SBOSAK0A June 2024 – August 2024 TLV9044-Q1
PRODMIX
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PW|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.2.1.2 Detailed Design Procedure
The transfer function of the circuit in Figure 7-1 is given in Equation 1.
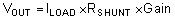
The load current (ILOAD) produces a voltage drop across the shunt resistor (RSHUNT). The load current is set from 0A to 1A. To keep the shunt voltage below 100mV at maximum load current, the largest shunt resistor is shown using Equation 2.
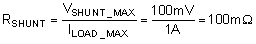
Using Equation 2, RSHUNT is calculated to be 100mΩ. The voltage drop produced by ILOAD and RSHUNT is amplified by the TLV904x-Q1 to produce an output voltage of approximately 0V to 4.9V. Use Equation 3 to calculate the gain the TLV904x-Q1 requires to product the necessary output voltage.
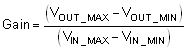
Using Equation 3, the required gain in this example is 49V/V, which is set with resistors RF and RG. Equation 4 sizes the resistors RF and RG to set the gain of the TLV904x-Q1 to 49V/V.
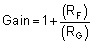
Selecting RF as 57.6kΩ and RG as 1.2kΩ provides a combination that equals 49V/V. Figure 7-2 shows the measured transfer function of the circuit shown in Figure 7-1. Notice that the gain is only a function of the feedback and gain resistors. This gain is adjusted by varying the ratio of the resistors and the actual resistors values are determined by the impedance levels that the designer wants to establish. The impedance level determines the current drain, the effect that stray capacitance has, and a few other behaviors. There is no single impedance selection that works for every system; you must choose an impedance that is designed for your system parameters.