpp, 217Hz signal applied to AVdd | 77 | dB | ||||
| Power Delivered | THD ≤ –40dB | 26.5 | mW | |||
| FS2 | Full scale output voltage (for THD ≤ –40dB) |
Load = 32Ω | 0.85 | V | ||
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio, A-weighted(1)(2) | All zeros fed to DAC input, Load = 32Ω | 96 | dB | ||
| Power Delivered | THD ≤ –40dB, Load = 32Ω | 22.5 | mW | |||
| AUDIO DAC – STEREO SINGLE-ENDED HEADPHONE OUTPUT (UNIPOLAR CIRCUIT CONFIGURATION) | ||||||
| Device Setup | Load = 16Ω (single-ended), 56pF, Headphone Output on AVdd Supply, Input and Output CM = 0.9V DOSR = 128, MCLK = 256 x fS, Channel Gain = 0dB Processing Block = PRB_P1, Power Tune = PTM_P3 |
|||||
| Full scale output voltage (0dB) | 0.5 | VRMS | ||||
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio, A-weighted(1)(2) | All zeros fed to DAC input | 87 | 100 | dB | |
| DR | Dynamic range, A-weighted (1)(2) | -60dB 1kHz input full-scale signal | 100 | dB | ||
| THD+N | Total Harmonic Distortion plus Noise | –3dB full-scale, 1kHz input signal | –83 | –70 | dB | |
(1) Ratio of output level with 1kHz full-scale sine wave input, to the output level with the inputs short circuited, measured A-weighted over a 20Hz to 20kHz bandwidth using an audio analyzer.
(2) All performance measured with 20kHz low-pass filter and, where noted, A-weighted filter. Failure to use such a filter may result in higher THD+N and lower SNR and dynamic range readings than shown in the Electrical Characteristics. The low-pass filter removes out-of-band noise, which, although not audible, may affect dynamic specification values.
8.9 Electrical Characteristics, Misc.
At 25°C, Vsys, AVdd, DVdd, IOVdd, DVdd_CP, DRVdd_HP = 1.8V, fS (Audio) = 48kHz, CREF = 1µF on REF PIN, PLL and Charge pump disabled unless otherwise noted.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REFERENCE | ||||||
| Reference Voltage Settings | CMMode = 0 (0.9V) | 0.9 | V | |||
| CMMode = 1 (0.75V) | 0.75 | |||||
| Reference Noise | CM = 0.9V, A-weighted, 20Hz to 20kHz bandwidth, CREF = 1μF | 1.1 | μVRMS | |||
| Decoupling Capacitor | 1 | μF | ||||
| Bias Current | 120 | μA | ||||
| miniDSP(1) | ||||||
| Maximum miniDSP clock frequency - ADC | DVdd = 1.65V | 58.9 | MHz | |||
| Maximum miniDSP clock frequency - DAC | DVdd = 1.65V | 58.9 | MHz | |||
| SHUTDOWN CURRENT | ||||||
| Device Setup | DVdd is provided externally, no clocks supplied, no digital activity, register values are retained | |||||
| I(total) | Sum of all supply currents, all supplies at 1.8V | <10 | μA | |||
(1) The miniDSP clock speed is specified by design and not tested in production.
