SPRS867A February 2013 – August 2016 TMS320DM369
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1TMS320DM369 Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
- 2Revision History
-
3Device Overview
- 3.1 Device Comparison
- 3.2 Device Characteristics
- 3.3 Device Compatibility
- 3.4
ARM Subsystem Overview
- 3.4.1 Components of the ARM Subsystem
- 3.4.2 ARM926EJ-S RISC CPU
- 3.4.3 CP15
- 3.4.4 MMU
- 3.4.5 Caches and Write Buffer
- 3.4.6 Tightly Coupled Memory (TCM)
- 3.4.7 Advanced High-performance Bus (AHB)
- 3.4.8 Embedded Trace Macrocell (ETM) and Embedded Trace Buffer (ETB)
- 3.4.9 ARM Memory Mapping
- 3.4.10 Peripherals
- 3.4.11 ARM Interrupt Controller (AINTC)
- 3.5 System Control Module
- 3.6 Power Management
- 3.7 Memory Map Summary
- 3.8 Pin Assignments
- 3.9 Terminal Functions
- 4Device Configurations
- 5System Interconnect
- 6Device Operating Conditions
-
7Peripheral Information and Electrical Specifications
- 7.1 Parameter Information Device-Specific Information
- 7.2 Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition Behavior
- 7.3 Power Supplies
- 7.4 Power-Supply Sequencing
- 7.5 Reset
- 7.6 Oscillators and Clocks
- 7.7 Power Management and Real Time Clock Subsystem (PRTCSS)
- 7.8 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 7.9 EDMA Controller
- 7.10
External Memory Interface (EMIF)
- 7.10.1 Asynchronous EMIF (AEMIF)
- 7.10.2 DDR2/mDDR Memory Controller
- 7.10.3
DDR2/mDDR Memory Controller Electrical Data/Timing
- 7.10.3.1
DDR2/mDDR Routing Specifications
- 7.10.3.1.1 DDR2/mDDR Interface
- 7.10.3.1.2 DDR2/mDDR Interface Schematic
- 7.10.3.1.3 Compatible JEDEC DDR2/mDDR Devices
- 7.10.3.1.4 PCB Stack Up
- 7.10.3.1.5 Placement
- 7.10.3.1.6 DDR2/mDDR Keep Out Region
- 7.10.3.1.7 Bulk Bypass Capacitors
- 7.10.3.1.8 High-Speed Bypass Capacitors
- 7.10.3.1.9 Net Classes
- 7.10.3.1.10 DDR2/mDDR Signal Termination
- 7.10.3.1.11 VREF Routing
- 7.10.3.1.12 DDR2/mDDR CK and ADDR_CTRL Routing
- 7.10.3.1
DDR2/mDDR Routing Specifications
- 7.11 MMC/SD
- 7.12 Video Processing Subsystem (VPSS) Overview
- 7.13 USB2.0
- 7.14 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
- 7.15 Serial Port Interface (SPI)
- 7.16 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
- 7.17 Multichannel Buffered Serial Port (McBSP)
- 7.18 Timer
- 7.19 Pulse Width Modulator (PWM)
- 7.20 Real Time Out (RTO)
- 7.21 Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC)
- 7.22 Management Data Input/Output (MDIO)
- 7.23 Host-Port Interface (HPI) Peripheral
- 7.24 Key Scan
- 7.25 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
- 7.26 Voice Codec
- 7.27 IEEE 1149.1 JTAG
- 8Device and Documentation Support
- 9Mechanical Packaging and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- ZCE|338
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
3 Device Overview
3.1 Device Comparison
Table 3-1 shows a comparison between devices, highlighting the differences.
Table 3-1 Device Comparison
| Features | Devices | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TMS320DM365 | TMS320DM368 | TMS320DM369 | DMVA1 | DMVA2 | |
| ARM MHz | 216 MHz (1.2 V) or 270 MHz (1.2 V) 300 MHz (1.35 V) |
432 MHz (1.35 V) | 432 MHz (1.35 V) | 300 MHz (1.35 V) | 432 MHz |
| DDR2 / mDDR | 540 MHz / 336 MHz | 680 MHz / 336 MHz | 680 MHz / 336 MHz | 540 MHz / 336 MHz | 680 MHz / 336 MHz |
| Noise Filtering Engine | NONE | NONE | YES | NONE | NONE |
| Vision Coprocessor | NONE | NONE | NONE | YES | YES |
3.2 Device Characteristics
Table 3-2 provides an overview of the DMSoC. The table shows significant features of the device, including the peripherals, capacity of on-chip RAM, ARM operating frequency, the package type with pin count, and so forth.
Table 3-2 Characteristics of the Processor
| HARDWARE FEATURES | DEVICE | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Peripherals Not all peripherals pins are available at the same time (For more detail, see Section 4). |
DDR2 / mDDR Memory Controller | DDR2 / mDDR (16-bit bus width) | |
| Asynchronous EMIF (AEMIF) | Asynchronous (8/16-bit bus width) RAM, Flash (NOR, NAND, OneNAND) | ||
| Flash Card Interfaces | Two MMC/SD One SmartMedia/xD |
||
| EDMA | 64 independent DMA channels Eight QDMA channels |
||
| Timers | Four 64-Bit General Purpose (each configurable as two separate 32-bit timers) One 64-Bit Watch Dog |
||
| UART | Two (one with RTS and CTS flow control) | ||
| SPI | Five (each supports two slave devices) | ||
| I2C | One (Master/Slave) | ||
| 10/100 Ethernet MAC with Management Data I/O | One | ||
| multichannel Buffered Serial Port [McBSP] | One McBSP | ||
| Power Management and Real Time Clock Subsystem (PRTCSS) | RTC (32.768kHz), GPIO | ||
| Key Scan | 4 x 4 Matrix, 5 x 3 Matrix | ||
| Voice Codec | One | ||
| Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) | 6-channel, 10-bit Interface | ||
| General-Purpose Input/Output Port | Up to 104 | ||
| Pulse width modulator (PWM) | Four outputs | ||
| Configurable Video Ports | One Input (VPFE) One Output (VPBE) |
||
| USB 2.0 | High Speed Device High Speed Host On The Go (HS-USB-OTG) |
||
| Wireless Interfaces | Through SDIO | ||
| RTO | Four Channels | ||
| On-Chip CPU Memory | Organization | ARM 16-KB I-cache, 8-KB D-cache, 32-KB RAM, 16-KB ROM |
|
| JTAG BSDL_ID | JTAGID register (address location: 0x01C4 0028) | See Section 7.27.1, JTAG Register Description | |
| CPU Frequency (Maximum) | MHz | ARM: 432-MHz | |
| Voltage | Core (V) | 1.35 V | |
| I/O (V) | 3.3 V, 1.8 V | ||
| PLL Options | Reference frequency options Configurable PLL controller |
19.2 MHz, 24 MHz, 27 MHz, 36 MHz PLL bypass, programmable PLL |
|
| BGA Package | 13 x 13 mm | 338-Pin BGA (ZCE) | |
| Process Technology | 65 nm | ||
| Product Status(1) | Product Preview (PP), Advance Information (AI), or Production Data (PD) |
PD | |
3.3 Device Compatibility
The ARM926EJ-S RISC CPU is compatible with other ARM9 CPUs from ARM Holdings plc.
3.4 ARM Subsystem Overview
The ARM Subsystem contains components required to provide the ARM926EJ-S (ARM) master control of the overall device system, including the components of the ARM Subsystem, the peripherals, and the external memories.
The ARM is responsible for handling system functions such as system-level initialization, configuration, user interface, user command execution, connectivity functions, interface and control of the subsystem, etc. The ARM is master and performs these functions because it has a large program memory space and fast context switching capability, and is thus suitable for complex, multi-tasking, and general-purpose control tasks.
3.4.1 Components of the ARM Subsystem
The ARM Subsystem consists of the following components:
- ARM926EJ-S RISC processor, including:
- coprocessor 15 (CP15)
- MMU
- 16KB Instruction cache
- 8KB Data cache
- Write Buffer
- Java accelerator
- ARM Internal Memories
- 32KB Internal RAM (32-bit-wide access)
- 16KB Internal ROM (ARM bootloader for non-AEMIF boot modes)
- Embedded Trace Module and Embedded Trace Buffer (ETM/ETB)
- System Control Peripherals
- ARM Interrupt Controller
- PLL Controller
- Power and Sleep Controller
- System Control Module
The ARM also manages/controls all the device peripherals.
Figure 3-1 shows the functional block diagram of the ARM Subsystem.
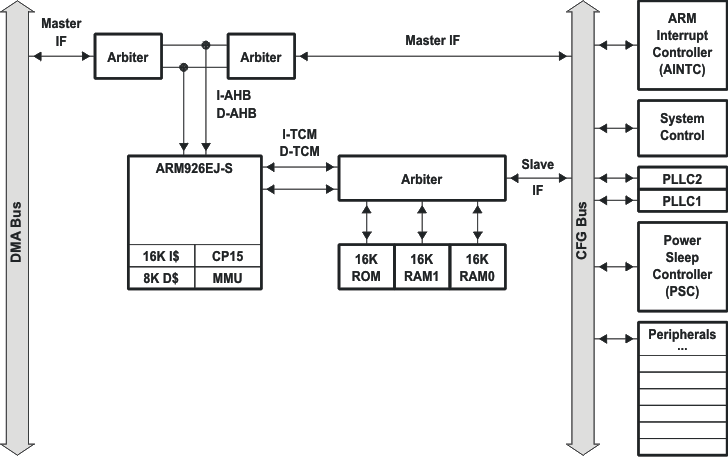 Figure 3-1 ARM Subsystem Block Diagram
Figure 3-1 ARM Subsystem Block Diagram
3.4.2 ARM926EJ-S RISC CPU
The ARM Subsystem integrates the ARM926EJ-S processor. The ARM926EJ-S processor is a member of ARM9 family of general-purpose microprocessors. This processor is targeted at multi-tasking applications where full memory management, high performance, low die size, and low power are all important. The ARM926EJ-S processor supports the 32-bit ARM and 16 bit THUMB instruction sets, enabling the user to trade off between high performance and high code density. Specifically, the ARM926EJ-S processor supports the ARMv5TEJ instruction set, which includes features for efficient execution of Java byte codes, providing Java performance similar to Just in Time (JIT) Java interpreter, but without associated code overhead.
The ARM926EJ-S processor supports the ARM debug architecture and includes logic to assist in both hardware and software debug. The ARM926EJ-S processor has a Harvard architecture and provides a complete high performance subsystem, including:
- ARM926EJ -S integer core
- CP15 system control coprocessor
- Memory Management Unit (MMU)
- Separate instruction and data Caches
- Write buffer
- Separate instruction and data Tightly-Coupled Memories (TCMs) [internal RAM] interfaces
- Separate instruction and data AHB bus interfaces
- Embedded Trace Module and Embedded Trace Buffer (ETM/ETB)
For more complete details on the ARM9, see the ARM926EJ-S Technical Reference Manual, available at www.arm.com.
3.4.3 CP15
The ARM926EJ-S system control coprocessor (CP15) is used to configure and control instruction and data caches, Tightly-Coupled Memories (TCMs), Memory Management Unit (MMU), and other ARM subsystem functions. The CP15 registers are programmed using the MRC and MCR ARM instructions, when the ARM in a privileged mode such as supervisor or system mode.
3.4.4 MMU
The ARM926EJ-S MMU provides virtual memory features required by operating systems such as Linux, WindowCE, ultron, ThreadX, etc. A single set of two level page tables stored in main memory is used to control the address translation, permission checks and memory region attributes for both data and instruction accesses. The MMU uses a single unified Translation Lookaside Buffer (TLB) to cache the information held in the page tables. The MMU features are:
- Standard ARM architecture v4 and v5 MMU mapping sizes, domains and access protection scheme.
- Mapping sizes are:
- 1MB (sections)
- 64KB (large pages)
- 4KB (small pages)
- 1KB (tiny pages)
- Access permissions for large pages and small pages can be specified separately for each quarter of the page (subpage permissions)
- Hardware page table walks
- Invalidate entire TLB, using CP15 register 8
- Invalidate TLB entry, selected by MVA, using CP15 register 8
- Lockdown of TLB entries, using CP15 register 10
3.4.5 Caches and Write Buffer
The size of the Instruction Cache is 16KB, Data cache is 8KB. Additionally, the Caches have the following features:
- Virtual index, virtual tag, and addressed using the Modified Virtual Address (MVA)
- Four-way set associative, with a cache line length of eight words per line (32-bytes per line) and with two dirty bits in the Dcache
- Dcache supports write-through and write-back (or copy back) cache operation, selected by memory region using the C and B bits in the MMU translation tables.
