SBVS187G February 2012 – February 2019 TPS3700
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power-Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DSE|6
- DDC|6
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
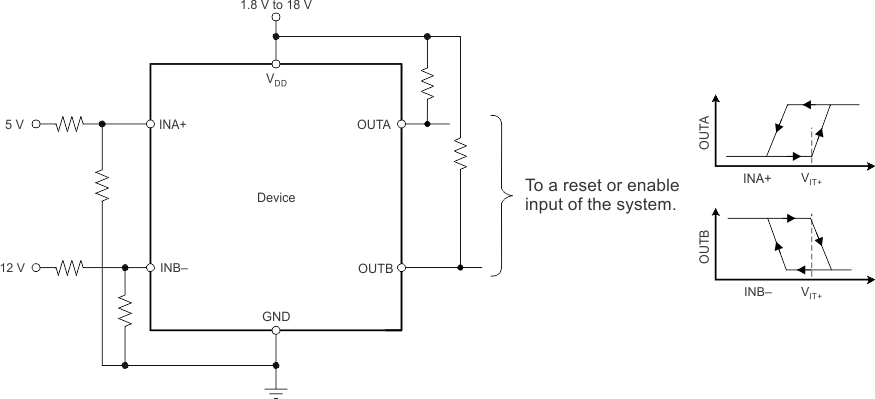
8.1.4 Monitoring Overvoltage and Undervoltage for Separate Rails
Some applications may want to monitor for overvoltage conditions on one rail while also monitoring for undervoltage conditions on a different rail. In these applications two independent resistor dividers must be used.
NOTE:
In this case, OUTA is driven low when an undervoltage condition is detected at the 5-V rail and OUTB is driven low when an overvoltage condition is detected at the 12-V rail.