8.10 Electrical Characteristics, Logic Levels(1)
At 25°C, AVDD, DVDD, IOVDD = 1.8 V| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOGIC FAMILY CMOS | ||||||
| VIH | Logic Level | IIH = 5 μA, IOVDD > 1.6V | 0.7 × IOVDD | V | ||
| IIH = 5μA, 1.2V ≤ IOVDD < 1.6V | 0.9 × IOVDD | V | ||||
| IIH = 5μA, IOVDD < 1.2V | IOVDD | V | ||||
| VIL | IIL = 5 μA, IOVDD > 1.6V | –0.3 | 0.3 × IOVDD | V | ||
| IIL = 5μA, 1.2V ≤ IOVDD < 1.6V | 0.1 × IOVDD | V | ||||
| IIL = 5μA, IOVDD < 1.2V | 0 | V | ||||
| VOH | IOH = 2 TTL loads | 0.8 × IOVDD | V | |||
| VOL | IOL = 2 TTL loads | 0.1 × IOVDD | V | |||
| Capacitive Load | 10 | pF | ||||
(1) Applies to all DI, DO, and DIO pins shown in Pin Configuration and Functions
8.11 I2S/LJF/RJF Timing in Master Mode (see Figure 1)
All specifications at 25°C, DVdd = 1.8 V Figure 1. I2S/LJF/RJF Timing in Master Mode
Figure 1. I2S/LJF/RJF Timing in Master Mode
8.12 I2S/LJF/RJF Timing in Slave Mode (see Figure 2)
| IOVDD=1.8V | IOVDD=3.3V | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | MAX | MIN | MAX | |||
| tH(BCLK) | BCLK high period | 35 | 35 | ns | ||
| tL(BCLK) | BCLK low period | 35 | 35 | |||
| ts(WS) | WCLK setup | 8 | 8 | |||
| th(WS) | WCLK hold | 8 | 8 | |||
| td(DO-WS) | WCLK to DOUT delay (For LJF mode only) | 20 | 20 | |||
| td(DO-BCLK) | BCLK to DOUT delay | 22 | 22 | |||
| ts(DI) | DIN setup | 8 | 8 | |||
| th(DI) | DIN hold | 8 | 8 | |||
| tr | Rise time | 4 | 4 | |||
| tf | Fall time | 4 | 4 | |||
 Figure 2. I2S/LJF/RJF Timing in Slave Mode
Figure 2. I2S/LJF/RJF Timing in Slave Mode
8.13 DSP Timing in Master Mode (see Figure 3)
All specifications at 25°C, DVdd = 1.8 V| IOVDD=1.8V | IOVDD=3.3V | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | MAX | MIN | MAX | |||
| td(WS) | WCLK delay | 30 | 20 | ns | ||
| td(DO-BCLK) | BCLK to DOUT delay | 22 | 20 | ns | ||
| ts(DI) | DIN setup | 8 | 8 | ns | ||
| th(DI) | DIN hold | 8 | 8 | ns | ||
| tr | Rise time | 24 | 12 | ns | ||
| tf | Fall time | 24 | 12 | ns | ||
 Figure 3. DSP Timing in Master Mode
Figure 3. DSP Timing in Master Mode
8.14 DSP Timing in Slave Mode (see Figure 4)
| IOVDD=1.8V | IOVDD=3.3V | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | MAX | MIN | MAX | |||
| tH(BCLK) | BCLK high period | 35 | 35 | ns | ||
| tL(BCLK) | BCLK low period | 35 | 35 | ns | ||
| ts(WS) | WCLK setup | 8 | 8 | ns | ||
| th(WS) | WCLK hold | 8 | 8 | ns | ||
| td(DO-BCLK) | BCLK to DOUT delay | 22 | 22 | ns | ||
| ts(DI) | DIN setup | 8 | 8 | ns | ||
| th(DI) | DIN hold | 8 | 8 | ns | ||
| tr | Rise time | 4 | 4 | ns | ||
| tf | Fall time | 4 | 4 | ns | ||
 Figure 4. DSP Timing in Slave Mode
Figure 4. DSP Timing in Slave Mode
8.15 Digital Microphone PDM Timing (see Figure 5)
Based on design simulation. Not tested in actual silicon.| IOVDD = 1.8V | IOVDD = 3.3V | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | MAX | MIN | MAX | |||
| ts | DIN setup | 20 | 20 | ns | ||
| th | DIN hold | 5 | 5 | ns | ||
| tr | Rise time | 4 | 4 | ns | ||
| tf | Fall time | 4 | 4 | ns | ||
 Figure 5. PDM Input Timing
Figure 5. PDM Input Timing
8.16 I2C Interface Timing
| Standard-Mode | Fast-Mode | UNIT | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | TYP | MAX | MIN | TYP | MAX | |||
| fSCL | SCL clock frequency | 0 | 100 | 0 | 400 | kHz | ||
| tH(STA) | Hold time (repeated) START condition. After this period, the first clock pulse is generated. | 4.0 | 0.8 | μs | ||||