- Critical-word first cache refilling
- Cache lockdown registers enable control over which cache ways are used for allocation on a line fill, providing a mechanism for both lockdown, and controlling cache corruption
- Dcache stores the Physical Address TAG (PA TAG) corresponding to each Dcache entry in the TAG RAM for use during the cache line write-backs, in addition to the Virtual Address TAG stored in the TAG RAM. This means that the MMU is not involved in Dcache write-back operations, removing the possibility of TLB misses related to the write-back address.
- Cache maintenance operations provide efficient invalidation of, the entire Dcache or Icache, regions of the Dcache or Icache, and regions of virtual memory.
The write buffer is used for all writes to a noncachable bufferable region, write-through region and write misses to a write-back region. A separate buffer is incorporated in the Dcache for holding write-back for cache line evictions or cleaning of dirty cache lines. The main write buffer has 16-word data buffer and a four-address buffer. The Dcache write-back has eight data word entries and a single address entry.
3.4.6 Tightly Coupled Memory (TCM)
ARM internal RAM is provided for storing real-time and performance-critical code/data and the Interrupt Vector table. ARM internal ROM boot modes include NAND, MMC/SD, UART, USB, SPI, EMAC, and HPI. The RAM and ROM memories interfaced to the ARM926EJ-S via the tightly coupled memory interface that provides for separate instruction and data bus connections. Since the ARM TCM does not allow instructions on the D-TCM bus or data on the I-TCM bus, an arbiter is included so that both data and instructions can be stored in the internal RAM/ROM. The arbiter also allows accesses to the RAM/ROM from extra-ARM sources (e.g., EDMA or other masters). The ARM926EJ-S has built-in DMA support for direct accesses to the ARM internal memory from a non-ARM master. Because of the time-critical nature of the TCM link to the ARM internal memory, all accesses from non-ARM devices are treated as DMA transfers.
Instruction and Data accesses are differentiated via accessing different memory map regions, with the instruction region from 0x0000 through 0x7FFF and data from 0x10000 through 0x17FFF. Placing the instruction region at 0x0000 is necessary to allow the ARM Interrupt Vector table to be placed at 0x0000, as required by the ARM architecture. The internal 32-KB RAM is split into two physical banks of 16KB each, which allows simultaneous instruction and data accesses to be accomplished if the code and data are in separate banks.
3.4.7 Advanced High-performance Bus (AHB)
The ARM Subsystem uses the AHB port of the ARM926EJ-S to connect the ARM to the configuration bus and the external memories. Arbiters are employed to arbitrate access to the separate D-AHB and I-AHB by the configuration bus and the external memories bus.
3.4.8 Embedded Trace Macrocell (ETM) and Embedded Trace Buffer (ETB)
To support real-time trace, the ARM926EJ-S processor provides an interface to enable connection of an Embedded Trace Macrocell (ETM). The ARM926ES-J Subsystem also includes the Embedded Trace Buffer (ETB). The ETM consists of two parts:
- Trace Port provides real-time trace capability for the ARM9.
- Triggering facilities provide trigger resources, which include address and data comparators, counter, and sequencers.
The device trace port is not pinned out and is instead only connected to the Embedded Trace Buffer. The ETB has a 4KB buffer memory. ETB enabled debug tools are required to read/interpret the captured trace data.
3.4.9 ARM Memory Mapping
The ARM memory map is shown in Table 3-4 and Table 3-5. This section describes the memories and interfaces within the ARM's memory map.
3.4.9.1 ARM Internal Memories
The ARM has access to the following ARM internal memories:
- 32KB ARM Internal RAM on TCM interface, logically separated into two 16KB pages to allow simultaneous access on any given cycle if there are separate accesses for code (I-TCM bus) and data (D-TCM) to the different memory regions.
- 16KB ARM Internal ROM
3.4.9.2 External Memories
The ARM has access to the following External memories:
- DDR2/mDDR Synchronous DRAM
- Asynchronous EMIF / OneNAND / NOR
- NAND Flash
- Flash card devices:
- MMC/SD
- xD
- SmartMedia
3.4.10 Peripherals
The ARM has access to all of the peripherals on the device.
3.4.11 ARM Interrupt Controller (AINTC)
The device ARM Interrupt Controller (AINTC) has the following features:
- Supports up to 64 interrupt channels (16 external channels)
- Interrupt mask for each channel
- Each interrupt channel can be mapped to a Fast Interrupt Request (FIQ) or to an Interrupt Request (IRQ) type of interrupt.
- Hardware prioritization of simultaneous interrupts
- Configurable interrupt priority (2 levels of FIQ and 6 levels of IRQ)
- Configurable interrupt entry table (FIQ and IRQ priority table entry) to reduce interrupt processing time
The ARM core supports two interrupt types: FIQ and IRQ. See the ARM926EJ-S Technical Reference Manual for detailed information about the ARM’s FIQ and IRQ interrupts. Each interrupt channel is mappable to an FIQ or to an IRQ type of interrupt, and each channel can be enabled or disabled. The INTC supports user-configurable interrupt-priority and interrupt entry addresses. Entry addresses minimize the time spent jumping to interrupt service routines (ISRs). When an interrupt occurs, the corresponding highest priority ISR’s address is stored in the INTC’s ENTRY register. The IRQ or FIQ interrupt routine can read the ENTRY register and jump to the corresponding ISR directly. Thus, the ARM does not require a software dispatcher to determine the asserted interrupt.
3.5 System Control Module
The system control module is a system-level module containing status and top-level control logic required by the device. The system control module consists of a miscellaneous set of status and control registers, accessible by the ARM and supporting all of the following system features and operations:
- Device identification
- Device configuration
- Pin multiplexing control
- Device boot configuration status
- ARM interrupt and EDMA event multiplexing control
- Special peripheral status and control
- Timer64
- USB PHY control
- VPSS clock and video DAC control and status
- DDR VTP control
- Clockout circuitry
- GIO de-bounce control
- Power management
- Deep sleep
- Bandwidth Management
- Bus master DMA priority control
For more information on the System Control Module, see Section 4, Device Configurations and the TMS320DM36x DMSoC ARM Subsystem User's Guide.
3.6 Power Management
The device is designed for minimal power consumption. There are two components to power consumption: active power and leakage power. Active power is the power consumed to perform work and scales with clock frequency and the amount of computations being performed. Active power can be reduced by controlling the clocks in such a way as to either operate at a clock setting just high enough to complete the required operation in the required time-line or to run at a clock setting until the work is complete and then drastically cut the clocks (e.g. to PLL Bypass mode) until additional work must be performed. Leakage power is due to static current leakage and occurs regardless of the clock rate. Leakage, or standby power, is unavoidable while power is applied and scales roughly with the operating junction temperatures. Leakage power can only be avoided by removing power completely from a device or subsystem. The device includes several power management modes which are briefly described in Table 3-3. See the TMS320DM36x DMSoC ARM Subsystem User's Guide (SPRUFG5) for more information on power management.
Table 3-3 Power Management Conditions
| POWER MGMT. APPLICATION SCENARIO |
PRTCSS | CORE POWER |
OSC. POWER |
PLL CNTRLR. |
ARM926 CLOCK |
GIO, UART, I2C CLOCKS |
SPI, PWM, TIMER CLOCKS |
OTHER PERIPH. CLOCKS | DDR CLOCK/ MODE |
DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRTCSS | Active | Off | Off | Off | Off | Off | Off | Off | Off | This condition consumes the lowest possible power, except for the PRTCSS. |
| Deep Sleep Mode(1) | Active | On | Off | Bypass Mode (not Active) |
Off | Off | Off | Off | Suspend / "Self-Refresh" |
This mode consumes the second lowest possible power, except for PRTCSS and core power, where only the deep sleep circuit is on in this mode. |
| Standby | Active | On | On | Bypass Mode | Off | On | Off | Off | Suspend / "Self-Refresh" |
This condition keeps the minimum possible modules powered-on in order to wake up the device. Clocks are suspended except for GIO (interrupts), UART, and I2C (in slave mode). |
| Low-power (PLL Bypass Mode) |
Active | On | On | Bypass Mode | On | On / Off | On / Off | On / Off | Suspend / "Self-Refresh" |
Most clocks are suspended, except for ARM, GIO, UART, SPI, I2C, PWM, and timers. Since ARM will not have access to DDR, its internal Cache will be either frozen or not accessed. |
| System Running (PLL Mode) |
Active | On | On | PLL Mode | On | On / Off | On / Off | On / Off | Nominal Clock / Operation |
The device, including system PLLs, are on. This condition conserves the least amount of power. |
3.7 Memory Map Summary
Table 3-4 shows the memory map address ranges of the device. Table 3-5 depicts the expanded map of the Configuration Space (0x01C0 0000 through 0x01FF FFFF). The device has multiple on-chip memories associated with its processor and various subsystems. To help simplify software development a unified memory map is used where possible to maintain a consistent view of device resources across all bus masters. The bus masters are the ARM, EDMA, EMAC, USB, HPI, MJCP, HDVICP and VPSS. The Master Peripherals are EMAC, USB, and HPI. Please see Section 5, System Interconnect, for more details.
