SBOSA26A December 2020 – February 2021 TMP9A00-EP
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Introduction to Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DCK|5
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.1.1 Example 1
Determine the linear transfer function for –40 °C to 110 °C.
TMIN = –40 °C; TMAX = 110 °C; therefore, T = 35 °C
m = –11.77 mV/°C
VOUT (110 °C) = 0.5520 V
VOUT (35 °C) = 1.4566 V
b = 1.8576 V
The linear transfer function for –40 °C to 110 °C is shown in Equation 6:
Equation 6. 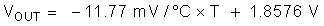
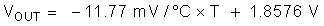
Table 7-1 lists common temperature ranges of interest and the corresponding linear transfer functions for these ranges. Note that the error (maximum deviation) of the linear equation from the parabolic equation increases as the temperature ranges widen.
Table 7-1 Common Temperature Ranges and
Corresponding Linear Transfer Functions
| TEMPERATURE RANGE | LINEAR EQUATION (V) | MAXIMUM DEVIATION OF LINEAR EQUATION FROM PARABOLIC EQUATION (°C) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TMIN (°C) | TMAX (°C) | ||
| –55 | 130 | VOUT = –11.79 mV/°C × T + 1.8528 | ±1.41 |
| –40 | 110 | VOUT = –11.77 mV/°C × T + 1.8577 | ±0.93 |
| –30 | 100 | VOUT = –11.77 mV/°C × T + 1.8605 | ±0.70 |
| –40 | 85 | VOUT = –11.67 mV/°C × T + 1.8583 | ±0.65 |
| –10 | 65 | VOUT = –11.71 mV/°C × T + 1.8641 | ±0.23 |
| 35 | 45 | VOUT = –11.81 mV/°C × T + 1.8701 | ±0.004 |
| 20 | 30 | VOUT = –11.69 mV/°C × T + 1.8663 | ±0.004 |