| tLOW | LOW period of the SCL clock | 4.7 | 1.3 | μs | ||||
| tHIGH | HIGH period of the SCL clock | 4.0 | 0.6 | μs | ||||
| tSU(STA) | Setup time for a repeated START condition | 4.7 | 0.8 | μs | ||||
| tH(DAT) | Data hold time: For I2C bus devices | 0 | 3.45 | 0 | 0.9 | μs | ||
| tSU(DAT) | Data set-up time | 250 | 100 | ns | ||||
| tr | SDA and SCL Rise Time | 1000 | 20+0.1Cb | 300 | ns | |||
| tf | SDA and SCL Fall Time | 300 | 20+0.1Cb | 300 | ns | |||
| tSU(STO) | Set-up time for STOP condition | 4.0 | 0.8 | μs | ||||
| tBUF | Bus free time between a STOP and START condition | 4.7 | 1.3 | μs | ||||
| Cb | Capacitive load for each bus line | 400 | 400 | pF | ||||
 Figure 6. I2C Interface Timing
Figure 6. I2C Interface Timing
8.17 SPI Interface Timing
| IOVDD=1.8V | IOVDD=3.3V | UNIT | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | TYP | MAX | MIN | TYP | MAX | |||
| tsck | SCLK Period | 100 | 50 | ns | ||||
| tsckh | SCLK Pulse width High | 50 | 25 | ns | ||||
| tsckl | SCLK Pulse width Low | 50 | 25 | ns | ||||
| tlead | Enable Lead Time | 30 | 20 | ns | ||||
| tlag | Enable Lag Time | 30 | 20 | ns | ||||
| td | Sequential Transfer Delay | 40 | 20 | ns | ||||
| ta | Slave DOUT access time | 40 | 20 | ns | ||||
| tdis | Slave DOUT disable time | 40 | 20 | ns | ||||
| tsu | DIN data setup time | 15 | 10 | ns | ||||
| th(DIN) | DIN data hold time | 15 | 10 | ns | ||||
| tv(DOUT) | DOUT data valid time | 25 | 18 | ns | ||||
| tr | SCLK Rise Time | 4 | 4 | ns | ||||
| tf | SCLK Fall Time | 4 | 4 | ns | ||||

At 25°C, DVDD = 1.8 V
Figure 7. SPI Interface Timing Diagram
8.18 Typical Characteristics
8.18.1 Typical Performance
 Figure 8. ADC SNR vs Channel Gain
Figure 8. ADC SNR vs Channel Gain
 Figure 10. Total Harmonic Distortion Unipolar Configuration vs Headphone Output Power
Figure 10. Total Harmonic Distortion Unipolar Configuration vs Headphone Output Power
 Figure 12. Headphone SNR and Output Power vs Output Common Mode Setting
Figure 12. Headphone SNR and Output Power vs Output Common Mode Setting
 Figure 9. Total Harmonic Distortion GCHP Configuration vs Headphone Output Power
Figure 9. Total Harmonic Distortion GCHP Configuration vs Headphone Output Power
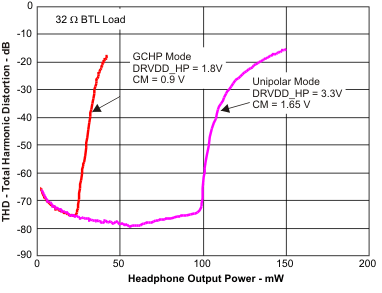 Figure 11. Total Harmonic Distortion vs Headphone Output Power
Figure 11. Total Harmonic Distortion vs Headphone Output Power
8.18.2 FFT
 Figure 13. Single Ended Line Input to ADC FFT at -1dBr vs Frequency
Figure 13. Single Ended Line Input to ADC FFT at -1dBr vs Frequency
 Figure 15. DAC Playback to Headphone FFT at -1dBFS (Ground-Centered Mode) vs Frequency
Figure 15. DAC Playback to Headphone FFT at -1dBFS (Ground-Centered Mode) vs Frequency
 Figure 17. Line Input to Headphone FFT at 446 mVrms (Unipolar Mode) vs Frequency
Figure 17. Line Input to Headphone FFT at 446 mVrms (Unipolar Mode) vs Frequency
 Figure 14. DAC Playback to Headphone FFT at -1dBFS (Unipolar Mode) vs Frequency
Figure 14. DAC Playback to Headphone FFT at -1dBFS (Unipolar Mode) vs Frequency
 Figure 16. DAC Playback to Line-Out FFT at -1dBFS to Frequency
Figure 16. DAC Playback to Line-Out FFT at -1dBFS to Frequency
 Figure 18. Line Input to Line-Out FFT at 446 mVrms (PGA Mode) vs Frequency
Figure 18. Line Input to Line-Out FFT at 446 mVrms (PGA Mode) vs Frequency