Table 3-4 Memory Map
| Start Address | End Address | Size (Bytes) | ARM Mem Map |
EDMA Mem Map |
Master Periph Mem Map |
VPSS Mem Map |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x0000 0000 | 0x0000 3FFF | 16K | ARM RAM0 (Instruction) |
|||
| 0x0000 4000 | 0x0000 7FFF | 16K | ARM RAM1 (Instruction) |
Reserved | Reserved | |
| 0x0000 8000 | 0x0000 BFFF | 16K | ARM ROM (Instruction) | |||
| 0x0000 C000 | 0x0000 FFFF | 16K | Reserved | |||
| 0x0001 0000 | 0x0001 3FFF | 16K | ARM RAM0 (Data) | ARM RAM0 | ARM RAM0 | |
| 0x0001 4000 | 0x0001 7FFF | 16K | ARM RAM1 (Data) | ARM RAM1 | ARM RAM1 | |
| 0x0001 8000 | 0x0001 BFFF | 16K | ARM ROM | ARM ROM | ARM ROM | |
| 0x0001 C000 | 0x000F FFFF | 912K | Reserved | |||
| 0x0010 0000 | 0x01BB FFFF | 26M | ||||
| 0x01BC 0000 | 0x01BC 0FFF | 4K | ARM ETB Mem | |||
| 0x01BC 1000 | 0x01BC 17FF | 2K | ARM ETB Reg | Reserved | ||
| 0x01BC 1800 | 0x01BC 18FF | 256 | ARM IceCrusher | Reserved | ||
| 0x01BC 1900 | 0x01BC FFFF | 59136 | Reserved | |||
| 0x01BD 0000 | 0x01BF FFFF | 192K | ||||
| 0x01C0 0000 | 0x01FF FFFF | 4M | CFG Bus Peripherals | CFG Bus Peripherals | CFG Bus Peripherals | |
| 0x0200 0000 | 0x09FF FFFF | 128M | ASYNC EMIF (Data) | ASYNC EMIF (Data) | ||
| 0x0A00 0000 | 0x11EF FFFF | 127M - 16K | Reserved | Reserved | ||
| 0x11F0 0000 | 0x11F1 FFFF | 128K | MJCP DMA Port | MJCP DMA Port | ||
| 0x11F2 0000 | 0x11FF FFFF | 896K | Reserved | Reserved | ||
| 0x1200 0000 | 0x1207 FFFF | 512K | HDVICP DMA Port1 | HDVICP DMA Port1 | HDVICP DMA Port1 | |
| 0x1208 0000 | 0x120F FFFF | 512K | Reserved | HDVICP DMA Port2 | Reserved | |
| 0x1210 0000 | 0x1217 FFFF | 512K | HDVICP DMA Port3 | |||
| 0x1218 0000 | 0x1FFF FFFF | 222.5M | Reserved | |||
| 0x2000 0000 | 0x2000 7FFF | 32K | DDR EMIF Control Regs | DDR EMIF Control Regs | ||
| 0x2000 8000 | 0x41FF FFFF | 544M-32K | ||||
| 0x4200 0000 | 0x49FF FFFF | 128M | Reserved | Reserved | ||
| 0x4A00 0000 | 0x7FFF FFFF | 864M | ||||
| 0x8000 0000 | 0x8FFF FFFF | 256M | DDR EMIF | DDR EMIF | DDR EMIF | DDR EMIF |
| 0x9000 0000 | 0xFFFF FFFF | 1792M | Reserved | Reserved | Reserved | Reserved |
Table 3-5 ARM Configuration Bus Access to Peripherals
| Address | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region | Start | End | Size | |
| EDMA CC | 0x01C0 0000 | 0x01C0 FFFF | 64K | |
| EDMA TC0 | 0x01C1 0000 | 0x01C1 03FF | 1K | |
| EDMA TC1 | 0x01C1 0400 | 0x01C1 07FF | 1K | |
| EDMA TC2 | 0x01C1 0800 | 0x01C1 0BFF | 1K | |
| EDMA TC3 | 0x01C1 0C00 | 0x01C1 0FFF | 1K | |
| Reserved | 0x01C1 1000 | 0x01C1 FFFF | 60 K | |
| UART0 | 0x01C2 0000 | 0x01C2 03FF | 1K | |
| Reserved | 0x01C2 0400 | 0x01 20 7FFF | 1K | |
| Timer 3 | 0x01C2 0800 | 0x01C2 0BFF | 1K | |
| Real-time out | 0x01C2 0C00 | 0x01C2 0FFF | 1K | |
| I2C | 0x01C2 1000 | 0x01C2 13FF | 1K | |
| Timer 0 | 0x01C2 1400 | 0x01C2 17FF | 1K | |
| Timer 1 | 0x01C2 1800 | 0x01C2 1BFF | 1K | |
| Timer 2 | 0x01C2 1C00 | 0x01C2 1FFF | 1K | |
| PWM0 | 0x01C2 2000 | 0x01C2 23FF | 1K | |
| PWM1 | 0x01C2 2400 | 0x01C2 27FF | 1K | |
| PWM2 | 0x01C2 2800 | 0x01C2 2BFF | 1K | |
| PWM3 | 0x01C2 2C00 | 0x01C2 2FFF | 1K | |
| SPI4 | 0x01C2 3000 | 0x01C2 37FF | 2K | |
| Timer 4 | 0x01C2 3800 | 0x01C2 3BFF | 1K | |
| ADCIF | 0x01C2 3C00 | 0x01C2 3FFF | 1K | |
| Reserved | 0x01C2 4000 | 0x01C3 4FFF | 112K | |
| System Module | 0x01C4 0000 | 0x01C4 07FF | 2K | |
| PLL Controller 1 | 0x01C4 0800 | 0x01C4 0BFF | 1K | |
| PLL Controller 2 | 0x01C4 0C00 | 0x01C4 0FFF | 1K | |
| Power/Sleep Controller | 0x01C4 1000 | 0x01C4 1FFF | 4K | |
| Reserved | 0x01C4 2000 | 0x01C4 7FFF | 24K | |
| ARM Interrupt Controller | 0x01C4 8000 | 0x01C4 83FF | 1K | |
| Reserved | 0x01 C4 8400 | 0x01C63FFF | 111K | |
| USB OTG 2.0 Regs / RAM | 0x01C6 4000 | 0x01C6 5FFF | 8K | |
| SPI0 | 0x01C6 6000 | 0x01C6 67FF | 2K | |
| SPI1 | 0x01C6 6800 | 0x01C6 6FFF | 2K | |
| GPIO | 0x01C6 7000 | 0x01C6 77FF | 2K | |
| SPI2 | 0x01C6 7800 | 0x01C6 FFFF | 2K | |
| SPI3 | 0x01C6 8000 | 0x01C6 87FF | 2K | |
| Reserved | 0x01C6 8800 | 0x01C6 87FF | 2K | |
| PRTCSS Interface Registers | 0x01C6 9000 | 0x01C6 93FF | 1K | |
| KEYSCAN | 0x01C6 9400 | 0x01C6 97FF | 1K | |
| HPI | 0x01C6 9800 | 0x01C6 9FFF | 2K | |
| Reserved | 0x01C6 A000 | 0x01C6 FFFF | 24K | |
| VPSS Subsystem | ||||
| ISP System Configuration Registers | 0x01C7 0000 | 0x01C7 00FF | 256 | |
| VPBE Clock Control Register | 0x01C7 0200 | 0x01C7 02FF | 256 | |
| Resizer Registers | 0x01C7 0400 | 0x01C7 07FF | 1K | |
| IPIPE Registers | 0x01C7 0800 | 0x01C7 0FFF | 2K | |
| ISIF Registers | 0x01C7 1000 | 0x01C7 11FF | 512 | |
| IPIPEIF Registers | 0x01C7 1200 | 0x01C7 12FF | 768 | |
| H3A Registers | 0x01C7 1400 | 0x01C7 14FF | 256 | |
| FDIF Registers | 0x01C7 1800 | 0x01C7 1BFF | 1K | |
| OSD Registers | 0x01C7 1C00 | 0x01C7 1CFF | 256 | |
| Reserved | 0x01C7 1D00 | 0x01C7 1DFF | 256 | |
| VENC Registers | 0x01C7 1E00 | 0x01C7 1FFF | 512 | |
| Reserved | 0x01C7 2000 | 0x01CF FFFF | 568K | |
| Multimedia / SD 1 | 0x01D0 0000 | 0x01D0 1FFF | 8K | |
| McBSP | 0x01D0 2000 | 0x01D0 3FFF | 8K | |
| Reserved | 0x01D0 4000 | 0x01D0 5FFF | 8K | |
| UART1 | 0x01D0 6000 | 0x01D0 63FF | 1K | |
| Reserved | 0x01D0 6400 | 0x01D0 7FFF | 3K | |
| EMAC Control Registers | 0x01D0 7000 | 0x01D0 9FFF | 0x01D0 7FFF | 4K |
| EMAC Control Module RAM | 0x01D0 8000 | 8K | ||
| EMAC Control Module Registers | 0x01D0 A000 | 0x01D0 AFFF | 4K | |
| EMAC MDIO Control Registers | 0x01D0 B000 | 0x01D0 B7FF | 2K | |
| Voice Codec | 0x01D0 C000 | 0x01D0 C3FF | 1K | |
| Reserved | 0x01D0 C400 | 0x01D0 FFFF | 17K | |
| ASYNC EMIF Control | 0x01D1 0000 | 0x01D1 0FFF | 4K | |
| Multimedia / SD 0 | 0x01D1 1000 | 0x01D1 FFFF | 60K | |
| Reserved | 0x01D2 0000 | 0x01D3 FFFF | 128K | |
| Reserved | 0x01D4 0000 | 0x01DF FFFF | 768K | |
| Reserved | 0x01E0 0000 | 0x01FF FFFF | 2M | |
| ASYNC EMIF Data (CE0) | 0x0200 0000 | 0x03FF FFFF | 32M | |
| ASYNC EMIF Data (CE1) | 0x0400 0000 | 0x05FF FFFF | 32M | |
| Reserved | 0x0600 0000 | 0x09FF FFFF | 64M | |
| Reserved | 0x0A00 0000 | 0x0FFF FFFF | 96M | |
3.8 Pin Assignments
Extensive use of pin multiplexing is used to accommodate the largest number of peripheral functions in the smallest possible package. Pin multiplexing is controlled using a combination of hardware configuration at device reset and software programmable register settings.
3.8.1 Pin Map (Bottom View)
Figure 3-2 through Figure 3-5 show the pin assignments in four quadrants (A, B, C, and D).
3.9 Terminal Functions
Table 3-6 provides a complete pin description list which shows external signal names, the associated pin (ball) numbers along with the mechanical package designator, the pin type, whether the pin has any internal pullup or pulldown resistors, and a functional pin description. For more detailed information on device configuration, peripheral selection, multiplexed/shared pins, and debugging considerations, see Section 4, Device Configurations.
Table 3-6 Pin Descriptions
| Name | BGA ID |
Type (1) |
Group | Power Supply(2) |
IPU IPD(3) |
Reset State |
Description(4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CIN7(5) | A15 | I/O | ISIF | VDD_ISIF18_33 | IPD | Input | Standard ISIF Analog Front End (AFE): raw[7] |
| YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between chroma: CB/CR[07] | |||||||
| YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[07] | |||||||
| CIN6(5) | C15 | I/O | ISIF | VDD_ISIF18_33 | IPD | Input | Standard ISIF Analog Front End (AFE): raw[6] |
| YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between chroma: CB/CR[06] | |||||||
| YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[06] | |||||||
| CIN5(5) | B16 | I/O | ISIF | VDD_ISIF18_33 | IPD | Input | Standard ISIF Analog Front End (AFE): raw[5] |
| YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between chroma: CB/CR[05] | |||||||
| YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[05] | |||||||
| CIN4(5) | A16 | I/O | ISIF | VDD_ISIF18_33 | IPD | Input | Standard ISIF Analog Front End (AFE): raw[4] |
| YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between chroma: CB/CR[04] | |||||||
| YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[04] | |||||||
| CIN3 (5) | A17 | I/O | ISIF | VDD_ISIF18_33 | IPD | Input | Standard ISIF Analog Front End (AFE): raw[3] |
| YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between chroma: CB/CR[03] | |||||||
| YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[03] | |||||||
| CIN2(5) | C16 | I/O | ISIF | VDD_ISIF18_33 | IPD | Input | Standard ISIF Analog Front End (AFE): raw[2] |
| YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between chroma: CB/CR[02] | |||||||
| YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[02] | |||||||
| CIN1(5) | A18 | I/O | ISIF | VDD_ISIF18_33 | IPD | Input | Standard ISIF Analog Front End (AFE): raw[1] |
| YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between chroma: CB/CR[01] | |||||||
| YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[01] | |||||||
| CIN0(5) | B17 | I/O | ISIF | VDD_ISIF18_33 | IPD | Input | Standard ISIF Analog Front End (AFE): raw[0] |
| YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between chroma: CB/CR[00] | |||||||
| YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the upper channel. Y/CB/CR[00] | |||||||
| YIN7(5) / GIO103 /SPI3_SCLK | C12 | I/O | ISIF/ GIO / SPI3 | VDD_ISIF18_33 | IPD | Input | Standard ISIF Analog Front End (AFE): raw[15] |
| YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between luma: Y[07] | |||||||
| YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the lower channel. Y/CB/CR[07] | |||||||
| GIO: GIO[103] | |||||||
| SPI3: Clock | |||||||
| YIN6(5) / GIO102 /SPI3_SIMO | A13 | I/O | ISIF / GIO / SPI3 | VDD_ISIF18_33 | IPD | Input | Standard ISIF Analog Front End (AFE): raw[14] |
| YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between luma: Y[06] | |||||||
| YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the lower channel. Y/CB/CR[06] | |||||||
| GIO: GIO[102] | |||||||
| SPI3: Slave Input Master Output Data Signal | |||||||
| YIN5(5) / GIO101 /SPI3_SCS[0] | B13 | I/O | ISIF / GIO / SPI3 | VDD_ISIF18_33 | IPD | Input | Standard ISIF Analog Front End (AFE): raw[13] |
| YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between luma: Y[05] | |||||||
| YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the lower channel. Y/CB/CR[05] | |||||||
| GIO: GIO[101] | |||||||
| SPI3: Chip Select 0 | |||||||
| YIN4(5) / GIO100 / SPI3_SOMI / SPI3_SCS[1] | D12 | I/O | ISIF / GIO / SPI3 | VDD_ISIF18_33 | IPD | Input | Standard ISIF Analog Front End (AFE): raw[12] |
| YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between luma: Y[04] | |||||||
| YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the lower channel. Y/CB/CR[04] | |||||||
| GIO: GIO[100] | |||||||
| SPI3: Slave Output Master Input Data Signal | |||||||
| SPI3: Chip Select 1 | |||||||
| YIN3(5) / GIO99 | A14 | I/O | ISIF / GIO | VDD_ISIF18_33 | IPD | Input | Standard ISIF Analog Front End (AFE): raw[11] |
| YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between luma: Y[03] | |||||||
| YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the lower channel. Y/CB/CR[03] | |||||||
| GIO: GIO[99] | |||||||
| YIN2(5) / GIO98 | B15 | I/O | ISIF / GIO | VDD_ISIF18_33 | IPD | Input | Standard ISIF Analog Front End (AFE): raw[10] |
| YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between luma: Y[02] | |||||||
| YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the lower channel. Y/CB/CR[02] | |||||||
| GIO: GIO[98] | |||||||
| YIN1(5) / GIO97 | D14 | I/O | ISIF / GIO | VDD_ISIF18_33 | IPD | Input | Standard ISIF Analog Front End (AFE): raw[09] |
| YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between luma: Y[01] | |||||||
| YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the lower channel. Y/CB/CR[01] | |||||||
| GIO: GIO[97] | |||||||
| YIN0(5) / GIO96 | D15 | I/O | ISIF / GIO | VDD_ISIF18_33 | IPD | Input | Standard ISIF Analog Front End (AFE): raw[08] |
| YCC 16-bit: time multiplexed between luma: Y[00] | |||||||
| YCC 08-bit (which allows for 2 simultaneous decoder inputs), it is time multiplexed between luma and chroma of the lower channel. Y/CB/CR[00] | |||||||
| GIO: GIO[96] | |||||||
| HD / GIO95 | C14 | I/O | ISIF / GIO | VDD_ISIF18_33 | IPD | Input | Horizontal synchronization signal that can be either an input (slave mode) or an output (master mode). Tells the ISIF when a new line starts. |
| GIO: GIO[95] | |||||||
| VD / GIO94 | B14 | I/O | ISIF / GIO | VDD_ISIF18_33 | IPD | Input | Vertical synchronization signal that can be either an input (slave mode) or an output (master mode). Tells the ISIF when a new frame starts. |
| GIO: GIO[94] | |||||||
| C_WE_FIELD / GIO93 / CLKOUT0 / USBDRVVBUS | E13 | I/O | ISIF / GIO / CLKOUT / USB | VDD_ISIF18_33 | IPD | Input | Write enable input signal is used by external device (AFE/TG) to gate the DDR output of the ISIF module. |
| Alternately, the field identification input signal is used by external device (AFE/TG) to indicate the which of two frames is input to the ISIF module for sensors with interlaced output. ISIF handles 1- or 2-field sensors in hardware. | |||||||
| GIO: GIO[93] | |||||||
| CLKOUT0: Clock Output | |||||||
| USB: Digital output to control external 5 V supply | |||||||
| PCLK | D13 | I/O/Z | ISIF | VDD_ISIF18_33 | IPD | Input | Pixel clock input (strobe for lines CI7 through YI0) |
| YOUT7(R7)(6) | G16 | I/O | VENC | VDDS33 | Input |
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function(4). For more details, see the DM36x DMSoC Video Processor Back End User's Guide (SPRUFG9). |
|
| YOUT6(R6)(6) | G19 | I/O | VENC | VDDS33 | Input |
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function(4). For more details, see the DM36x DMSoC Video Processor Back End User's Guide (SPRUFG9). |
|
| YOUT5(R5)(6) | F15 | I/O | VENC | VDDS33 | Input |
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function(4). For more details, see the DM36x DMSoC Video Processor Back End User's Guide (SPRUFG9). |
|
| YOUT4(R4)(6) | F18 | I/O | VENC | VDDS33 | Input |
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function(4). For more details, see the DM36x DMSoC Video Processor Back End User's Guide (SPRUFG9). |
|
| YOUT3(R3)(6) | F16 | I/O | VENC | VDDS33 | Input |
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function(4). For more details, see the DM36x DMSoC Video Processor Back End User's Guide (SPRUFG9). |
|
| YOUT2(G7)(6) | F19 | I/O | VENC | VDDS33 | Input |
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function(4). For more details, see the DM36x DMSoC Video Processor Back End User's Guide (SPRUFG9). |
|
| YOUT1(G6)(6) | F17 | I/O | VENC | VDDS33 | Input |
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function(4). For more details, see the DM36x DMSoC Video Processor Back End User's Guide (SPRUFG9). |
|
| YOUT0(G5)(6) | E16 | I/O | VENC | VDDS33 | Input |
Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function(4). For more details, see the DM36x DMSoC Video Processor Back End User's Guide (SPRUFG9). |
|
| HSYNC / GIO84 | G15 | I/O | VENC / GIO | VDDS33 | Input | Video Encoder: Horizontal Sync(4) | |
| GIO: GIO[84] | |||||||
| VSYNC / GIO83 | G18 | I/O | VENC / GIO | VDDS33 | Input | Video Encoder: Vertical Sync(4) | |
| GIO: GIO[83] | |||||||
| LCD_OE / GIO82 | C19 | I/O | VENC / GIO | VDDS33 | Output | Video Encoder: Data valid duration (4) | |
| GIO: GIO[82] | |||||||
| GIO80 / EXTCLK / B2 / PWM3 | B19 | I/O | GIO / VENC / PWM3 | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[80] |
| Video Encoder: External clock Input, used if clock rates > 27 MHz are needed, e.g. 74.25 MHz for HDTV digital output. | |||||||
| Digital Video Out: B2(4). For more details, see the DM36x DMSoC Video Processor Back End User's Guide (SPRUFG9). |
|||||||
| PWM3: PWM3 Output | |||||||
| VCLK / GIO79 | B18 | I/O | VENC / GIO | VDDS33 | Input | Video Encoder: Video Output Clock(4) | |
| GIO: GIO[79] | |||||||
| GIO92 / COUT7(G4)(6) / PWM0 | E18 | I/O | GIO / VENC / PWM0 | VDDS33 | Input | GIO: GIO[92] | |
| Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function(4). For more details, see the DM36x DMSoC Video Processor Back End User's Guide (SPRUFG9). |
|||||||
| PWM0: PWM0 Output | |||||||
| GIO91 / COUT6(G3)(6) / PWM1 | E19 | I/O | GIO / VENC / PWM1 | VDDS33 | Input | GIO: GIO[91] | |
| Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function(4). For more details, see the DM36x DMSoC Video Processor Back End User's Guide (SPRUFG9). |
|||||||
| PWM1: PWM1 Output | |||||||
| GIO90 / COUT5(G2)(6) / PWM2 / RTO0 | E15 | I/O | GIO / VENC /PWM2 / RTO0 | VDDS33 | Input | GIO: GIO[90] | |
| Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function(4). For more details, see the DM36x DMSoC Video Processor Back End User's Guide (SPRUFG9). |
|||||||
| PWM2: PWM2 Output | |||||||
| RTO0: RTO0 Output | |||||||
| GIO89 / COUT4(B7) (6)/ PWM2 / RTO1 | E17 | I/O | GIO / VENC / PWM2 / RTO1 | VDDS33 | Input | GIO: GIO[89] | |
| Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function(4). For more details, see the DM36x DMSoC Video Processor Back End User's Guide (SPRUFG9). |
|||||||
| PWM2: PWM2 Output | |||||||
| RTO1: RTO1 Output | |||||||
| GIO88 / COUT3(B6) (6)/ PWM2 / RTO2 | D16 | I/O | GIO / VENC / PWM2 / RTO2 | VDDS33 | Input | GIO: GIO[88] | |
| Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function(4). For more details, see the DM36x DMSoC Video Processor Back End User's Guide (SPRUFG9). |
|||||||
| PWM2: PWM2 Output | |||||||
| RTO2: RTO2 Output | |||||||
| GIO87 / COUT2(B5)(6) / PWM2 / RTO3 | D19 | I/O | GIO / VENC /PWM2 / RTO3 | VDDS33 | Input | GIO: GIO[87] | |
| Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function(4). For more details, see the DM36x DMSoC Video Processor Back End User's Guide (SPRUFG9). |
|||||||
| PWM2: PWM2 Output | |||||||
| RTO3: RTO3 Output | |||||||
| GIO86 / COUT1(B4)(6) / PWM3 / STTRIG | D18 | I/O | GIO / VENC / PWM3 | VDDS33 | Input | GIO: GIO[86] | |
| Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function(4). For more details, see the DM36x DMSoC Video Processor Back End User's Guide (SPRUFG9). |
|||||||
| PWM3: PWM3 Output | |||||||
| STTRIG: Camera FLASH control trigger signal | |||||||
| GIO85 / COUT0(B3) (6)/ PWM3 | D17 | I/O | GIO / VENC / PWM3 | VDDS33 | Input | GIO: GIO[85] | |
| Digital Video Out: VENC settings determine function(4). For more details, see the DM36x DMSoC Video Processor Back End User's Guide (SPRUFG9). |
|||||||
| PWM3: PWM3 Output | |||||||
| GIO81(OSCCFG) / LCD_FIELD / R2 / PWM3 | C18 | I/O | GIO / VENC / PWM3 | VDDS33 | Input | GIO: GIO[81] Note: This pin will be used as oscillator configuration (OSCCFG). The GIO81(OSCCFG) state is latched during reset, and it specifies the oscillation frequency range mode of the pin. See Section 4.7.6 for more details. |
|
| Video Encoder: Field identifier for interlaced display formats(4). For more details, see the DM36x DMSoC Video Processor Back End User's Guide (SPRUFG9). |
|||||||
| Digital Video Out: R2(4) | |||||||
| PWM3: PWM3 Output | |||||||
| VREF | D11 | A I | Video DAC | VDDA18_DAC | Video DAC: Reference voltage for DAC. For more details, see Section 7.12.2.4, DAC and Video Buffer Electrical Data/Timing. Note: If the DAC peripheral is not used, this pin must be tied directly to VSS for proper device operation. |
||
| IREF | A11 | A I/O | Video DAC | VDDA18_DAC | Video DAC: Sets reference current for DAC. An external resistor with nominal value, 2400 ohms, is connected between IREF and VSS. For more details, see Section 7.12.2.4, DAC and Video Buffer Electrical Data/Timing. Note: If the DAC peripheral is not used, this pin must be tied directly to VSS for proper device operation. |
||
| IDACOUT | B11 | A I/O | Video DAC | VDDA18_DAC | Video DAC: Current source input from DAC. An external resistor with nominal value, 2100 ohms, is connected between IDACOUT and VFB. For more details, see Section 7.12.2.4, DAC and Video Buffer Electrical Data/Timing. Note: If the DAC peripheral is not used at all in the application, this pin can either be connected to VSS or be left open. |
||
| VFB | B10 | A I/O | Video DAC | VDDA18_DAC | Video DAC: Amplifier feedback node. An external resistor with nominal value, 2150 ohms, is connected between VFB and TVOUT. For more details, see Section 7.12.2.4, DAC and Video Buffer Electrical Data/Timing. Note: If the DAC peripheral is not used at all in the application, this pin can either be connected to VSS or be left open. |
||
| TVOUT | A10 | A I/O | Video DAC | VDDA18_DAC | Video DAC: DAC1video output. An external resistor with nominal value, 2150 ohms, is connected between TVOUT and VFB. This is the output node that drives the load (75 ohms). For more details, see Section 7.12.2.4, DAC and Video Buffer Electrical Data/Timing. Note: If the DAC peripheral is not used at all in the application, this pin can either be connected to VSS or be left open. |
||
| COMPY | B12 | A O | Video DAC | VDDA18_DAC | Video DAC: Analog video signal component output Y Note: If the DAC peripheral is not used at all in the application, this pin can either be connected to VSS or be left open. |
||
| COMPPB | A12 | A O | Video DAC | VDDA18_DAC | Video DAC: Analog video signal component output Pb Note: If the DAC peripheral is not used at all in the application, this pin can either be connected to VSS or be left open. |
||
| COMPPR | C11 | A O | Video DAC | VDDA18_DAC | Video DAC: Analog video signal component output Pr Note: If the DAC peripheral is not used at all in the application, this pin can either be connected to VSS or be left open. |
||
| VDDA18_DAC | D10 | PWR | Video DAC | VDDA18_DAC | Video DAC: Analog 1.8-V power Note: If the DAC peripheral is not used, this pin must be tied directly to VSS for proper device operation. |
||
| VDDA12_DAC | E12 | PWR | Video Dac | VDDA12_DAC | Video DAC: Analog 1.2-V power Note: If the DAC peripheral is not used, this pin must be tied directly to VSS for proper device operation. |
||
| VSSA18_DAC | E11 | GND | Video DAC | Video DAC: Analog 1.8-V ground Note: If the DAC peripheral is not used, this pin must be tied directly to VSS for proper device operation. |
|||
| VSSA12_DAC | F11 | GND | Video DAC | Video DAC: Analog 1.2-V ground Note: If the DAC peripheral is not used, this pin must be tied directly to VSS for proper device operation. |
|||
| DDR_CLK | W11 | O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Data Clock | ||
| DDR_CLK | W12 | O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Complementary Data Clock | ||
| DDR_RAS | U12 | O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Row Address Strobe | ||
| DDR_CAS | V12 | O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Column Address Strobe | ||
