SLIS136C September 2011 – September 2019 TPL0501-100
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DCN|8
Orderable Information
7.4.1 Voltage Divider Mode
The digital potentiometer generates a voltage divider when all three terminals are used. The voltage divider at wiper-to-H and wiper-to-L is proportional to the input voltage at H to L (see Figure 12).
 Figure 12. Equivalent Circuit for Voltage Divider Mode
Figure 12. Equivalent Circuit for Voltage Divider Mode For example, connecting terminal H to 5 V and terminal L to ground, the output voltage at terminal W can range from 0 V to 5 V (see Equation 1).
Equation 1. 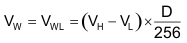
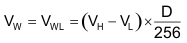
The voltage difference between terminal H and terminal W can also be calculated in Equation 2.
Equation 2. 

where
- D is the decimal value of the wiper code.