SNIS236 January 2024 TMP119
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5
Programming
- 7.5.1 EEPROM Programming
- 7.5.2 Pointer Register
- 7.5.3 I2C and SMBus Interface
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- YBG|6
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.4.1 Continuous Conversion Mode
When the MOD[1:0] bits are set to 00 or 10 in the configuration register, the device operates in continuous conversion mode. The device continuously performs temperature conversions in this mode, as shown in Figure 7-4, and updates the temperature result register at the end of every active conversion. The user can read the configuration register or the temperature result register to clear the Data_Ready flag. Therefore, the Data_Ready flag can be used to determine when the conversion completes so that an external controller can synchronize reading the result register with conversion result updates. The user can set the DR/nAlert_EN bit in the configuration register to monitor the state of the Data_Ready flag on the ALERT pin.
Every conversion cycle consists of an active conversion period followed by a standby period. The device typically consumes 135µA during active conversion and only 1.25µA during the low-power standby period. Figure 7-4 shows a current consumption profile of a conversion cycle while in continuous current mode. The duration of the active conversion period and standby period can be configured using the CONV[2:0] and AVG[1:0] bits in the configuration register, thereby allowing the average current consumption of the device to be optimized based on the application requirements. Changing the conversion cycle period also affects the temperature result update rate because the temperature result register is updated at the end of every active conversion.
Use Equation 1 to calculate the average current consumption of the device in continuous conversion mode.
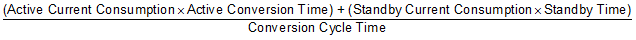
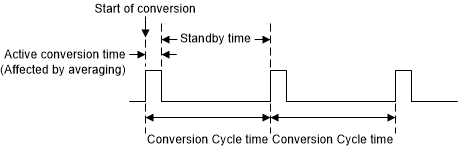 Figure 7-4 Conversion Cycle Timing Diagram
Figure 7-4 Conversion Cycle Timing Diagram