| DDR_WE | W13 | O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Write Enable | ||
| DDR_CS | T12 | O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Chip Select | ||
| DDR_CKE | R13 | O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Clock Enable | ||
| DDR_DQM[1] | W6 | O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | Data mask input for DDR_DQ[15:8] | ||
| DDR_DQM[0] | T11 | O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | Data mask input for DDR_DQ[7:0] | ||
| DDR_DQS[1] | T7 | I/O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | Data strobe input/outputs for each byte of the 16-bit data bus used to synchronize the data transfers. Output to DDR2 when writing and inputs when reading. They are used to synchronize the data transfers. | ||
| DDR_DQS1: For DDR_DQ[15:8] | |||||||
| DDR_DQS[0] | T10 | I/O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | Data strobe input/outputs for each byte of the 16-bit data bus used to synchronize the data transfers. Output to DDR2 when writing and inputs when reading. They are used to synchronize the data transfers. | ||
| DDR_DQS0: For DDR_DQ[7:0] | |||||||
| DDR_DQSN[1] | U6 | I/O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR: Complimentary data strobe input/outputs for each byte of the 16-bit data bus. They are outputs to the DDR2 when writing and inputs when reading. They are used to synchronize the data transfers. | ||
| Note: This signal is used in double ended differential memory interfaces supported by the device. | |||||||
| DDR_DQSN[0] | U9 | I/O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR: Complimentary data strobe input/outputs for each byte of the 16-bit data bus. They are outputs to the DDR2 when writing and inputs when reading. They are used to synchronize the data transfers. | ||
| Note: This signal is used in double ended differential memory interfaces supported by the device. | |||||||
| DDR_BA[2] | V13 | O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | Bank select outputs. Two are required for 1Gb DDR2 memories. | ||
| DDR_BA[1] | T13 | O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | Bank select outputs. Two are required for 1Gb DDR2 memories. | ||
| DDR_BA[0] | W14 | O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | Bank select outputs. Two are required for 1Gb DDR2 memories. | ||
| DDR_A13 | T16 | O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Address Bus bit 13 | ||
| DDR_A12 | V17 | O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Address Bus bit 12 | ||
| DDR_A11 | W18 | O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Address Bus bit 11 | ||
| DDR_A10 | V16 | O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Address Bus bit 10 | ||
| DDR_A9 | U16 | O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Address Bus bit 09 | ||
| DDR_A8 | W17 | O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Address Bus bit 08 | ||
| DDR_A7 | T15 | O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Address Bus bit 07 | ||
| DDR_A6 | W16 | O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Address Bus bit 06 | ||
| DDR_A5 | V15 | O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Address Bus bit 05 | ||
| DDR_A4 | U15 | O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Address Bus bit 04 | ||
| DDR_A3 | T14 | O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Address Bus bit 03 | ||
| DDR_A2 | W15 | O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Address Bus bit 02 | ||
| DDR_A1 | V14 | O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Address Bus bit 01 | ||
| DDR_A0 | U14 | O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Address Bus bit 00 | ||
| DDR_DQ15 | V6 | I/O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Data Bus bit 15 | ||
| DDR_DQ14 | V7 | I/O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Data Bus bit 14 | ||
| DDR_DQ13 | R7 | I/O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Data Bus bit 13 | ||
| DDR_DQ12 | W7 | I/O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Data Bus bit 12 | ||
| DDR_DQ11 | V8 | I/O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Data Bus bit 11 | ||
| DDR_DQ10 | R8 | I/O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Data Bus bit 10 | ||
| DDR_DQ9 | U8 | I/O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Data Bus bit 09 | ||
| DDR_DQ8 | W8 | I/O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Data Bus bit 08 | ||
| DDR_DQ7 | R9 | I/O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Data Bus bit 07 | ||
| DDR_DQ6 | W9 | I/O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Data Bus bit 06 | ||
| DDR_DQ5 | V9 | I/O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Data Bus bit 05 | ||
| DDR_DQ4 | W10 | I/O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Data Bus bit 04 | ||
| DDR_DQ3 | V10 | I/O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Data Bus bit 03 | ||
| DDR_DQ2 | R10 | I/O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Data Bus bit 02 | ||
| DDR_DQ1 | V11 | I/O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Data Bus bit 01 | ||
| DDR_DQ0 | U11 | I/O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR Data Bus bit 00 | ||
| DDR_ DQGATE0 |
T8 | O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR: Loopback signal for external DQS gating. Route to DDR and back to DDR_DQGATE1 with same constraints as used for DDR clock and data. | ||
| DDR_ DQGATE1 |
T9 | I | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR: Loopback signal for external DQS gating. Route to DDR and back to DDR_DQGATE0 with same constraints as used for DDR clock and data. | ||
| DDR_VREF | P11 | PWR | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR: DDR_VREF is .5* VDD18_DDR = 0.9V for SSTL2 specific reference voltage. | ||
| DDR_PADREFP | R11 | O | DDR | VDD18_DDR | DDR: External resistor ( 50 ohm to ground) | ||
| EM_A13 / GIO78 / BTSEL[2] | V18 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / GIO / BTSEL[2] | VDD_AEMIF1_18_33 | IPU/IPD disabled by default | Input | Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[13] |
| GIO: GIO[78] | |||||||
| BTSEL[2]: See Section 4.2, Device Boot Modes for system usage of these pins. | |||||||
| EM_A12 / GIO77 / BTSEL[1] | U18 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / GIO / BTSEL[1] | VDD_AEMIF1_18_33 | IPU/IPD disabled by default | Input | Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[12] |
| GIO: GIO[77] | |||||||
| BTSEL[1]: See Section 4.2, Device Boot Modes for system usage of these pins. | |||||||
| EM_A11 / GIO76 / BTSEL[0] | V19 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / GIO / BTSEL[0] | VDD_AEMIF1_18_33 | IPU/IPD disabled by default | Input | Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[11] |
| GIO: GIO[76] | |||||||
| BTSEL[0]: See Section 4.2, Device Boot Modes for system usage of these pins. | |||||||
| EM_A10 / GIO75 / AECFG[2] | U19 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / GIO / AECFG[2] | VDD_AEMIF1_18_33 | IPU/IPD disabled by default | Input | Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[10] |
| GIO: GIO[75] | |||||||
| AECFG[2]: See Section 4.2, Device Boot Modes and Table 4-14, AECFG (Async EMIF Configuration) for system usage of these pins. | |||||||
| EM_A9 / GIO74 / AECFG[1] | T18 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / GIO / AECFG[1] | VDD_AEMIF1_18_33 | IPU/IPD disabled by default | Input | Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[09] |
| GIO: GIO[74] | |||||||
| AECFG[1]: See Section 4.2, Device Boot Modes and Table 4-14, AECFG (Async EMIF Configuration) for system usage of these pins. | |||||||
| EM_A8 / GIO73 / AECFG[0] | T19 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / GIO / AECFG[0] | VDD_AEMIF1_18_33 | IPU/IPD disabled by default | Input | Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[08] |
| GIO: GIO[73] | |||||||
| AECFG[0]: See Section 4.2, Device Boot Modes and Table 4-14, AECFG (Async EMIF Configuration) for system usage of these pins. | |||||||
| EM_A7 / GIO72 / KEYA3 | T17 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / GIO / KEYSCAN | VDD_AEMIF1_18_33 | Input | Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[07] | |
| GIO: GIO[72] | |||||||
| Keyscan: A3 | |||||||
| EM_A6 / GIO71 / KEYA2 | R18 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / GIO / KEYSCAN | VDD_AEMIF1_18_33 | Input | Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[06] | |
| GIO: GIO[71] | |||||||
| Keyscan: A2 | |||||||
| EM_A5 / GIO70 / KEYA1 | R16 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / GIO / KEYSCAN | VDD_AEMIF1_18_33 | Input | Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[05] | |
| GIO: GIO[70] | |||||||
| Keyscan: A1 | |||||||
| EM_A4 / GIO69 / KEYA0 | R19 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / GIO/KEYSCAN | VDD_AEMIF1_18_33 | Input | Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[04] | |
| GIO: GIO[69] | |||||||
| Keyscan: A0 | |||||||
| EM_A3 / GIO68 / KEYB3 | R15 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / GIO/ KEYSCAN | VDD_AEMIF1_18_33 | Input | Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[03] | |
| GIO: GIO[68] | |||||||
| Keyscan: B3 | |||||||
| EM_A2 / HCNTLA | M18 | I/O/Z | AEMIF/HPI | VDD_AEMIF2_18_33 | Output | Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[02] | |
| HPI: The state of HCNTLA and HCNTLB determines if address, data, or control information is being transmitted between an external host and the device. Note: HPI is pin multiplexed with Asynchronous EMIF at the output pin. HPI is available only when boot mode selected is HPI boot mode. In this configuration, the device will always act as a slave. |
|||||||
| EM_A1 / HHWIL | M19 | I/O/Z | AEMIF/HPI | VDD_AEMIF2_18_33 | Output | Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[01] | |
| HPI: This pin is half-word identification input HHWIL. Note: HPI is pin multiplexed with Asynchronous EMIF at the output pin. HPI is available only when boot mode selected is HPI boot mode. In this configuration, the device will always act as a slave. |
|||||||
| EM_A0 / GIO67 / KEYB2 / HCNTLB | L17 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / GIO / KEYSCAN / HPI | VDD_AEMIF2_18_33 | Input | Async EMIF: Address Bus bit[00] Note that the EM_A0 is always a 32-bit address | |
| GIO: GIO[56] | |||||||
| Keyscan: B2 | |||||||
| HPI: The state of HCNTLA and HCNTLB determines if address, data, or control information is being transmitted between an external host and the device. Note: HPI is pin multiplexed with Asynchronous EMIF at the output pin. HPI is available only when boot mode selected is HPI boot mode. In this configuration, the device will always act as a slave. |
|||||||
| EM_BA1 / GIO66 / KEYB1 / HINTN | R17 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / GIO / KEYSCAN / HPI | VDD_AEMIF1_18_33 | Input | Async EMIF: Bank Address 1 signal = 16-bit address. In 16-bit mode, lowest address bit. In 8-bit mode, second lowest address bit |
|
| GIO: GIO[66] | |||||||
| Keyscan: B1 | |||||||
| HPI: This pin is host interrupt output HINT
Note: HPI is pin multiplexed with Asynchronous EMIF at the output pin. HPI is available only when boot mode selected is HPI boot mode. In this configuration, the device will always act as a slave. |
|||||||
| EM_BA0 / EM_A14 / GIO65 / KEYB0 | P17 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / GIO / KEYSCAN | VDD_AEMIF1_18_33 | Input | Async EMIF: Bank Address 0 signal = 8-bit address. In 8-bit mode, lowest address bit. |
|
| Async EMIF: Address line (bit[14] when using 16-bit memories. | |||||||
| GIO: GIO[65] | |||||||
| Keyscan: B0 | |||||||
| EM_D15 / GIO64 / HD15 | P18 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / GIO / HPI | VDD_AEMIF1_18_33 | Input | Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[15] | |
| GIO: GIO[64] | |||||||
| HPI: Data bus bit [15] Note: HPI is pin multiplexed with Asynchronous EMIF at the output pin. HPI is available only when boot mode selected is HPI boot mode. In this configuration, the device will always act as a slave. |
|||||||
| EM_D14 / GIO63 / HD14 | P16 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / GIO / HPI | VDD_AEMIF1_18_33 | Input | Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[14] | |
| GIO: GIO[63] | |||||||
| HPI: Data bus bit [14] Note: HPI is pin multiplexed with Asynchronous EMIF at the output pin. HPI is available only when boot mode selected is HPI boot mode. In this configuration, the device will always act as a slave. |
|||||||
| EM_D13 / GIO62 / HD13 | P19 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / GIO / HPI | VDD_AEMIF1_18_33 | Input | Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[13] | |
| GIO: GIO[62] | |||||||
| HPI: Data bus bit [13] Note: HPI is pin multiplexed with Asynchronous EMIF at the output pin. HPI is available only when boot mode selected is HPI boot mode. In this configuration, the device will always act as a slave. |
|||||||
| EM_D12 / GIO61 / HD12 | P15 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / GIO / HPI | VDD_AEMIF1_18_33 | Input | Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[12] | |
| GIO: GIO[61] | |||||||
| HPI: Data bus bit [12] Note: HPI is pin multiplexed with Asynchronous EMIF at the output pin. HPI is available only when boot mode selected is HPI boot mode. In this configuration, the device will always act as a slave. |
|||||||
| EM_D11 / GIO60 / HD11 | N16 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / GIO / HPI | VDD_AEMIF1_18_33 | Input | Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[11] | |
| GIO: GIO[60] | |||||||
| HPI: Data bus bit [11] Note: HPI is pin multiplexed with Asynchronous EMIF at the output pin. HPI is available only when boot mode selected is HPI boot mode. In this configuration, the device will always act as a slave. |
|||||||
| EM_D10 / GIO59 / HD10 | N18 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / GIO / HPI | VDD_AEMIF1_18_33 | Input | Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[10] | |
| GIO: GIO[59] | |||||||
| HPI: Data bus bit [10] Note: HPI is pin multiplexed with Asynchronous EMIF at the output pin. HPI is available only when boot mode selected is HPI boot mode. In this configuration, the device will always act as a slave. |
|||||||
| EM_D9 / GIO58 / HD9 | N19 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / GIO / HPI | VDD_AEMIF1_18_33 | Input | Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[09] | |
| GIO: GIO[58] | |||||||
| HPI: Data bus bit [9] Note: HPI is pin multiplexed with Asynchronous EMIF at the output pin. HPI is available only when boot mode selected is HPI boot mode. In this configuration, the device will always act as a slave. |
|||||||
| EM_D8 / GIO57 / HD8 | N15 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / GIO / HPI | VDD_AEMIF1_18_33 | Input | Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[08] | |
| GIO: GIO[57] | |||||||
| HPI: Data bus bit [8] Note: HPI is pin multiplexed with Asynchronous EMIF at the output pin. HPI is available only when boot mode selected is HPI boot mode. In this configuration, the device will always act as a slave. |
|||||||
| EM_D7 / HD7 | L16 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / HPI | VDD_AEMIF2_18_33 | Input | Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[07] | |
| HPI: Data bus bit [7] Note: HPI is pin multiplexed with Asynchronous EMIF at the output pin. HPI is available only when boot mode selected is HPI boot mode. In this configuration, the device will always act as a slave. |
|||||||
| EM_D6 / HD6 | L18 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / HPI | VDD_AEMIF2_18_33 | Input | Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[06] | |
| HPI: Data bus bit [6] Note: HPI is pin multiplexed with Asynchronous EMIF at the output pin. HPI is available only when boot mode selected is HPI boot mode. In this configuration, the device will always act as a slave. |
|||||||
| EM_D5 / HD5 | L19 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / HPI | VDD_AEMIF2_18_33 | Input | Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[05] | |
| HPI: Data bus bit [5] Note: HPI is pin multiplexed with Asynchronous EMIF at the output pin. HPI is available only when boot mode selected is HPI boot mode. In this configuration, the device will always act as a slave. |
|||||||
| EM_D4 / HD4 | L15 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / HPI | VDD_AEMIF2_18_33 | Input | Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[04] | |
| HPI: Data bus bit [4] Note: HPI is pin multiplexed with Asynchronous EMIF at the output pin. HPI is available only when boot mode selected is HPI boot mode. In this configuration, the device will always act as a slave. |
|||||||
| EM_D3 / HD3 | K15 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / HPI | VDD_AEMIF2_18_33 | Input | Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[03] | |
| HPI: Data bus bit [3] Note: HPI is pin multiplexed with Asynchronous EMIF at the output pin. HPI is available only when boot mode selected is HPI boot mode. In this configuration, the device will always act as a slave. |
|||||||
| EM_D2 / HD2 | K19 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / HPI | VDD_AEMIF2_18_33 | Input | Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[02] | |
| HPI: Data bus bit [2] Note: HPI is pin multiplexed with Asynchronous EMIF at the output pin. HPI is available only when boot mode selected is HPI boot mode. In this configuration, the device will always act as a slave. |
|||||||
| EM_D1 / HD1 | K16 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / HPI | VDD_AEMIF2_18_33 | Input | Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[01] | |
| HPI: Data bus bit [1] Note: HPI is pin multiplexed with Asynchronous EMIF at the output pin. HPI is available only when boot mode selected is HPI boot mode. In this configuration, the device will always act as a slave. |
|||||||
| EM_D0 / HD0 | K18 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / HPI | VDD_AEMIF2_18_33 | Input | Async EMIF: Data Bus bit[00] | |
| HPI: Data bus bit [0] Note: HPI is pin multiplexed with Asynchronous EMIF at the output pin. HPI is available only when boot mode selected is HPI boot mode. In this configuration, the device will always act as a slave. |
|||||||
| EM_CE[0] / GIO56 / HCS | M17 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / GIO / HPI | VDD_AEMIF1_18_33 | Output | Async EMIF: Lowest numbered Chip Select. Can be programmed to be used for standard asynchronous memories (example:flash), OneNand or NAND memory. Used for the default boot and ROM boot modes. | |
| GIO: GIO[56] | |||||||
| HPI: this pin is HPI chip select input. Note: HPI is pin multiplexed with Asynchronous EMIF at the output pin. HPI is available only when boot mode selected is HPI boot mode. In this configuration, the device will always act as a slave. |
|||||||
| EM_CE[1] / GIO55 / HAS | J17 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / GIO / HPI | VDD_AEMIF2_18_33 | Output | Async EMIF: Second Chip Select., Can be programmed to be used for standard asynchronous memories (example: flash), OneNand or NAND memory. | |
| GIO: GIO[55] | |||||||
| HPI: This pin is host address strobe. Note: HPI is pin multiplexed with Asynchronous EMIF at the output pin. HPI is available only when boot mode selected is HPI boot mode. In this configuration, the device will always act as a slave. |
|||||||
| EM_WE / GIO54 / HDS2 | J15 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / GIO / HPI | VDD_AEMIF2_18_33 | Output | Async EMIF: Write Enable | |
| GIO: GIO[54] | |||||||
| HPI: This pin is host data strobe input 2. Note: HPI is pin multiplexed with Asynchronous EMIF at the output pin. HPI is available only when boot mode selected is HPI boot mode. In this configuration, the device will always act as a slave. |
|||||||
| EM_OE / GIO53 / HDS1 | J19 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / GIO / HPI | VDD_AEMIF2_18_33 | Output | Async EMIF: Output Enable | |
| GIO: GIO[53] | |||||||
| HPI: This pin is host data strobe input 1. | |||||||
| EM_WAIT / GIO52 / HRDY | J18 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / GIO / HPI | VDD_AEMIF2_18_33 | IPU | Input | Async EMIF: Async WAIT |
| GIO: GIO[52] | |||||||
| HPI: This pin is host ready output from DSP to host. | |||||||
| EM_ADV / GIO51 / HR/W | M16 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / GIO / HPI | VDD_AEMIF1_18_33 | Output | Async EMIF: Address Valid Detect for OneNAND interface | |
| GIO: GIO[51] | |||||||
| HPI: This pin is host read or write select input. | |||||||
| EM_CLK / GIO50 | M15 | I/O/Z | AEMIF / GIO | VDD_AEMIF1_18_33 | Output | Async EMIF: Clock signal for OneNAND flash interface | |
| GIO: GIO[50] | |||||||
| GIO49 / McBSP_DX | D5 | I/O/Z | GIO / McBSP | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[49] |
| McBSP: Transmit Data | |||||||
| GIO48 / McBSP_CLKX | A5 | I/O/Z | GIO / McBSP | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[48] |
| McBSP: Transmit Clock | |||||||
| GIO47 / McBSP_FSX | C6 | I/O/Z | GIO / McBSP | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[47] |
| McBSP: Transmit Frame Sync | |||||||
| GIO46 / McBSP_DR | E6 | I/O/Z | GIO / McBSP | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[46] |
| McBSP: Receive Data | |||||||
| GIO45 / McBSP_CLKR | B6 | I/O/Z | GIO / McBSP | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[45] |
| McBSP: Receive Clock | |||||||
| GIO44 / McBSP_FSR | E7 | I/O/Z | GIO / McBSP | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[44] |
| McBSP: Receive Frame Sync | |||||||
| GIO43 / MMCSD1_CLK / EM_A20 | T6 | I/O/Z | GIO / MMCSD1 / AEMIF | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[43] |
| MMCSD1: Clock | |||||||
| Async EMIF: Address bit[20] | |||||||
| GIO42 / MMCSD1_CMD / EM_A19 | R6 | I/O/Z | GIO / MMCSD1 / AEMIF | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[42] |
| MMCSD1: Command | |||||||
| Async EMIF: Address bit[19] | |||||||
| GIO41 / MMCSD1_DATA3 / EM_A18 | W5 | I/O/Z | GIO / MMCSD / AEMIF | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[41] |
| MMCSD1: DATA3 | |||||||
| Async EMIF: Address bit[18] | |||||||
| GIO40 / MMCSD1_DATA2 / EM_A17 | U5 | I/O/Z | GIO / MMCSD1 / AEMIF | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[40] |
| MMCSD1: DATA2 | |||||||
| Async EMIF: Address bit[17] | |||||||
| GIO39 / MMCSD1_DATA1 / EM_A16 | R5 | I/O/Z | GIO / MMCSD1 / AEMIF | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[39] |
| MMCSD1: DATA1 | |||||||
| Async EMIF: Address bit[16] | |||||||
| GIO38 / MMCSD1_DATA0 / EM_A15 | V5 | I/O/Z | GIO / MMCSD1 / AEMIF | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[38] |
| MMCSD1: DATA0 | |||||||
| Async EMIF: Address bit[15] | |||||||
