SNIS217C december 2020 – may 2023 TMP139
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 Register Map
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- YAH|6
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.1 Power-Up Sequence
The TMP139 has two supply pins: VDDSPD which is the core supply, and VDDIO which is the IO supply. To ensure that the device starts up correctly, the application must power up VDDSPD first followed by VDDIO. Additionally, the power-on reset (POR) circuit is implemented to prevent improper operation in case of an incorrect power-up sequence.
As shown in Figure 7-2, the VDDSPD supply is applied first and must rise monotonically between VPON(min) and VDDSPD(min) without ring back. The VDDIO supply must ramp up next and must reach the correct level before any operation can be performed.
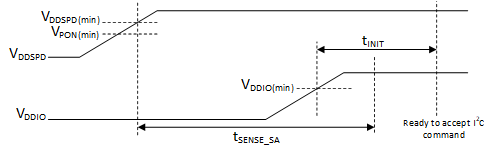 Figure 7-2 Power-Up Sequence
Figure 7-2 Power-Up SequenceWhen the VDDSPD and VDDIO supply have ramped up above the minimum threshold values, the TMP139 performs the following steps:
- Within the time tSENSE_SA, the device samples the SA pin to configure the LID code which forms part of the device address.
- Within time tINIT, enables the interface to accept the command from the host.
The device always powers up in the I2C mode of operation.