SNOSDF0 May 2024 TLV4H290-SEP , TLV4H390-SEP
ADVANCE INFORMATION
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
-
7 Application and Implementation
- 7.1 Application Information
- 7.2 Typical Applications
- 7.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 7.4 Layout
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DYY|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6.4.2 Power-On Reset (POR)
The TLV4H290-SEP and TLV4H390-SEP has an internal Power-on-Reset (POR) circuit for known start-up or power-down conditions. While the power supply (Vs) is ramping up or ramping down, the POR circuitry will be activated for up to 30µs after the minimum supply voltage threshold of 1.5V is crossed, or immediately when the supply voltage drops below 1.5V. When the supply voltage is equal to or greater than the minimum supply voltage, and after the delay period, the comparator output reflects the state of the differential input (VID).
The POR circuit will keep the output high impedance (HI-Z) during the POR period (ton).
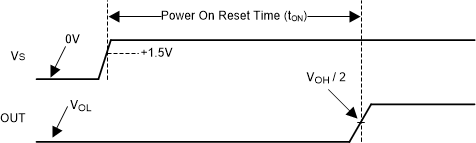 Figure 6-1 Power-On Reset Timing Diagram
Figure 6-1 Power-On Reset Timing DiagramNote that it the nature of an open collector output that the output will rise with the pull-up voltage during the POR period.
For the TLV4H390-SEP push-pull output devices, the output is "floating" during the POR period. A light pull-up (to V+) or pull-down (to V-) resistor can be used to pre-bias the output condition to prevent the output from floating. If output high is the desired start-up condition, then use the open collector TLV4H290-SEP, since a pull-up resistor is already required.