| GIO37 / SPI4_SCS[0]/ McBSP_CLKS / CLKOUT0 | T5 | I/O/Z | GIO / SPI4 / McBSP / CLKOUT | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[37] |
| SPI4: SPI4 Chip Select 0 | |||||||
| McBSP: CLKS pin to source an external clock | |||||||
| CLKOUT: Output Clock 0 | |||||||
| GIO36 / SPI4_SCLK / EM_A21 / EM_A14 | W4 | I/O/Z | GIO / SPI4 / AEMIF | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[36] |
| SPI4: Clock | |||||||
| Async EMIF: Address bit[21] | |||||||
| Async EMIF: Address bit[14] | |||||||
| GIO35 / SPI4_SOMI / SPI4_SCS[1] / CLKOUT1 | W3 | I/O/Z | GIO / SPI4 /CLKOUT | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[35] |
| SPI4: Slave Out Master In data | |||||||
| SPI4: SPI4 Chip Select 1 | |||||||
| CLKOUT: Output Clock 1 | |||||||
| GIO34 / SPI4_SIMO / SPI4_SOMI / UART1_RXD | V4 | I/O/Z | GIO / SPI4 / UART1 | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[34] |
| SPI4: Slave In Master Out data | |||||||
| SPI4: Slave Out Master In data. | |||||||
| UART1: RXD | |||||||
| GIO33 / SPI2_SCS[0] / USBDRVVBUS / R1 | V3 | I/O/Z | GIO / SPI2 / USB /VENC | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[33] |
| SPI3: SPI3 Chip Select 0 | |||||||
| USB: USB: Digital output to control external 5 V supply | |||||||
| VENC: Red output data bit 1 | |||||||
| GIO32 / SPI2_SCLK / R0 | W2 | I/O/Z | GIO / SPI2 / VENC | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[32] |
| SPI2: Clock | |||||||
| VENC: Red output data bit 0 | |||||||
| GIO31 / SPI2_SOMI / SPI2_SCS[1] / CLKOUT2 | U4 | I/O/Z | GIO / SPI2 / CLKOUT | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[31] |
| SPI2: Slave Out Master In data | |||||||
| SPI2: SPI2 Chip Select 1 | |||||||
| CLKOUT: Output Clock 2 | |||||||
| GIO30 / SPI2_SIMO / G1 | T4 | I/O/Z | GIO / SPI2 / VENC | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[30] |
| SPI2: Slave In Master Out data | |||||||
| VENC: Green output data bit 1 | |||||||
| GIO29 / SPI1_SCS[0] / G0 | U2 | I/O/Z | GIO / SPI1 / VENC | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[29] |
| SPI1: SPI1 Chip Select 0 | |||||||
| VENC: Green output data bit 0 | |||||||
| GIO28 / SPI1_SCLK / B1 | V1 | I/O/Z | GIO / SPI1 / VENC | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[28] |
| SPI1: Clock | |||||||
| VENC: Blue output data bit 1 | |||||||
| GIO27 / SPI1_SOMI / SPI1_SCS[1] / B0 | T2 | I/O/Z | GIO / SPI1 / VENC | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[27] |
| SPI1: Slave Out Master In data | |||||||
| SPI1: SPI1 Chip Select 1 | |||||||
| VENC: Blue output data bit 1 | |||||||
| GIO26 / SPI1_SIMO | U1 | I/O/Z | GIO / SPI1 | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[26] |
| SPI1: Slave In Master Out data | |||||||
| GIO25 / SPI0_SCS[0] / PWM1 / UART1_TXD | T1 | I/O/Z | GIO / SPI0 / PWM1 / UART1 | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[25] |
| SPI0: SPI0 Chip Select 0 | |||||||
| PWM1: Output | |||||||
| UART1: Transmit data | |||||||
| GIO24 / SPI0_SCLK | T3 | I/O/Z | GIO / SPI0 | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[24] |
| SPI0: Clock | |||||||
| GIO23 / SPI0_SOMI / SPI0_SCS[1] / PWM0 | V2 | I/O/Z | GIO / SPI0 / PWM0 | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[23] |
| SPI0: Slave Out Master In data | |||||||
| SPI0: SPI0 Chip Select 1 | |||||||
| PWM0: Output | |||||||
| GIO22 / SPI0_SIMO | R2 | I/O/Z | GIO / SPI0 | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[22] |
| SPI0: Slave In Master Out data | |||||||
| GIO21 / UART1_RTS / I2C_SDA | F3 | I/O/Z | GIO / UART1 / I2C | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[21] |
| UART1: RTS | |||||||
| I2C: Serial Data | |||||||
| GIO20 / UART1_CTS / I2C_SCL | F1 | I/O/Z | GIO / UART1 / I2C | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[20] |
| UART1: CTS | |||||||
| I2C: Serial Clock | |||||||
| GIO19 / UART0_RXD | E3 | I/O/Z | GIO / UART0 | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[19] |
| UART0: Receive data | |||||||
| GIO18 / UART0_TXD | E2 | I/O/Z | GIO / UART0 | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[18] |
| UART0: Transmit data | |||||||
| GIO17 / EMAC_TX_EN / UART1_RXD | E4 | I/O/Z | GIO / EMAC / UART1 | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[17] |
| EMAC: Transmit enable output | |||||||
| UART1: Receive Data | |||||||
| GIO16 / EMAC_TX_CLK / UART1_TXD | E1 | I/O/Z | GIO / EMAC / UART1 | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[16] |
| EMAC: Transmit clock | |||||||
| UART1: Transmit Data | |||||||
| GIO15 / EMAC_COL | D2 | I/O/Z | GIO / EMAC | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[15] |
| EMAC: Collision Detect input | |||||||
| GIO14 / EMAC_TXD3 | D1 | I/O/Z | GIO / EMAC | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[14] |
| EMAC: Transmit Data 3 output | |||||||
| GIO13 / EMAC_TXD2 | D3 | I/O/Z | GIO / EMAC | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[13] |
| EMAC: Transmit Data 2 output | |||||||
| GIO12 / EMAC_TXD1 | C1 | I/O/Z | GIO / EMAC | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[12] |
| EMAC: Transmit Data 1 output | |||||||
| GIO11 / EMAC_TXD0 | B1 | I/O/Z | GIO / EMAC | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[11] |
| EMAC: Transmit Data 0 output | |||||||
| GIO10 / EMAC_RXD3 | B2 | I/O/Z | GIO / EMAC | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[10] |
| EMAC: Receive Data 3 output | |||||||
| GIO9 / EMAC_RXD2 | C2 | I/O/Z | GIO / EMAC | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[09] |
| EMAC: Receive Data 2 output | |||||||
| GIO8 / EMAC_RXD1 | A2 | I/O/Z | GIO / EMAC | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[08] |
| EMAC: Receive Data 1 output | |||||||
| GIO7 / EMAC_RXD0 | A3 | I/O/Z | GIO / EMAC | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[07] |
| EMAC: Receive Data 0 output | |||||||
| GIO6 / EMAC_RX_CLK | B3 | I/O/Z | GIO / EMAC | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[06] |
| EMAC: Receive clock | |||||||
| GIO5 / EMAC_RX_DV | B4 | I/O/Z | GIO / EMAC | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[05] |
| EMAC: Receive data valid input | |||||||
| GIO4 / EMAC_RX_ER | A4 | I/O/Z | GIO / EMAC | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[04] |
| EMAC: Receive error input | |||||||
| GIO3 / EMAC_CRS | C5 | I/O/Z | GIO / EMAC | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[03] |
| EMAC: Carrier sense input | |||||||
| GIO2 / MDIO | C4 | I/O/Z | GIO / EMAC | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[02] |
| EMAC: Management Data I/O | |||||||
| GIO1 / MDCLK | D6 | I/O/Z | GIO / EMAC | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[01] |
| EMAC: Management Data clock output | |||||||
| GIO0 | B5 | I/O/Z | GIO | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | GIO: GIO[00] |
| USB_DP | N1 | A I/O | USBPHY | VDDA33_USB | USB D+ (differential signal pair) Note: If the USB peripheral is not used at all in the application, this pin should be connected to 3.3V . |
||
| USB_DM | P1 | A I/O | USBPHY | VDDA33_USB | USB D- (differential signal pair) Note: If the USB peripheral is not used at all in the application, this pin should be connected to VSS. |
||
| VDDA33_USB | P4 | PWR | 3.3-V USB analog power supply | ||||
| Note: If the USB peripheral is not used at all in the application, this pin should be connected to 3.3V. | |||||||
| VSSA33_USB | P3 | GND | 3.3-V USB ground | ||||
| Note: If the USB peripheral is not used at all in the application, this pin should be connected to VSS. | |||||||
| VDDA12LDO_USB | M5 | PWR | Output | For proper device operation, even if the USB peripheral is not used, a 0.22µF capacitor must be connected as close as possible to the package, and the capacitor mst be connected to VSSA. | |||
| VDDA18_USB | N5 | PWR | 1.8-V USB analog power supply | ||||
| Note: If the USB peripheral is not used at all in the application, this pin should be connected to 1.8V. | |||||||
| VSSA18_USB | P2 | GND | 1.8-V USB ground | ||||
| Note: If the USB peripheral is not used at all in the application, this pin should be connected to VSS. | |||||||
| USB_ID | M1 | A I | USBPHY | VDDA33_USB | USB operating mode identification pin. | ||
| For device mode operation only, pull up this pin to VDD with a 1.5K ohm resistor. | |||||||
| For host mode operation only, pull down this pin to ground (VSS) with a 1.5K ohm resistor. | |||||||
| If using an OTG or mini-USB connector, this pin will be set properly via the cable/connector configuration. Note: If the USB peripheral is not used at all in the application, this pin should be connected to 3.3V. |
|||||||
| USB_VBUS | N2 | A I/O | USBPHY | USB_VBUS | This pin is used by the USB Controller to detect a presence of 5V power (4.4V is the threshold) on the USB_VBUS line for normal operation. This power is sourced by the USB Component that is assuming the role of a Host. In other words, the power on the USB_VBUS line is not sourced by the Device. From DM369 perspective, when operating as a Host, it ensures that the external power supply that the DM369 has sourced is within the required voltage level (>= 4.4V) and when DM369 is operating as a Device, the presence of a 5V power on the VBUS Line is used to signify the presence of an external Host. | ||
| Note 1: When the DM369 is operating as a Device, it uses the power on the USB_VBUS line to power up its internal pullup resistor on the D+ line. | |||||||
| Note2: If the USB peripheral is not used at all in the application, this pin should be connected to VSS. | |||||||
| MMCSD0_CLK | J16 | O | MMCSD0 | VDDS33 | out | MMCSD0: Clock | |
| MMCSD0_CMD | H15 | I/O/Z | MMCSD0 | VDDS33 | Input | MMCSD0: Command | |
| MMCSD0_DATA3 | H16 | I/O/Z | MMCSD0 | VDDS33 | Input | MMCSD0: DATA3 | |
| MMCSD0_DATA2 | H17 | I/O/Z | MMCSD0 | VDDS33 | Input | MMCSD0: DATA2 | |
| MMCSD0_DATA1 | H19 | I/O/Z | MMCSD0 | VDDS33 | Input | MMCSD0: DATA1 | |
| MMCSD0_DATA0 | H18 | I/O/Z | MMCSD0 | VDDS33 | Input | MMCSD0: DATA0 | |
| MICIP | B8 | AI | VCODEC | VDDA33_VC
or VDDA18_VC |
MIC positive input Note: If the Voice Codec peripheral is not used, this pin must be tied directly to VSS for proper device operation. |
||
| MICIN | C8 | AI | VCODEC | VDDA33_VC
or VDDA18_VC |
MIC negative input Note: If the Voice Codec peripheral is not used, this pin must be tied directly to VSS for proper device operation. |
||
| LINEO | C9 | AO | VCODEC | VDDA33_VC
or VDDA18_VC |
Line driver output Note: If the Voice Codec peripheral is not used, this pin can be left open or can be connected directly to Vss for proper device operation. |
||
| SPP | B9 | AO | VCODEC | VDDA33_VC
or VDDA18_VC |
Speaker amplifier positive output Note: If the Voice Codec peripheral is not used, this pin can be left open or can be connected directly to Vss for proper device operation. |
||
| SPN | A9 | AO | VCODEC | VDDA33_VC
or VDDA18_VC |
Speaker amplifier negative output Note: If the Voice Codec peripheral is not used, this pin can be left open or can be connected directly to Vss for proper device operation. |
||
| VCOM | A8 | AO | VCODEC | VDDA33_VC
or VDDA18_VC |
Analog block common voltage. It is recommended that a 10µF capacitor be connected between this pin and ground to provide clean voltage. Note: If the Voice Codec peripheral is not used, this pin must be tied directly to VSS for proper device operation. |
||
