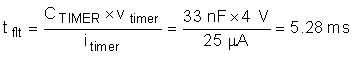SLVS503F November 2003 – February 2020 TPS2490 , TPS2491
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DGS|10
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2.2.4 Set Fault Timer
The fault timer runs when the hot swap is in power limit or current limit, which is the case during start-up. Thus the timer has to be sized large enough to prevent a time-out during start-up. If the part starts directly into current limit (ILIM x VDS < PLIM) the maximum start time can be computed with Equation 17:
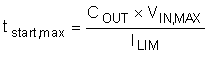
For most designs (including this example) ILIM x VDS > PLIM so the hot swap will start in power limit and transition into current limit. In that case the start time can be computed as follows:
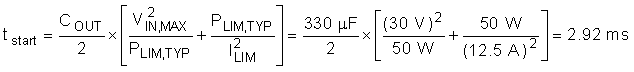
The actual startup time is slightly longer, as the power limit is a function of VDS and decreases as the output voltage increases. To ensure that the timer never times out during start-up, TI recommends to set the fault time (tflt) to be 1.75 x tstart or 5.11ms. This accounts for the variation in power limit, timer current, and timer capacitance. Thus CTIMER can be computed as follows:
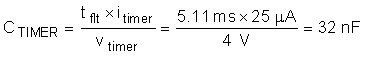
The next largest available CTIMER is chosen as 33 nF. Once the CTIMER is chosen the actual programmed fault time can be computed as follows: