SLVSE42B October 2017 – September 2019 TPS27S100
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|14
Orderable Information
7.3.4.4 Thermal Fault Detection
To protect the device in severe power stressing cases, the device implements two types of thermal fault detection, absolute temperature protection (thermal shutdown) and dynamic temperature protection (thermal swing). Respective temperature sensors are integrated close to each power FET, so the thermal fault is reported by each channel. This arrangement can help the device keep the cross-channel effect to a minimum when some channels are in a thermal fault condition.
Thermal shutdown is active when the absolute temperature TJ > T(SD). When thermal shutdown occurs, the respective output turns off.
Thermal swing activates when the power FET temperature is increasing sharply, that is, when ΔT = T(FET) – T(Logic) > T(sw), then the output turns off. The output automatically recovers and the fault signal clears when ΔT = T(FET) – T(Logic) < T(sw) – T(hys). Thermal swing function improves the device reliability when subjected to repetitive fast thermal variation.
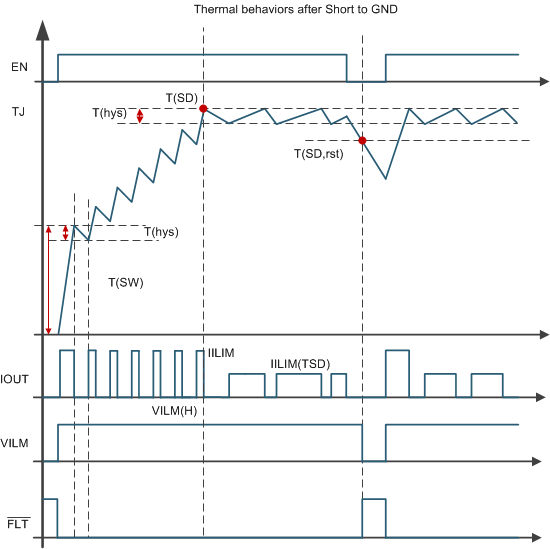 Figure 30. Thermal Behavior Diagram
Figure 30. Thermal Behavior Diagram