| VDDA18_VC | E9 | PWR | 1.8-V Voice Codec module analog power supply Note: If the Voice Codec peripheral is not used, this pin must be tied directly to VSS for proper device operation. |
||||
| VSSA18_VC | F9 | GND | 1.8-V Voice Codec module ground Note: If the Voice Codec peripheral is not used, this pin must be tied directly to VSS for proper device operation. |
||||
| VDDA33_VC | E10 | PWR | 3.3-V Voice Codec module power supply Note: If the Voice Codec peripheral is not used, this pin must be tied directly to VSS for proper device operation. |
||||
| VSSA33_VC | D9 | GND | 3.3-V Voice Codec module ground Note: If the Voice Codec peripheral is not used, this pin must be tied directly to VSS for proper device operation. |
||||
| ADC_CH0 | E8 | AI | ADC | VDDA18_ADC | Analog-to-Digital converter channel 0 Note: If the ADC is not used, it is recommended to either leave this pin open, as no connect, or tie this pin along with the other ADC_CHs together to a single resistor to ground. |
||
| ADC_CH1 | B7 | AI | ADC | VDDA18_ADC | Analog-to-Digital converter channel 1 Note: If the ADC is not used, it is recommended to either leave this pin open, as no connect, or tie this pin along with the other ADC_CHs together to a single resistor to ground. |
||
| ADC_CH2 | A7 | AI | ADC | VDDA18_ADC | Analog-to-Digital converter channel Note: If the ADC is not used, it is recommended to either leave this pin open, as no connect, or tie this pin along with the other ADC_CHs together to a single resistor to ground. |
||
| ADC_CH3 | D8 | AI | ADC | VDDA18_ADC | Analog-to-Digital converter channel 3 Note: If the ADC is not used, it is recommended to either leave this pin open, as no connect, or tie this pin along with the other ADC_CHs together to a single resistor to ground. |
||
| ADC_CH4 | D7 | AI | ADC | VDDA18_ADC | Analog-to-Digital converter channel 4 Note: If the ADC is not used, it is recommended to either leave this pin open, as no connect, or tie this pin along with the other ADC_CHs together to a single resistor to ground. |
||
| ADC_CH5 | A6 | AI | ADC | VDDA18_ADC | Analog-to-Digital converter channel 5 Note: If the ADC is not used, it is recommended to either leave this pin open, as no connect, or tie this pin along with the other ADC_CHs together to a single resistor to ground. |
||
| VDDA18_ADC | G9 | PWR | 1.8- V Analog-to-Digital converter analog power supply Note: If the ADC is not used at all in an application, this pin can be directly connected to the 1.8-V supply without any filtering or to ground. |
||||
| VSSA_ADC | F8 | GND | 1.8- V Analog-to-Digital converter ground | ||||
| PWCTRIO0 | J3 | I/O/Z | PRTCSS | VDD18_PRTCSS | Input | PRTCSS: General Input / Output Signal 0 For more pin termination details, see Section 7.7, Power Management and Real Time Clock Subsystem (PRTCSS). |
|
| PWCTRIO1 | J2 | I/O/Z | PRTCSS | VDD18_PRTCSS | Input | PRTCSS: General Input / Output Signal 1 For more pin termination details, see Section 7.7, Power Management and Real Time Clock Subsystem (PRTCSS). |
|
| PWCTRIO2 | J1 | I/O/Z | PRTCSS | VDD18_PRTCSS | Input | PRTCSS: General Input / Output Signal 2 For more pin termination details, see Section 7.7, Power Management and Real Time Clock Subsystem (PRTCSS). |
|
| PWCTRIO3 | J5 | I/O/Z | PRTCSS | VDD18_PRTCSS | Input | PRTCSS: General Input / Output Signal 3 For more pin termination details, see Section 7.7, Power Management and Real Time Clock Subsystem (PRTCSS). |
|
| PWCTRIO4 | J4 | I/O/Z | PRTCSS | VDD18_PRTCSS | Input | PRTCSS: General Input / Output Signal 4 For more pin termination details, see Section 7.7, Power Management and Real Time Clock Subsystem (PRTCSS). |
|
| PWCTRIO5 | K5 | I/O/Z | PRTCSS | VDD18_PRTCSS | Input | PRTCSS: General Input / Output Signal 5 For more pin termination details, see Section 7.7, Power Management and Real Time Clock Subsystem (PRTCSS). |
|
| PWCTRIO6 | K4 | I/O/Z | PRTCSS | VDD18_PRTCSS | Input | PRTCSS: General Input / Output Signal 6 For more pin termination details, see Section 7.7, Power Management and Real Time Clock Subsystem (PRTCSS). |
|
| PWCTRO0 | K2 | O | PRTCSS | VDD18_PRTCSS | Output | PRTCSS: General Output Signal 0 For more pin termination details, see Section 7.7, Power Management and Real Time Clock Subsystem (PRTCSS). |
|
| PWCTRO1 | L5 | O | PRTCSS | VDD18_PRTCSS | Output | PRTCSS: General Output Signal 1 For more pin termination details, see Section 7.7, Power Management and Real Time Clock Subsystem (PRTCSS). |
|
| PWCTRO2 | L4 | I/O/Z | PRTCSS | VDD18_PRTCSS | Output | PRTCSS: General Output Signal 2 For more pin termination details, see Section 7.7, Power Management and Real Time Clock Subsystem (PRTCSS). |
|
| PWCTRO3 | L3 | O | PRTCSS | VDD18_PRTCSS | Output | PRTCSS: General Output Signal 3 For more pin termination details, see Section 7.7, Power Management and Real Time Clock Subsystem (PRTCSS). |
|
| RTCXI | G1 | I | PRTCSS | VDD12_PRTCSS | Input | PRTCSS: Crystal Input for PRTCSS oscillator Note: If the RTC calendar is not used, this pin should be pulled down. For more pin termination details, see Section 7.7, Power Management and Real Time Clock Subsystem (PRTCSS). |
|
| RTCXO | H1 | O | PRTCSS | VDD12_PRTCSS | Output | PRTCSS: Crystal Output for PRTCSS oscillator Note: If the RTC calendar is not used, this pin should be left unconnected. For more pin termination details, see Section 7.7, Power Management and Real Time Clock Subsystem (PRTCSS). |
|
| PWRST | M3 | I | PRTCSS | VDD12_PRTCSS | Input | PRTCSS: Reset signal for PRTCSS For more pin termination details, see Section 7.7, Power Management and Real Time Clock Subsystem (PRTCSS). |
|
| PWRCNTON | M2 | I | PRTCSS | VDD12_PRTCSS | Input | PRTCSS: Reset pin for system power sequencing For more pin details, see Section 7.7. |
|
| RESET | H3 | I | VDDS33 | Input | Global chip reset | ||
| MXI1 | L1 | I | CLOCKS | VDDMXI | Input | Crystal input for system oscillator Note: If an external oscillator is to be used, the external oscillator clock signal should be connected to the MXI1 pin with a 1.8V amplitude. The MXO1 should be left unconnected and the VSS_MX1 signal should be connected to board ground (Vss). |
|
| MXO1 | K1 | O | CLOCKS | VDDMXI | Output | Output for system oscillator Note: If an external oscillator is to be used, the external oscillator clock signal should be connected to the MXI1 pin with a 1.8V amplitude. The MXO1 should be left unconnected and the VSS_MX1 signal should be connected to board ground (Vss). |
|
| TCK | F4 | I | EMULATION | VDDS33 | IPU | Input | JTAG test clock input |
| TDI | F5 | I | EMULATION | VDDS33 | IPU | Input | JTAG test data input |
| TDO | G4 | O | EMULATION | VDDS33 | Output | JTAG test data output | |
| TMS | G2 | I | EMULATION | VDDS33 | IPU | Input | JTAG test mode select |
| TRST | H5 | I | EMULATION | VDDS33 | IPD | Input | JTAG test logic reset |
| RTCK | F2 | O | EMULATION | VDDS33 | Output | JTAG test clock output | |
| EMU0 | G5 | I/O | EMULATION | VDDS33 | IPU | Input | JTAG emulation 0 I/O |
| EMU1 | H4 | I/O | EMULATION | VDDS33 | IPU | Input | JTAG emulation 1 I/O |
| EMU[1:0] = 00 - Force Debug Scan chain (ARM and ARM ETB TAPs connected) | |||||||
| EMU[1:0] = 11 - Normal Scan chain (ICEpick only) | |||||||
| RSV2 | R4 | I | For proper device operation, this pin must be tied to ground. | ||||
| RSV1 | R1 | O | For proper device operation, this pin must be left unconnected. | ||||
| RSV0 | A1 | O | For proper device operation, this pin must be left unconnected. | ||||
| CVDD | G6 | PWR | Core power (1.35-V). | ||||
| G8 | |||||||
| H7 | |||||||
| H8 | |||||||
| H12 | |||||||
| J8 | |||||||
| J12 | |||||||
| J14 | |||||||
| K8 | |||||||
| K12 | |||||||
| L13 | |||||||
| M6 | |||||||
| M10 | |||||||
| M12 | |||||||
| M13 | |||||||
| VDD12_PRTCSS | J6 | PWR | Power supply for RTC oscillator, PRTCSS, and PRTCSS I/O (1.35-V). | ||||
| K7 | |||||||
| VDDA18_PLL | N4 | PWR | Analog power for PLL (1.8 V). | ||||
| VDDRAM | D4 | O | Output | For proper device operation, this pin must be connected to a 1.0uF (6.2V) capacitor, and the other end of the capacitor must be connected to Vss. Note: this pin is an internal power supply pin and should not be connected to any external power supply.” |
|||
| VDDS18 | G14 | PWR | Power supply for 1.8-V I/O. | ||||
| H11 | |||||||
| H14 | |||||||
| J7 | |||||||
| M14 | |||||||
| P7 | |||||||
| VDD18_PRTCSS | K6 | PWR | Power supply for PRTCSS (1.8 V). | ||||
| VDDMXI | L6 | PWR | Power supply for PLL oscillator (1.8 V). | ||||
| VDD18_SLDO | E5 | PWR | Power supply for internal RAM. For proper device operation, this pin must always be connected to VDDS18. |
||||
| VDD18_DDR | N9 | PWR | Power supply for DDR (1.8 V). | ||||
| N11 | |||||||
| P9 | |||||||
| P10 | |||||||
| P12 | |||||||
| R12 | |||||||
| VDDS33 | F10 | PWR | Power supply for 3.3-V I/O. | ||||
| F6 | |||||||
| F7 | |||||||
| H6 | |||||||
| H13 | |||||||
| L12 | |||||||
| N6 | |||||||
| P5 | |||||||
| P6 | |||||||
| VDD_AEMIF1_18_33 | P14 | PWR | Power supply for switchable AEMIF (3.3/1.8 V). VDD_AEMIF1_18_33 : can be used as a power supply for EM_A[3:13], EM_BA0, EM_BA1, EM_CE[0], EM_ADV, EM_CLK, EM_D[8:15] or as GPIO pins. See AEMIF pin descriptions. VDD_AEMIF2_18_33: can be used as a power supply for EM_A[0:2], EM_CE[1], EM_WE, EM_OE, EM_WAIT, EM_D[0:7] pins, HPI, or GPIO pins. See AEMIF pin descriptions. Example 1: VDD_AEMIF2_18_33 at 1.8-V for 8-bit NAND VDD_AEMIF1_18_33 at 3.3-V for GPIO. Example 2: VDD_AEMIF1_18_33 and VDD_AEMIF2_18_33 at 1.8-V for 16-bit NAND. |
||||
| R14 | |||||||
| VDD_AEMIF2_18_33 | K14 | PWR | |||||
| L14 | |||||||
| VDD_ISIF18_33 | F12 | PWR | Power supply for switchable ISIF (3.3/1.8 V). Example 1 VDD_ISIF_18_33 power supply can be at 1.8V for VPFE pin functionality or it can be at 3.3V if other peripherals pin functionality is to be used like SPI3 or GPIO or CLKOUT0, or USBDRVVBUS. |
||||
| F13 | PWR | ||||||
| VPP | R3 | PWR | For proper device operation, this pin must always be connected to CVDD. | ||||
| VSS | A19 | GND | Digital ground | ||||
| E14 | |||||||
| F14 | |||||||
| G11 | |||||||
| G12 | |||||||
| H9 | |||||||
| H10 | |||||||
| J9 | |||||||
| J10 | |||||||
| J11 | |||||||
| J13 | |||||||
| K9 | |||||||
| K10 | |||||||
| K11 | |||||||
| L7 | |||||||
| L8 | |||||||
| L9 | |||||||
| L10 | |||||||
| L11 | |||||||
| M7 | |||||||
| M8 | |||||||
| M9 | |||||||
| M11 | |||||||
| N8 | |||||||
| N12 | |||||||
| N14 | |||||||
| P8 | |||||||
| P13 | |||||||
| W1 | |||||||
| W19 | |||||||
| VSS_MX1 | L2 | GND | System oscillator - ground Note: If an external oscillator is used, this pin must be connected to board ground (Vss). |
||||
| VSS_32K | H2 | GND | PRTCSS oscillator - ground | ||||
| VSSA | M4 | GND | Analog ground |
IF YCINSWP bit is 0 (default) YIN[7:0] = Y signal / CIN[7:0] = C signal .
IF YCINSWP bit is 1 YIN[7:0] = C signal / CIN[7:0] = Y signal
For more information, see the TMS320DM36x Video Processing Front End (VPFE) User's Guide (SPRUFG8).
![TMS320DM369 ZCE Pin Map [Quadrant
A] TMS320DM369 quada_pinmap_prs457.gif](/ods/images/SPRS867A/quada_pinmap_prs457.gif)
![TMS320DM369 ZCE Pin Map [Quadrant
B]
TMS320DM369 quadb_pinmap_prs457.gif](/ods/images/SPRS867A/quadb_pinmap_prs457.gif)
![TMS320DM369 ZCE Pin Map [Quadrant
C] TMS320DM369 quadc_pinmap_prs457.gif](/ods/images/SPRS867A/quadc_pinmap_prs457.gif)
![TMS320DM369 ZCE Pin Map [Quadrant
D] TMS320DM369 quadd_pinmap_prs457.gif](/ods/images/SPRS867A/quadd_pinmap_prs457.gif)