SNOSDF0A May 2024 – December 2024 TLV4H290-SEP , TLV4H390-SEP
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2 Typical Applications
- 8.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 8.4 Layout
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DYY|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6 Typical Characteristics
TA = 25°C, VS = 5V, RPULLUP = 2.5k, CL = 15pF, VCM = 0V, VUNDERDRIVE = 100mV, VOVERDRIVE = 100mV unless otherwise noted.
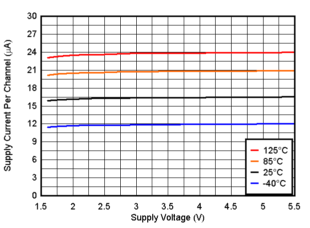 Figure 6-1 Supply Current vs. Supply Voltage
Figure 6-1 Supply Current vs. Supply Voltage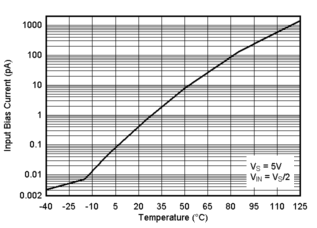 Figure 6-3 Input Bias Current vs. Temperature
Figure 6-3 Input Bias Current vs. Temperature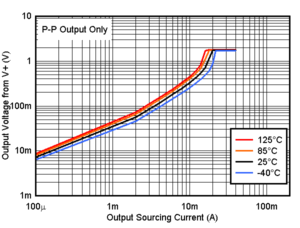 Figure 6-5 Output Sourcing Current vs. Output Voltage, 1.8V
Figure 6-5 Output Sourcing Current vs. Output Voltage, 1.8V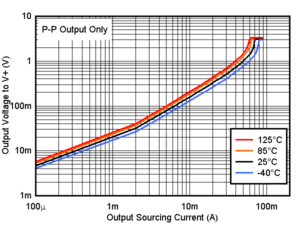 Figure 6-7 Output Sourcing Current vs. Output Voltage, 3.3V
Figure 6-7 Output Sourcing Current vs. Output Voltage, 3.3V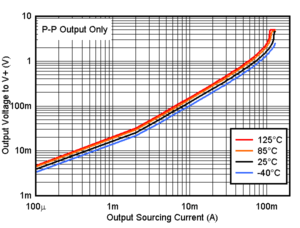 Figure 6-9 Output Sourcing Current vs. Output Voltage, 5V
Figure 6-9 Output Sourcing Current vs. Output Voltage, 5V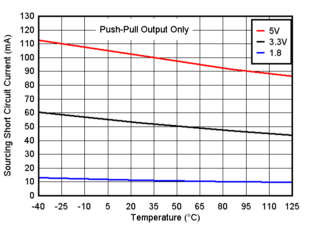 Figure 6-11 Sourcing Short Circuit Current vs. Temperature
Figure 6-11 Sourcing Short Circuit Current vs. Temperature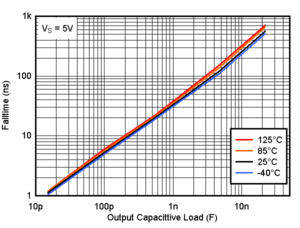 Figure 6-13 Falltime vs. Capacitive Load
Figure 6-13 Falltime vs. Capacitive Load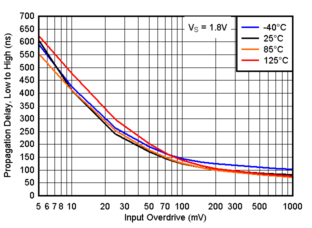 Figure 6-15 Propagation Delay, Low to High, 1.8V
Figure 6-15 Propagation Delay, Low to High, 1.8V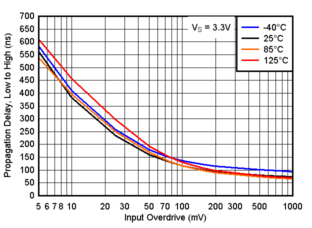 Figure 6-17 Propagation Delay, Low to High, 3.3V
Figure 6-17 Propagation Delay, Low to High, 3.3V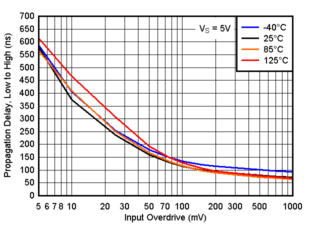 Figure 6-19 Propagation Delay, Low to High, 5V
Figure 6-19 Propagation Delay, Low to High, 5V Figure 6-21 Offset Voltage vs. Common-Mode at 25°C, 5V
