SLUSAQ4G October 2011 – September 2022 TPS40422
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 PMBus Interface Protocol General Description
- 8.3.2 Voltage Reference
- 8.3.3 Output Voltage
- 8.3.4 Voltage Feed Forward
- 8.3.5 Current Sensing
- 8.3.6 Overcurrent Protection
- 8.3.7 Current Sharing
- 8.3.8 Linear Regulators
- 8.3.9 BP Switch-over
- 8.3.10 Switching Frequency Setting
- 8.3.11 Switching Node and BOOT Voltage
- 8.3.12 Reading the Output Current
- 8.3.13 Soft-Start Time
- 8.3.14 Turn-On/Turn-Off Delay and Sequencing
- 8.3.15 Pre-Biased Output Start-Up
- 8.3.16 Undervoltage Lockout
- 8.3.17 Overvoltage and Undervoltage Fault Protection
- 8.3.18 Power Good
- 8.3.19 Overtemperature Fault Protection
- 8.3.20 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.3.21 Programmable Fault Responses
- 8.3.22 User Data
- 8.3.23 Adjustable Anti-Cross Conduction Delay
- 8.3.24 Connection of Unused Pins
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1
Supported Commands
- 8.6.1.1 PAGE (00h)
- 8.6.1.2 OPERATION (01h)
- 8.6.1.3 ON_OFF_CONFIG (02h)
- 8.6.1.4 CLEAR_FAULTS (03h)
- 8.6.1.5 WRITE_PROTECT (10h)
- 8.6.1.6 STORE_USER_ALL (15h)
- 8.6.1.7 RESTORE_USER_ALL (16h)
- 8.6.1.8 CAPABILITY (19h)
- 8.6.1.9 VOUT_MODE (20h)
- 8.6.1.10 VIN_ON (35h)
- 8.6.1.11 VIN_OFF (36h)
- 8.6.1.12 IOUT_CAL_GAIN (38h)
- 8.6.1.13 IOUT_CAL_OFFSET (39h)
- 8.6.1.14 IOUT_OC_FAULT_LIMIT (46h)
- 8.6.1.15 IOUT_OC_FAULT_RESPONSE (47h)
- 8.6.1.16 IOUT_OC_WARN_LIMIT (4Ah)
- 8.6.1.17 OT_FAULT_LIMIT (4Fh)
- 8.6.1.18 OT_WARN_LIMIT (51h)
- 8.6.1.19 TON_RISE (61h)
- 8.6.1.20 STATUS_BYTE (78h)
- 8.6.1.21 STATUS_WORD (79h)
- 8.6.1.22 STATUS_VOUT (7Ah)
- 8.6.1.23 STATUS_IOUT (7Bh)
- 8.6.1.24 STATUS_TEMPERATURE (7Dh)
- 8.6.1.25 STATUS_CML (7Eh)
- 8.6.1.26 STATUS_MFR_SPECIFIC (80h)
- 8.6.1.27 READ_VOUT (8Bh)
- 8.6.1.28 READ_IOUT (8Ch)
- 8.6.1.29 READ_TEMPERATURE_2 (8Eh)
- 8.6.1.30 PMBUS_REVISION (98h)
- 8.6.1.31 MFR_SPECIFIC_00 (D0h)
- 8.6.1.32 VREF_TRIM (MFR_SPECIFIC_04) (D4h)
- 8.6.1.33 STEP_VREF_MARGIN_HIGH (MFR_SPECIFIC_05) (D5h)
- 8.6.1.34 STEP_VREF_MARGIN_LOW (MFR_SPECIFIC_06) (D6h)
- 8.6.1.35 PCT_VOUT_FAULT_PG_LIMIT (MFR_SPECIFIC_07) (D7h)
- 8.6.1.36 126
- 8.6.1.37 SEQUENCE_TON_TOFF_DELAY (MFR_SPECIFIC_08) (D8h)
- 8.6.1.38 128
- 8.6.1.39 OPTIONS (MFR_SPECIFIC_21) (E5h)
- 8.6.1.40 DEVICE_CODE (MFR_SPECIFIC_44) (FCh)
- 8.6.1
Supported Commands
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1
Dual-Output Converter
- 9.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.1.2.1 Custom Design with WEBENCH® Tools
- 9.2.1.2.2 Step 1: Inductor Selection
- 9.2.1.2.3 Step 2: Output Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.1.2.4 Step 3: Input Capacitance Selection
- 9.2.1.2.5 Step 4: MOSFET Selection
- 9.2.1.2.6 Step 5: Snubber Circuit Design
- 9.2.1.2.7 Step 6: Soft-Start Time
- 9.2.1.2.8
Step 7: Peripheral Component Design
- 9.2.1.2.8.1 RT (Pin 1) Switching Frequency Setting
- 9.2.1.2.8.2 FB1 (Pin 2) and FB2 (Pin 8) Output Voltage Setting
- 9.2.1.2.8.3 Compensation Network Using COMP1 (Pin 3) , COMP2 (Pin 7), FB1 (Pin 2) FB2 DIFFO1 (Pin 8) (Pin 39)
- 9.2.1.2.8.4 Remote Sensing Using VSNS1 (Pin 37), GSNS1 (Pin 38) , VSNS2 (Pin 15), and GSNS2 (Pin 14)
- 9.2.1.2.8.5 Temperate Sensing Using TSNS1 (Pin36) and TSNS2 (Pin 16)
- 9.2.1.2.8.6 Current Sensing Network Design Using CS1P (Pin 34), CS1N (Pin 35) , CS2P (Pin 18), and CS2N (Pin 17)
- 9.2.1.2.8.7 PMBus Address ADDR1 (Pin 9) , and ADDR0 (Pin 10)
- 9.2.1.2.8.8
Voltage Decoupling Capacitors
- 9.2.1.2.8.8.1 VDD (Pin 31)
