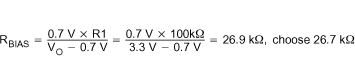SLUS593J December 2003 – June 2022 TPS40054 , TPS40055 , TPS40057
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Setting the Switching Frequency (Programming the Clock Oscillator)
- 7.3.2 Programming The Ramp Generator Circuit
- 7.3.3 UVLO Operation
- 7.3.4 BP5 and BP10 Internal Voltage Regulators
- 7.3.5 Programming Soft Start
- 7.3.6 Programming Current Limit
- 7.3.7 Synchronizing to an External Supply
- 7.3.8 Loop Compensation
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Calculate Maximum and Minimum Duty Cycles
- 8.2.2.2 Select Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.3 Select ΔI
- 8.2.2.4 Calculate the High-Side MOSFET Power Losses
- 8.2.2.5 Calculate Synchronous Rectifier Losses
- 8.2.2.6 Calculate the Inductor Value
- 8.2.2.7 Set the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.8 Program the Ramp Generator Circuit
- 8.2.2.9 Calculate the Output Capacitance (CO)
- 8.2.2.10 Calculate the Soft-Start Capacitor (CSS/SD)
- 8.2.2.11 Calculate the Current Limit Resistor (RILIM)
- 8.2.2.12 Calculate Loop Compensation Values
- 8.2.2.13 Calculate the Boost and BP10V Bypass Capacitance
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2.2.12 Calculate Loop Compensation Values
Calculate the DC modulator gain (AMOD) from Equation 12:
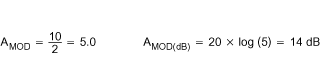
Calculate the output filter L-CO poles and CO ESR zeros from Equation 13 and Equation 14:
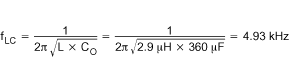
and

Select the close-loop 0 dB crossover frequency, fC. For this example fC = 20 kHz.
Select the double zero location for the Type III compensation network at the output filter double pole at 4.93 kHz.
Select the double pole location for the Type III compensation network at the output capacitor ESR zero at 73.7 kHz.
The amplifier gain at the crossover frequency of 20 kHz is determined by the reciprocal of the modulator gain AMOD at the crossover frequency from Equation 22:

And also from Equation 22:
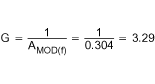
Choose R1 = 100 kΩ
The poles and zeros for a type III network are described in Equation 17 through Equation 21.

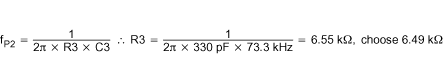

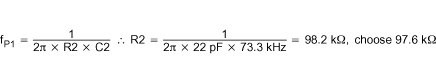

Calculate the value of RBIAS from Equation 15 with R1 = 100 kΩ.