SLVSGG5C november 2021 – april 2023 TPS2597
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO and UVP)
- 8.3.2 Overvoltage Lockout (OVLO)
- 8.3.3 Overvoltage Clamp (OVC)
- 8.3.4 Inrush Current, Overcurrent, and Short Circuit Protection
- 8.3.5 Analog Load Current Monitor
- 8.3.6 Overtemperature Protection (OTP)
- 8.3.7 Fault Response and Indication (FLT)
- 8.3.8 Power-Good Indication (PG)
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RPW|10
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.3.4.3 Active Current Limiting
The active current limit variants (TPS25970x and TPS25972x) respond to output overcurrent conditions by actively limiting the current after a user adjustable transient fault blanking interval. When the load current exceeds the set overcurrent threshold (ILIM) set by the ILM pin resistor (RILM), but stays lower than the short-circuit threshold (2 × ILIM), the device starts discharging the ITIMER pin capacitor using an internal 2-μA pulldown current. If the load current drops below the overcurrent threshold before the ITIMER capacitor (CITIMER) discharges by ΔVITIMER, the ITIMER is reset by pulling it up to VINT internally and the current limit action is not engaged. This event allows short load transient pulses to pass through the device without getting current limited. If the overcurrent condition persists, the CITIMER continues to discharge and after it discharges by ΔVITIMER, the current limit starts regulating the HFET to actively limit the current to the set overcurrent threshold (ILIM). At the same time, the CITIMER is charged up to VINT again so that it is at its default state before the next overcurrent event. This event ensures the full blanking timer interval is provided for every overcurrent event. Use Equation 7 to calculate the RILM value for a desired overcurrent threshold.
- Leaving the ILM pin open sets the current limit to nearly zero and results in the part entering current limit with the slightest amount of loading at the output.
- The current limit circuit employs a foldback mechanism. The current limit threshold in the foldback region (0 V < VOUT < VFB) is lower than the steady state current limit threshold (ILIM).
- Shorting the ILM pin to ground at any point during normal operation is detected as a fault and the part shuts down. There’s a minimum current (IFLT) which the part allows in this condition before the pin short condition is detected.
The duration for which transients are allowed can be adjusted using an appropriate capacitor value from ITIMER pin to ground. Use Equation 8 to calculate the CITIMER value needed to set the desired transient overcurrent blanking interval.
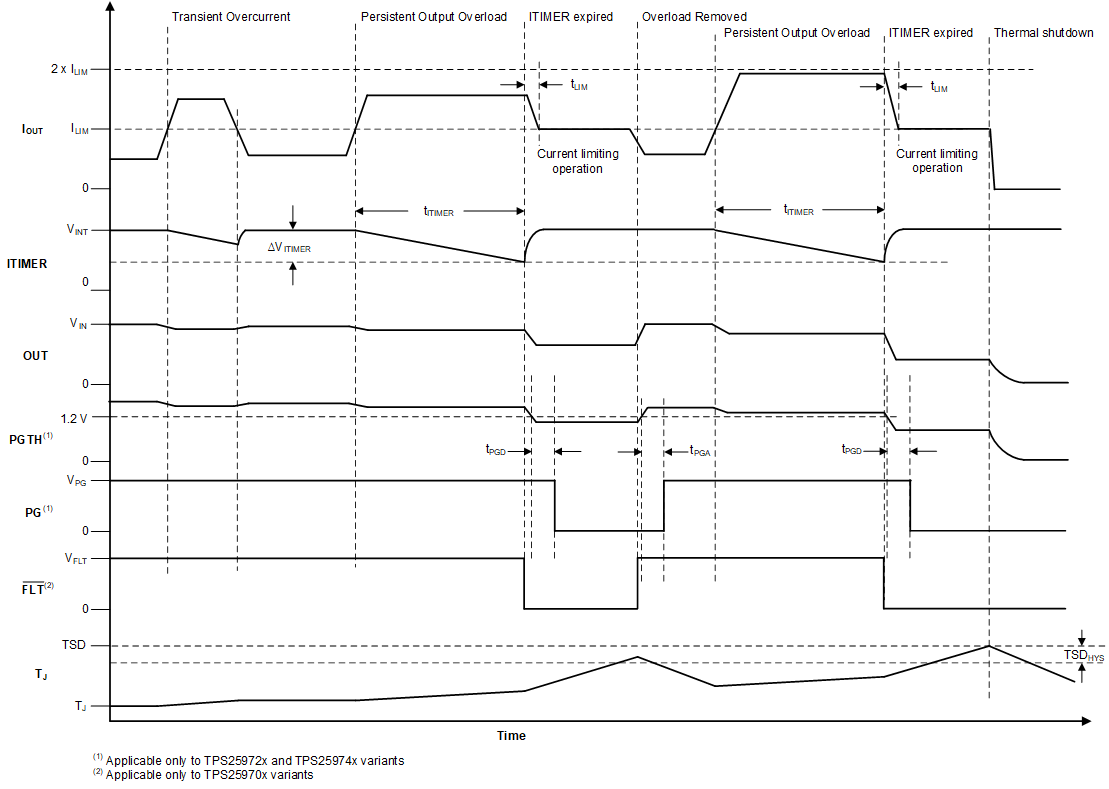 Figure 8-10 TPS25970x and TPS25972x Active Current Limit Response
Figure 8-10 TPS25970x and TPS25972x Active Current Limit Response- Leave the ITIMER pin open to allow the part to limit the current with the minimum possible delay.
- Shorting the ITIMER pin to ground results in minimum overcurrent response delay (similar to ITIMER pin open condition), but increases the device current consumption. This action is not a recommended mode of operation.
- Active current limiting based on RILM is active during start-up for TPS25970x, TPS25972x (active current limit) as well as TPS25974x (circuit-breaker) variants. In case the start-up current exceeds ILIM, the device regulates the current to the set limit. However, during start-up the current limit is engaged without waiting for the ITIMER delay.
- For the TPS25972x variants, during overvoltage clamp condition, if an overcurrent event occurs, the current limit is engaged without waiting for the ITIMER delay.
- Increasing the CITIMER value extends the overcurrent blanking interval, but it also extends the time needed for the CITIMER to recharge up to VINT. If the next overcurrent event occurs before the CITIMER is recharged fully, it takes lesser time to discharge to the ITIMER expiry threshold, thereby providing a shorter blanking interval than intended.
During active current limit, the output voltage drops, resulting in increased device power dissipation across the HFET. If the device internal temperature (TJ) exceeds the thermal shutdown threshold (TSD), the HFET is turned off. After the part shuts down due to TSD fault, it either stays latched off (TPS2597xL variants) or restarts automatically after a fixed delay (TPS2597xA variants). See Overtemperature Protection (OTP) for more details on device response to overtemperature.