- 9.2.1.2.8.8.2 BP3 (Pin 32)
- 9.2.1.2.8.8.3 BNEXT (Pin 24)
- 9.2.1.2.8.8.4 BP6 (Pin 25)
- 9.2.1.2.8.8.5 Power Good PGOOD1 (Pin 33), PGOOD2 (Pin 19)
- 9.2.1.2.8.8.6 Bootstrap Capacitors BOOT1 (Pin 30), and BOOT2 (Pin 20)
- 9.2.1.2.8.8.7 High-Side MOSFET (Gate) Resistor
- 9.2.1.2.8.8.8 Synchronization Setting SYNC (Pin 40)
- 9.2.1.2.8.8.9 BP6 (Pin 25)
- 9.2.1.2.8.8.10 DIFFO (Pin 39)
- 9.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 9.2.1
Dual-Output Converter
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.3.6 Overcurrent Protection
The TPS4022 device has overcurrent fault and warning thresholds for each channel which can be independently set, when operating in dual-output mode. When operating in two-phase mode, both channels share the same overcurrent fault and warning thresholds. The overcurrent thresholds are set via the PMBus interface using the IOUT_OC_FAULT_LIMIT and IOUT_OC_WARN_LIMIT commands. (See the Section 8.5.1 section for more details.)
The device generates an internal voltage corresponding to the desired overcurrent threshold, using the IOUT_OC_FAULT_LIMIT threshold and the IOUT_CAL_GAIN setting, and adjusting for temperature using the measured external temperature value. The current sense amplifier amplifies the sensed current signal with a fixed gain of 15 and then compares that value to this internal voltage threshold. The device uses a similar structure to activate an overcurrent warning based on the IOUT_OC_WARN_LIMIT threshold.
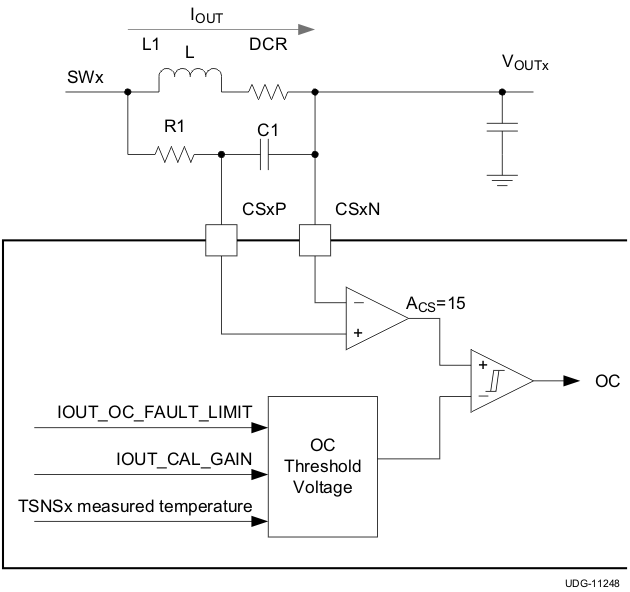 Figure 8-4 Overcurrent Protection
Figure 8-4 Overcurrent ProtectionThe programmable range of the overcurrent fault and warning voltage thresholds places a functional limit on the input voltage of the current sense amplifier. The minimum overcurrent fault and warning thresholds correspond to a voltage from CSxP to CSxN of 6 mV and 4.7 mV, respectively. If the voltage across these pins does not exceed the minimum thresholds, then overcurrent fault and warning cannot be tripped, regardless of the setting of IOUT_OC_FAULT_LIMIT and IOUT_OC_WARN_LIMIT. There is also maximum overcurrent fault and warning thresholds corresponding to a voltage from CSxP to CSxN of 60 mV and 59 mV, respectively. If the voltage across these pins exceeds this maximum threshold, the overcurrent fault or warning will be tripped, regardless of the setting of IOUT_OC_FAULT_LIMIT and IOUT_OC_WARN_LIMIT. The result is that for higher values of inductor DCR, a resistor across the current sensing capacitor may be required to create a voltage divider into the current sensing inputs.
The TPS4022 device implements cycle-by-cycle current limit when the peak sensed current exceeds the set threshold. In a time constant matched current sensor network, the signal across the CSxP and CSxN pins has both dc and ac inductor current information, so an overcurrent fault trips when the dc current plus half of the ripple current exceeds the set threshold. When the time constant is not well-matched, the dc current which trips the overcurrent changes accordingly.
When the controller counts three consecutive clock cycles of an overcurrent condition, the high-side and low-side MOSFETs are turned off and the controller enters hiccup mode or latches the output off, depending on the IOUT_OC_FAULT_RESPONSE register. In continuous restart hiccup mode, after seven soft-start cycles, normal switching is attempted. If the overcurrent has cleared, normal operation resumes; otherwise, the sequence repeats.