Figure 6-21 Offset Voltage vs. Common-Mode at 25°C, 5V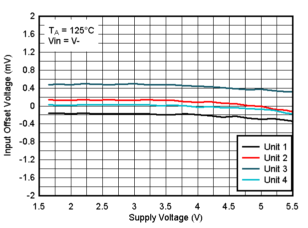 Figure 6-23 Offset Voltage vs. Supply Voltage at 125°C, VIN=V-
Figure 6-23 Offset Voltage vs. Supply Voltage at 125°C, VIN=V-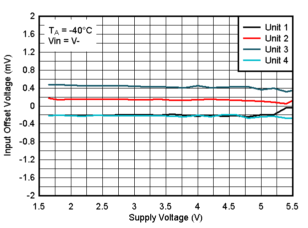 Figure 6-25 Offset Voltage vs. Supply Voltage at -40°C, VIN=V-
Figure 6-25 Offset Voltage vs. Supply Voltage at -40°C, VIN=V-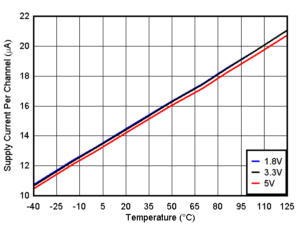 Figure 6-2 Supply Current vs. Temperature
Figure 6-2 Supply Current vs. Temperature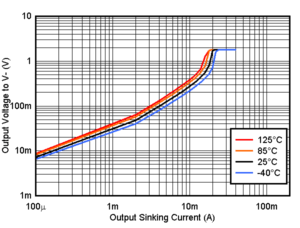 Figure 6-4 Output Sinking Current vs. Output Voltage, 1.8V
Figure 6-4 Output Sinking Current vs. Output Voltage, 1.8V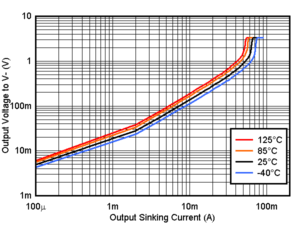 Figure 6-6 Output Sinking Current vs. Output Voltage, 3.3V
Figure 6-6 Output Sinking Current vs. Output Voltage, 3.3V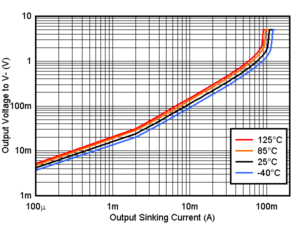 Figure 6-8 Output Sinking Current vs. Output Voltage, 5V
Figure 6-8 Output Sinking Current vs. Output Voltage, 5V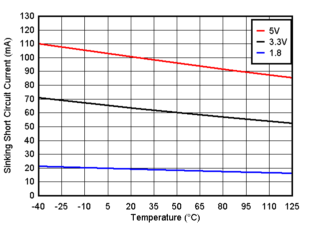 Figure 6-10 Sinking Short Circuit Current vs. Temperature
Figure 6-10 Sinking Short Circuit Current vs. Temperature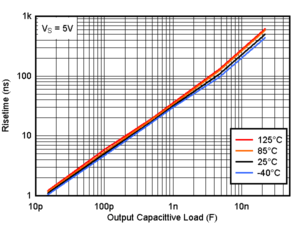 Figure 6-12 Risetime vs. Capacitive Load
Figure 6-12 Risetime vs. Capacitive Load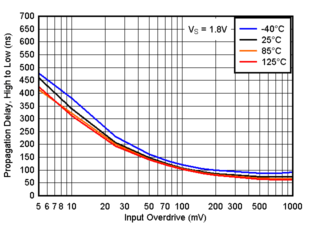 Figure 6-14 Propagation Delay, High to Low, 1.8V
Figure 6-14 Propagation Delay, High to Low, 1.8V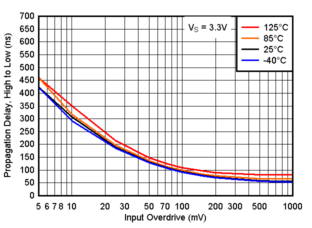 Figure 6-16 Propagation Delay, High to Low, 3.3V
Figure 6-16 Propagation Delay, High to Low, 3.3V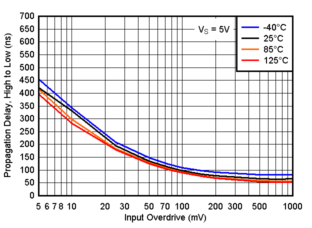 Figure 6-18 Propagation Delay, High to Low, 5V
Figure 6-18 Propagation Delay, High to Low, 5V Figure 6-20 Offset Voltage vs. Common-Mode at 125°C, 5V
Figure 6-20 Offset Voltage vs. Common-Mode at 125°C, 5V Figure 6-22 Offset Voltage vs. Common-Mode at -40°C, 5V
Figure 6-22 Offset Voltage vs. Common-Mode at -40°C, 5V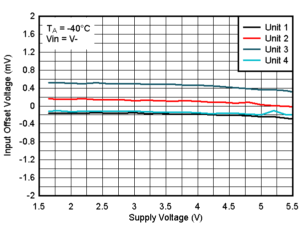 Figure 6-24 Offset Voltage vs. Supply Voltage at 25°C, VIN=V-
Figure 6-24 Offset Voltage vs. Supply Voltage at 25°C, VIN=V-